Time Period 4: 1914 - present
Outline
General Timeline

General Map
Map # 1: Europe

Course Content
World War 1:
Causes & Build-up of World War 1
Initial Nationalist Rivalries & Alliances
-
Germany was becoming most powerful nation in Europe, threatening other nations
-
France was defeated in 1871 (after Franco-Prussian war), so Germany sought to further weaken it
-
Otto von Bismarck (Germany) formed alliances with Austria-Hungary & Russia to isolate France
-
As William II (new German emperor) fired Bismarck in 1890, he repealed the alliances
-
France thus allied w/ Russia in 1894 against Germany
-
-
Britain also hated growing German power
-
German industrial power was approaching that of Britain
-
German military was threatening British navy
-
German colonial expansion was threatening British colonies
-
Britain thus improved relations w/ US & Japan, signed alliance w/ France in 1904
-
-
Germany declared French Morocco a free territory in 1905 to test the response of other nations
-
Britain, France, Russia opposed Germany, became known as Triple Entente (Allies)
-
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy formed alliance, known as Triple Alliance (Central Powers)
-
-
People believed war was heroic & good
-
Wanted to test their nation's nationalist response, often stimulating national pride
-
Ruling classes wanted to pursue a war to distract the lower classes from domestic issues
-
.jpeg)
Official Start of War
Archduke Francis Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary was visiting Sarajevo, capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina province
Gavrilo Princip, member of Serbian independence terrorist group, shot Ferdinand
Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia after Serbia refused to allow Austria-Hungary to investigate the crime
Germany refused to respect Belgian neutrality, so Britain declared war on Germany
Germany declared war on Russia & its ally, France. Wanted to attack France through Belgium
Russia declared war on Austria-Hungary to protect the Slavs. Later declared war on Germany as it allied with Austria-Hungary
Initial War Plans
- All nations were initially happy about war
- Believed war would be a quick victory
- Common saying: "the boys will be home by Christmas" (the war started in August)
- Nations formed specific timetables of when to attack whom, assuming the war would be quick
-
Schlieffen Plan was German military plan
-
Would initially attack France through Belgium
-
Then would attack Russia after defeating France
-
This failed as beating France took long
-
-
Germany used submarines to sink British boats, while Britain imposed a naval blockade on Germany
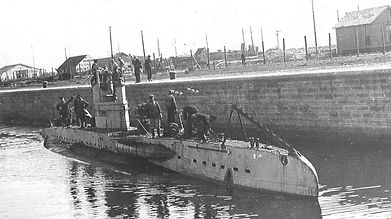
Battles of World War 1
German Battle on Western Front (with France)
Germany tried attacking France through Belgium (according to Schlieffen Plan)
France stopped Germany at River Marne. British also helped Belgian army attack Germans. Later attacked Germans at Battle of Somme
Battle was a stalemate for 4 years
Italy Joined Allies & Battle of Caporetto
Britain & France got Italy to join Allies in 1915, promised to give them Austria-Hungary if Allies won
Italy lost miserably at Battle of Caporetto (1917) against Austria-Hungary
Britain & France helped defend Italy from further invasion
German Battle on Eastern Front (with Russia)
Germany & Austria-Hungary invaded Balkans
Russia invaded Prussia to help Balkans
Germans invaded Russia, causing Russia to lose miserably
Germany acquired many Russian-occupied territories (present-day Poland, Belarus, Baltic nations). Russia still continued to fight
Trench Warfare & New Battle Techniques
- Trench warfare was used on the Western Front
- Soldiers would stay in dug-up trenches & occasionally come up and fire machine guns
- No Man's land was between trenches, very deadly as opposing side would easily fire machine guns & kill you
- Trenches were dirty as disease spread easily
- Trench warfare caused endless stalemates as no one would advance forward from their trench
-
New weapons were developed
-
Barbed wire was used to guard & fence trenches
-
Chemical weapons (poison/mustard gas) were used, caused harm to lungs & eyes of opponents
-
Airplanes were invented but mostly used during World War 2
-
Submarines were used by Germans to sink British boats
-

Home Front & Death Toll
- Government needed maximum production of resources, so it took full control of economy
- Imposed production quotas, wages, prices
- Put government control in all private enterprise, abolished laissez-faire economics
- Formed many unemployed people to work
- Labor unions got more power & were able to campaign for better rights
-
Many women went to work as men were at battle
-
Some worked as police or postal services
-
Worked as physicians, nurses, communications clerks at battle
-
Some worked in munitions industries & were exposed to dangerous conditions
-
-
Nations manipulated propaganda to support war
-
Portrayed enemies as weaker
-
Suppressed those who were against war effort
-
-
To control the home front, nations imposed military dictatorships
-
German generals Paul von Hindenburg & Erich Ludendorff removed chancellor Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg from office
-
-
Many people also revolted against war efforts
-
German socialists rioted in Berlin against the war
-
Irish nationalists declared independence from Britain in Easter Rising of 1916 (actually got independent a few years later)
-
French prime minister Georges Clemenceau suppressed anyone who opposed the war
-
Many soldiers became tired of war & mostly central powers were collapsing
-
-
Many people died from the war
-
8 million soldiers, 7-10 million civilians died
-
20 million died from the influenza pandemic of 1918 that followed the war
-
Germany had the worst fate as 10% of its civilians died
-
Many people were left orphaned or widowed
-
Many suffered from shell shock (PTSD)
-

Japan's Entry into World War 1
Japan wanted to remove German ships from East Asian waters. Japan also wanted to annex German-controlled Jiaozhou peninsula
Germany refused to comply
Japan declared war on Germany, joined Allies in August 1914. Took over German-controlled islands in Pacific
Battle of Gallipoli (1915-1916)
Britain wanted to take over Ottoman-controlled Dardanelles strait to get easy access to Russia
Britain lost miserably after attacking Ottomans at Dardanelles
Britain tried again, this time attacked Gallipoli Peninsula. Used troops from British colonies
Britain lost miserably. Led to weakened control over British colonies
War in the Middle East & Africa
- Ottoman Empire & Bulgaria joined the war with Central Powers against Allies
- Armenians (last major non-Muslim ethnic group in Ottoman Empire) sought Russian help to liberate them from Ottoman rule
-
Ottomans were against the Russians in the war, so Ottomans ordered mass deportation of all Armenians
-
Ottomans killed millions of Armenians
-
-
British allied with Arab states against the Ottomans, liberating them from the Ottomans
-
Hussein ibn-Ali, chief magistrate of Mecca, allied with British
-
British freed Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine from Ottoman rule
-
-
European nations also got people from their African colonies to help in the war
-
Many served in the army, others served as porters to carry equipment
-

End of World War 1
US Joins the War
- Woodrow Wilson (US president, 1913-1921) initially opposed the war
- US economy boomed as it exported munitions to Allies powers (Britain & France mostly)
- US also gave loans to Allies
- Only made financial sense for Allies to win, so US joined the war to help the Allies (1917)
-
German submarines sank British ship Lusitania, killing 128 US citizens
-
This was one reason why US joined the war against Germany
-
-
The main reason why US joined the war against Germany was because of Zimmerman telegram
-
Zimmerman telegram was sent from Germany to Mexico, asking Mexico to declare war against US so US wouldn't declare war on Germany
-
In exchange, Germany would help Mexico gain back its territories lost in Mexican-American War
-
However, US intercepted the telgram & declared war on Germany
-
- US intervention was the only reason Allies won

End of the War
British imposed a naval blockade on Germany, preventing food from reaching there. There were many German protests for more food
France also had a protest among soldiers, but Germans didn't hear it due to censorship
Germany decided to give one last attack westward to France
Bulgaria, Ottomans, Austria-Hungary, and Germany surrendered to the Allies (1918)
France easily defended, Germany ran out of resources
Paris Settlement & Treaty of Versailles (1920)
- Woodrow Wilson (US), Lloyd George (UK), George Clemenceau (France) led meeting at Paris
- 28 nations were invited, none of Central Powers
- Meeting was in chaos due to conflicting views
- Discussed how to punish Germany for the war
- Wilson's 14 Points
- Wilson previously drafted 14 Points, a document entailing potential post-war peace treaties
- Suggested reduction in armaments production, equal naval trade, self-determination (independence) for some colonies, etc.
- They established the League of Nations, an organization of nations to promote security
- League of Nations failed as it relied on collective security (nations agree to maintain security with each other)
- Eventually they passed Treaty of Versailles (1920)
- Made Germany pay reparations for the war
- Made Germany reduce armaments production
- Restricted size of German military
- Banned Germany from having air force & navy

Peace Settlement in the Middle East
-
When Britain & France allied with Arabs against Ottomans, they made vague promise of independence
-
In Sykes Picot Agreement (1916), Britain & France would establish mandates (protectorates) over the Arab states instead of giving independence
-
Britain had Palestine, Transjordan, Iraq
-
France had Lebanon, Syria, South Turkey
-
-
In Balfour Declaration (1917), Britain would create a Jewish state in Palestine
-
Eventually, as Palestinians revolted, this plan was canceled (the UN later created Israel in 1948)
-
-
Arab nationalists hated the mandate system & created General Syrian Congress (1919)
-
French hated this & took over Syria
-
-
Britain & France occupied parts of Turkey, and Greece also took some Turkish territory
-
Mustafa Kemal founded modern nation of Turkey
-
Treaty of Lausanne (1923) recognized nation of Turkey (Ottoman empire disintegrated)
-
Kemal was known as Ataturk ("father of the turks")
-
Made Turkey a secular nation
-
Kemal was a military general & helped defend Turkey from Britain & France
-

Revolution in Austria-Hungary & Germany
-
Austria-Hungary broke apart into Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, & Romania
-
A Serbian monarchy (under Austro-Hungarian control) became Yugoslavia
-
-
Germany experienced a radical democratic revolution
-
German republicans & liberalists crushed William II's authoritarian regime, established democratic Weimar republic
-
German socialists didn't take power because German SPD wanted gradual decline of capitalism & still wanted to retain civil liberties
-
Communism does not have civil liberties while republicanism does
-
-
-
Radical socialists Karl Liebknecht & Rosa Luxemburg attempted to seize power during Spartacist Uprising in Berlin (Jan 1919)
-
German democratic gov killed Liebknecht & Luxemburg, causing lots of protests
-
Communists & socialists depised the gov for murdering the 2 socialist leaders
-
Nazi party believed Germany didn't actually lose WW1 but was deteriorating due to German socialists
-

Russian Revolution
Fall of Tsarist Regime & Creation of Provisional Government
Germany defeated Russia in WW1, causing Russians to lose a lot of resources. Russia had weak leadership as tsar Nicholas II fled to battlefield, leaving his wife, Alexandria, in charge
In Mar 1917, Russians marched in St. Petersburg, wanting more food. WW1 wasted many resources, causing food shortages. Russian soldiers were ordered to attack the protestors but instead joined them
Duma (parliament) wanted more power, so Alexander Kerensky declared a provisional Russian government, and Nicholas II abdicated. Established basic civil liberties & supported participation in WW1
Ordered Summer Offensive (Jul 1917) against Germany (last Russian attack in WW1). Russia lost miserably, peasant soldiers were seizing land upon return, creating an anarchy
Soviets put military power in ordinary soldiers instead of officers, decreasing military power
A rival government, Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (Soviets) opposed participation in WW1. Acted as a parallel gov, weakened power of provisional gov
Lenin, Bolshevik Revolution, Russian Civil War
Lenin supported socialism & wanted to impose it in Russia. Wanted a violent socialist revolution with efficient human leadership
Other communists (Mensheviks "minority group") believed revolution should be led by a large group. Lenin's peers (Bolsheviks "majority group") believed revolution should be led by small group of elites
Lenin was exiled in Switzerland. Went to Russia & mounted coup on Russian provisional gov. Appealed to peasants & soldiers with promises of peace, land, bread
Allowed peasants to seize property & reform land. In Nov 1917 elections, Bolsheviks didn't win majority in Constituent Assembly, so Lenin declared Bolshevik dictatorship
At Congress of Soviets, Bolshevik majority put Lenin as leader. Lenin became leader due to efficient leadership, appeal to peasants, and Russian anarchy
Leon Trotsky led Bolsheviks against other communists. Built Bolshevik army, took over buildings in St. Petersburg, arrested members of provisional gov
Lenin signed Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (1918) w/ Germany, removing Russia from WW1. Gave Western territories (Poland, Belarus, etc) to Germany
Some Russians (White Army) hated Bolsheviks (Red Army), started Russian Civil War (1917-1922). Reds had strong army, "Red Terror" campaign executed all dissidents. Whites failed to receive efficient foreign aid
Reds initiated "War Communism," an economic policy mobilizing the entire home front for the civil war (nationalized all business). Reds won in Spring 1920, gained many territories previously ceded to Germany
Interwar Period:
Great Depression
US Stock Market Crash of 1929
In 1929, people were buying stocks on margin. They'd buy stocks & sell them after making a slight profit
People believed stocks would go down in price, so they all sold all their stocks
On Black Thursday (10/24/1929), all prices plummeted significantly, stock market crashed. People lost their life savings
Spread of Great Depression throughout Europe
-
After stock market crash of 1929, people lost confidence in the market, causing economic downfall
-
People bought less goods, so the price of goods fell, causing people to become poor as they couldn't make enough money from selling goods
-
Industrial goods had little demand, so factories produced less, so they fired more people
-
Thus, more people became unemployed & couldn't buy goods, causing factories to produce less & fire more people
-
-
-
Economic downfall spread from US to Europe quickly
-
US gave many loans to Europe during & after WW1
-
US bankers sought to repeal their loans & reclaim their money after this crises
-
Thus, Europeans had to quickly pay their loans, causing economic crisis
-
-
Austrian bank collapsed in 1931
-
Many European nations abolished gold standard for currency to decrease price of money
-
This actually led to more inflation
-
-
Nations increased tariffs to protect domestic industry, causing global trade to decline
-
As unemployment grew, marriages were delayed, fertility decreased, mental illness became more common

Responses to Great Depression
-
In the US, Franklin D. Roosevelt launched the New Deal to combat the Great Depression
-
Devalued the dollar to raise prices, allowing farmers to earn more
-
Promoted public works projects to employ people
-
-
Scandinavian countries were the most successful in combating the Great Depression
-
Social Democratic leadership allowed these nations to be successful
-
Very cooperative with their community, promoted public works projects to employ people
-
Increased social welfare benefits
-
-
Britain was also successful in combating the crisis
-
At first, it was unsuccessful as the unemployed people received few social welfare benefits
-
Later, they raised tariffs to protect domestic industry, & abolished gold standards for currency, which actually boosted domestic industry
-
While industrial goods like coal & textiles declined, other goods like automobiles & electrical appliances boomed
-
-
France was unsuccessful in combating the Great Depression due to political conflict within France
-
Had steady decline until 1935, later recovered slightly but never fully
-
French republican gov was challenged on both sides: Communists & Fascists competed for influence
-
Communists, Socialists, Radicals formed alliance called Popular Front against Fascists
-
Led by Leon Blum, initiated social reform programs (paid vacation, 40-hour work week, etc.)
-
This failed due to inflation & because Fascists and conservatives hated this
-
-
During Spanish Civil War (1936-1939), French communists supported Spanish republicans, while French conservatives supported Spanish fascists
-
All of this dissension within France caused its economy to recover slower than other nations
-

Problems in Germany & France
German Reparations
Germany didn't want to pay the WW1 reparations listed in the Treaty of Versailles. France needed these reparations for economic recovery
France allied with Central European nations against Germany because France needed German reparations
Germany agreed to pay $33 billion in reparations in annual installments of $2.5 billion
Germany told people of Rhine-Ruhr to stop working so French would leave. French sealed Rhine-Ruhr from rest of Germany (only allowing food to pass through) & forced inhabitants to pay war reparations
French & Belgian armies conquered Rhine-Ruhr region of Germany, forced them to pay reparations
Germany payed reparations in 1921 & 1922 but then called for 3 year moratorium. Britain accepted but France didn't
German economy was collapsing, printed paper money, which actually caused inflation. New German foreign minister Gustav Stresemann called for reexamination of Germany's ability to pay
French PM Raymond Poincare agreed. American banker Charles Dawes made Dawes Plan (1924), said reparations are proportional to German economic output
France & Germany accepted common border in 1925. In 1928, 15 nations signed Kellogg-Briand Pact, agreeing not to have war
Developments in Governance in Interwar Period
-
In Germany, the fascist regime was gaining momentum
-
Adolf Hitler sought to have a socialist revolution, but the German gov heard about this plan & imprisoned Hitler
-
Still, Hitler's regime attracted anti-Semites and extreme German nationalists
-
-
In Britain, the government became more socialistic
-
Ramsay MacDonald led the Labour Party, which advocated for workers
-
Unemployment was really high in 1926, so the Labour Party made policies in favor of them
-
Labour Party moved gradually to socialism
-
-
In 1922, Britain gave Southern Catholic colonies of Ireland autonomy after a guerilla war
.jpg)
Cultural, Artistic, and Intellectual Developments
Uncertainty & Pessimism
-
German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche attacked human progress
-
Believed we overused rationality & were entering a period of darkness
-
Believed religion was useless
-
Believed human society was meaningless
-
-
Still, Christianity experienced a revival
-
People believed you need to interpret the Bible to understand science & humanity
-
Believed people needed to use religion in times of anxiety & depression
-
-
New discoveries in physics proved the uncertainty of truth
-
Albert Einstein discovered theory of special relativity
-
Taught that time and space are relative to the viewer and not the same for everyone
-
-
Werner Heisenberg created the uncertainty principle
-
Taught that it's impossible to know the exact position & velocity of an object
-
-
These discoveries questioned the uncertainty of truth
-
-
Sigmund Freud created psychoanalytic theory
-
Believed human mind was irrational & governed by a subconscious mind
-
Promoted the idea of dreams
-

Developments in Art, Architecture, Literature, Music
-
Architects stressed function over form
-
Believed a building should focus on its functions & purposes rather than design
-
Bauhaus was a German architecture school that stressed this idea
-
Led to creation of tall glass buildings seen in in modern city skylines
-
-
Many artistic developments happened
-
Abstract art developed because since cameras were invented, real paintings were useless
-
Dadaism developed in Switzerland where artists made completely useless paintings to show how useless society is
-
Impressionism was a movement where artists used sensory impressions & often drew quick blurry scenes (rarely added their own feelings)
-
Some artists depicted the unconscious self, as seen in Freud's psychoanalytic theory
-
-
Literature depicted the uselessness of society
-
Often rejected society, talked about the truth of society
-
Some used monologues to depict the human soul & inner subconscious (psychoanalytic theory)
-
-
Composers used dissonant/random sounds in music, just like abstract art was full of random drawings
%20(1).jpeg)
Consumer Revolution
-
Consumer culture became more popular
-
With more factories, goods were produced at cheap prices, allowing more people to buy them
-
People produced variations of goods, and department stores sold all kinds of products
-
More women's products like perfume became common
-
-
Cinema & Radio also became common
-
Cinema was common in Europe, especially Britain
-
In some places, people went to the movie theatre once a week
-
By late 1930s, most households had a radio
-
Radios were used by communist leaders to broadcast messages
-
Sometimes used by democratic leaders as well to gain popularity
-
-
Cinema was sometimes used to show patriotism & spread propaganda
-

Rise of Totalitarianism
Definition of Communism & Fascism
-
Conservative authoritarianism was used before
-
Used bureaucracies to control society
-
Would jail or exile dissidents, sometimes didn't have the ability to jail all dissidents
-
-
Now, radical totalitarian regimes took power
-
These used violent methods of repressing dissidents
-
-
Communism & Fascism are on opposite sides of political spectrum
-
Both abolish parliament, civil liberties, etc.
-
Both suppress dissidents & censored mass media
-
Communism believes in abolishing class differences & having one social class rule the world
-
Fascism believes in having one race (still having multiple social classes) rule the world
-
Communists & fascists were very different, leading to ideological clashes & WW2
-

Rise of Stalin in Communist Russia
Lenin instituted New Economic Policy, allowing small businesses to be private
Lenin's death in 1924 led to struggle for power between Stalin & Trotsky: Stalin was good organizer & bad speaker, but Trotsky planned Bolshevik revolution & civil war victory
Stalin became Bolshevik's Central Committee's general secretary in 1922. Believed Russia could build communism on its own, while Trotsky believed rest of Europe also needed communism
Peasants revolted against collectivization of agriculture, so Stalin allowed families to own small plots of land for their own food
Created First Five-Year Plan. Promoted collectivization of agriculture (no private ownership of land) and heavy industry (steel, iron)
Stalin's view of communism (Russia could build communism on its own) appealed to Russians, so Stalin ordered his allies to crush Trotsky. Stalin gained power in 1927
Life During Stalin's Regime & "Great Purge" in Communist Russia
-
Stalin was very cruel in his reign
-
Suppressed labor unions, forced peasants to work in the cities (if not needed in farms)
-
Suppressed all dissidents
-
-
Life in cities was very bad
-
Families lacked housing, few families had one room for the entire family
-
Workers got social welfare benefits
-
Workers liked this lifestyle as they believed capitalism was bad
-
-
Skilled laborers had an advantage as their skills were needed
-
Often got higher salaries than unskilled factory workers
-
-
Women had equality but were still exploited
-
Women were regarded as equal to men
-
Women were still required to work as men's wages weren't enough for a family
-
-
All political dissidents were tortured, especially during "Great Purge" (1936-1938)
-
Sometimes used false evidence to accuse people
-
Tried 6 million people, murdered 1-2 million
-

Mussolini's Regime in Fascist Italy
-
Italy was in chaos during WW1
-
Italy promised universal male suffrage, but the Catholic church opposed it, creating tension
-
Italy promised land reform but failed to gain land during WW1
-
Many different political parties all opposed the Italian liberal government
-
-
Benito Mussolini created fascism
-
Fascism was a combination of socialism & nationalism, means "a union of forces"
-
Gained support from conservatives & middle-class as he opposed socialism
-
Created an army known as Black Shirts, removed Socialists from Northern Italy
-
Mussolini became known as a savior of order & property in Italy, became a mass movement
-
-
In Oct 1922, Mussolini's army marched into Rome to take over
-
King Victor Emmanuel III, who hated the Italian liberal gov, peacefully gave Mussolini power
-
-
Mussolini passed repressive policies
-
Abolished basic civil liberties
-
Arrested political dissidents
-
Held Fascist rallies & sporting events
-
All propaganda portrayed Mussolini as a leader
-
Disbanded labor unions, controlled Italy's schools
-
Used military to portray Italian power
-
Invaded Ethiopia in Oct 1935, won in 1936
-
Made close ties with Nazi Germany in 1937, passed anti-Semitic laws in 1938
-
-
-
Mussolini was forced to compromise his power with Italian elites
-
Didn't intervene in big businesses
-
Didn't implement land reform
-
Forced to sign Lateran Treaty (1929), recognizing Vatican City as an independent territory
-
Thus, he never created totalitarian support as he compromised his authority for some elites
-

Rise of Hitler's Regime & His Policies
-
Adolf Hitler was racist & believed Germans were superior
-
Went to Vienna, became exposed to ideals of racism & anti-Semitism
-
Joined extremist German Workers' Party in 1919
-
Believed Jews, gypsies, homosexuals, etc. were the causes for German loss in WW1
-
-
In 1923, Hitler organized armed uprising to take over German Weimar Republic, but he failed & was jailed
-
Hitler later gained followers by preaching German superiority
-
His party was National Socialist German Workers' Party (known as Nazi)
-
During Great Depression, he promised economic recovery
-
Many believed Weimar Republic was corrupt as it stopped gov spending in Great Depression
-
Appealed to lower classes through ideals of anti-capitalism
-
Appealed to middle class through ideals of racism
-
-
By 1930s, Nazis had more seats in Reichstag (German parliament) than other parties
-
Communists & Social democrats combined outnumbered Nazis but couldn't prevent Nazi takeover as they fought among each other
-
Hitler was appointed Chancellor by President Hindenburg in 1933
-
-
After taking control, he created one-party dictatorship
-
Abolished communist party & jailed its members
-
Executed or imprisoned all political dissidents
-
Put Nazi control of all German institutions
-
-
Hitler persecuted Jews & promoted German nationalism
-
Passed Nuremberg Laws in 1935, which persecuted Jews from German society
-
In 1938, his allies looted many Jewish businesses at night (known as kristallnacht or "night of broken glass")
-
Forced Jews to give their jobs to Germans
-
Sought to create a people's community among Germans
-
Created volkswagen (people's car)
-
-
Forced women to return to subordinate roles
-
Forced them out of their careers, promoted births & banned abortions
-
-
Nazis used eugenics to promote the births of Germans and mandate the abortions of "racially inferior" people
-

World War 2:
Causes & Start of World War 2
Initial German Aggression
-
Nazi Germany's main goal was aggression: They wanted to create a union of all German-speaking places
-
Nazis also sought to kill all the Jews ("racially inferior people") to create more living space for Germans
-
Signed alliance with Fascist Italy in 1936 (Rome-Berlin Axis)
-
Also signed alliance with Fascist Japan
-
Germany, Japan, Italy were Axis powers
-
US, Britain, France, China, Russia were Allies powers
-
Signed nonaggression pact with Stalin's Russia in 1939
-
Nazis first sought to conquer German-speaking Austria
-
Austria allowed Nazis to control part of it
-
-
Nazis later looked to Sudetenland, a region in Western Czechoslovakia with ethnic Germans
-
Britain & France didn't want war, so they agreed to let Hitler take it (1939)
-
-
-
Later, Nazis sought to conquer the rest of Europe
-
First wanted to conquer Danzig in Poland
-
Wanted to remove the Jews there to create more living space for Germans
-
France & Britain agreed to protect Poland, so once Nazis invaded Danzig, France & Britain declared war on Germany (WW2 had started)
-
-

Battles of World War 2
German Victories Throughout Europe
-
After invading Poland, Germany rapidly conquered the rest of Europe
-
Took over Poland while Russia invaded East Poland & Baltic States
-
Took over Denmark, Norway, Netherlands
-
Broke into France through Belgium in 1940
-
Germans trapped British army on French beach of Dunkirk
-
-
This war technique was known as blitzkrieg or "lightning war," where Germany quickly conquers other lands
-
-
By 1940, Hitler ruled most of Europe and sought to conquer Britain
-
He used his air force to bomb London & other British industrial cities
-
Britain thus produced more planes & had 3x more planes than Germany
-
Britain thus successfully defended against Germany
-
-
Still, Britain was devastated due to the damage caused by German planes
-
-
In 1941, Hitler broke his pact with Stalin and invaded Russia
-
Germany conquered Leningrad, Moscow, Ukraine
-
Known as Operation Barbarossa
-
-
After conquering Moscow, Hitler's army wasn't prepared for Russian wintertime, causing many German soldiers to die of cold & starvation
-

Nazi Administration Throughout Europe & Holocaust
-
Nazis cruelly ruled their conquered lands & forced them to support German war effort
-
Ruled each land based on racial hierarchy
-
France was divided into 2 parts
-
North was ruled by Nazis
-
South was ruled by Vichy regime (founded by WW1 veteran Marshal Henri-Philippe
-
South supported Nazi war effort & supplied all Jews to Nazis
-
-
-
Nazis stole goods & crops from these lands
-
Nazis forced these lands to pay for war cost & the cost of the Nazi governance itself
-
Nazis bought luxury goods for low prices and sent it to Germany to increase their standard of living
-
Often destroyed cities & factories
-
-
Nazis encouraged Germans to settle in these areas
-
Few resistance groups fought back because the different resistance groups weren't united among themselves
-
Nazis censored Polish press to remove any anti-Nazi propaganda
-
Still, Polish people had underground network of newspapers
-
A group of these people exiled in London would give German secrets to the Allies powers
-
-
-
Nazis initiated the Holocaust as they sought to kill the Jews
-
Most Jews were in Western Poland
-
Nazis enslaved Ukrainians, Russians, Poles
-
Forced Jews to live in communities called ghettos, which were poorly built & maintained
-
Later, Nazis came up with the idea of sending all Jews to concentration camps to kill them
-
Nazis sent Jews to one of 6 concentration camps
-
Largest camp, Auschwitz-Birkenau, killed 1 million Jews
-
-
In total, 6 million Jews died
-

Japanese Entry into War & Pearl Harbor Attack (1941)
German military victories inspired Japan
Japan conquered many places in Southeast Asia, including French Indochina
US imposed oil embargo on Japan to protect the French. Germany, Britain, Dutch supported embargo
US allied with Britain & USSR (Allies powers) against Germany, Italy, & Japan (Axis powers)
Germany & Italy responded by declaring war on US
Japan renounced tripartite pact (with Germany & Italy) and attacked Pearl Harbor in US (1941)
End of World War 2
Allies Victories
-
US, Britain, and Russia created Grand Alliance (China & France were also part of it later on)
-
Sought to kill the Nazis, then Japan
-
-
Germany started expanding into North Africa
-
At 2nd Battle of El Alamein in North Africa, Allies beat Axis, preventing further Axis expansion (known as "hinge of fate")
-
-
US & Britain took over Italy & overthrew Mussolini, but Germany rescued him & occupied North Italy
-
Thus, Allies had Southern Italy & Axis had Northern Italy
-
-
US & Britain developed sonar technologies to detect German submarines
-
German submarines previously would sink Allies ships, preventing food from reaching Allies
-
-
US & Britain also boosted their industrial production & bombed German industrial centers
-
Russian army later defeated Germans at Stalingrad, causing Germans to retreat

Allied Victory & Axis Surrender
-
On D-Day (6/6/1944), US & British troops landed in Normandy, France
-
2 million troops & 500,000 army vehicles from Allies pushed the German front lines all the way to the German border
-
By 1945, the Allies forces had crossed the Rhine into Germany
-
Also, Allies forces pushed Germans out of Italy in 1945
-
The same year, Italian communists executed Mussolini
-
-
-
Meanwhile, Russian forces defeated Germans & pushed westward into Germany
-
In 1944, the Polish underground army took over Warsaw (Warsaw Uprising), but Soviets didn't enter Warsaw as they predicted the uprising
-
Thus, Germans crushed the Warsaw Uprising & allowed Soviets to freely advance
-
Soviets took over Yugoslavia, Romania, Hungary
-
Soviets entered Germany from the east in Jan 1925 & met US & British forces there
-
-
Germans were forced to surrender on May 8, 1945
-
Hitler committed suicide a week earlier
-
-
In the Pacific, US took over many Japanese Pacific Islands & dropped atomic bombs in Hiroshima & Nagasaki
-
Japan surrendered in Sep 1945
-
-
Overall, WW2 killed 50 million people

Cold War:
Origins of Cold War
Legacy of World War 2 & Peace Settlement
-
World War 2 left lots of cities destroyed & costed many lives
-
50 million people died
-
Many people were homeless
-
-
Many people fled to escape violence but now had to return home
-
These people (Displaced Persons) needed food & shelter
-
Shelters were put in place for some Displaced People, but many struggled
-
-
Many Jews that fled were unwelcome in their home land
-
After World War 2, the 4 Allies (USSR, UK, US, France) would occupy Germany & Austria to prevent them from becoming powerful again
-
USSR was ruthless & confiscated all industrial machinery & railroads & sent it to the USSR
-
The 4 Allies held the Nuremberg Trials (1945-1946) where they tried high-ranking Nazi officials for war crimes, often sentencing them for year in jail
-
-
In Feb 1945, US, UK and USSR met in Yalta in Crimea to discuss post-war peace settlement
-
US & UK sought to hold off on peace settlement until this time because they didn't want conflict with communist Stalin
-
The 3 Allies decided that USSR will occupy nations in Eastern Europe & impose free elections
-
Known as Yalta Compromise
-
-
-
Later, Yalta Compromise started falling apart
-
Communist regimes started taking root in some Eastern European nations
-
At Postdam Conference (Jul 1945), Stalin changed his mind about Yalta Compromise
-
Stalin sought to impose communism in the other Eastern European nations
-
-
US sought to prevent the spread of communism & impose capitalism (free elections) there
-
-
This was the start of the Cold War: An indirect war between US & USSR over spreading capitalism vs communism

Developments in the West Bloc (US & its Allies)
-
US president Truman issued Truman Doctrine, stating that he seeks to contain the spread of communism
-
US initiated Marshall Plan, a bill giving $13 billion in aid to Western European countries
-
Allowed Western European nations to recover their economy
-
These Western European nations were anti-communist (capitalist)
-
-
US aided anti-communist forces in Greek Civil War (1946-1949), allowing the anti-communist forces to win
-
US prevented Soviet expansion in Turkey
-
US created NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), an organization of US's anti-communist allies
-
Included US & most of Western Europe as well as Turkey & Greece
-

Developments in the East Bloc (USSR & its Allies)
-
Stalin sought to promote the spread of communism, sometimes by force
-
Stalin initiated COMECON (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance), an organization giving aid to East Bloc nations
-
Allowed Eastern European nations to recover their economies
-
Similar to Marshall Plan of the US
-
-
Created Warsaw Pact (1955), a treaty organization of all communist nations of Eastern Europe
-
Included USSR as well as 7 other communist nations in Eastern Europe
-
These nations included Albania, Poland, Romania, Hungary, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria
-
-
-
Communist nations in East Bloc were formed when minority communist parties consolidated power & created one-party dictatorships

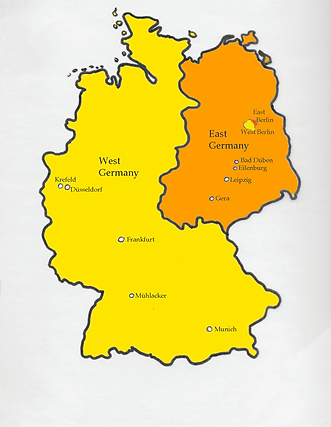
Divided Germany
-
As part of the Yalta Compromise, Germany would be divided among US, France, UK, and USSR to prevent it from becoming powerful & starting another war
-
US, UK, and France (West Bloc) took over West Germany while USSR (East Bloc) took over East Germany
-
Additionally, Berlin was completely surrounded by East Germany but was also divided among the West & East Bloc
-
Thus, West Germany was completely surrounded by East Germany
-
To get to West Germany, one had to travel through East Germany
-
-
USSR issued a blockade of West Germany, preventing people from accessing West Germany by traveling through East Germany
-
Thus, West Bloc members had to airlift supplies (e.g. food) to West Germany
-
-
Many East Germans crossed the border into West Germany to escape communist rule
-
Thus, a wall was built (Berlin Wall) to surround West Germany, preventing people from migrating there
-
The wall had multiple layers of barbed wire & many checkpoints that shoot anyone who crosses
-
Indirect Battles of the Cold War
Nuclear Arms Race
-
US & USSR had an indirect competition of building powerful nuclear weapons
-
Both nations sought to build more powerful weapons than the other nation
-
Eventually, they developed the nuclear bomb
-
Both nations had enough weapons to destroy the entire world
-
Known as Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD), where both nations can destroy each other
-
-
Developed missiles, spy satellites, nuclear submarines, nuclear bombs, etc.
-
-
Nuclear race also spread into space
-
In 1957, USSR launched Sputnik, the first man-made satellite to orbit the Earth
-
USSR sent first astronaut to orbit the Earth in 1960
-
US created NASA in 1958 to beat the USSR in the space race
-
Sent first man to moon in 1969
-
-
-
Development of more sophisticated computers helped with developing advanced aeronautical & military tech
-
Invention of transistor in 1947 made computers much less bulky
-
-
Scientific innovations also were useful for ordinary public
-
Green Revolution was an agricultural revolution that used genetic modification to increase crop yields
-
Transistors made radios & kitchen appliances less bulky & cheaper, allowing more people to buy them
-
.jpeg)
Korean War (1950-1953)
After WW2, US & USSR divided Korea into Communist North Korea (DPRK) & Democratic South Korea (ROK). US & USSR armed their Korean counterparts
DPRK pushed southward, attacked ROK & captured capital of Seoul (1950)
US & other NATO states helped ROK push back DPRK & capture Pyongyang
ROK & DPRK agreed to ceasefire in 1953
China & USSR helped DPRK push back ROK to original border
Vietnam War (1954-1976)
After Vietnamese independence from France (1954), Geneva Accord (1954) decided that Vietnam would be divided in Communist north & nationalist South
US president Dwight D. Eisenhower wanted entire Vietnam to be nationalist, so he provided US troops & aid to the South
Later US presidents (JFK & Lyndon B. Johnson) increased US aid in Vietnam
In 1976, North communists invaded the south. US refused to come help the south. South was forced to accept Unified Communist Vietnam
Richard Nixon wanted to withdraw US from war. Achieved peace with North that divided Vietnam into 2 (same as before the war)
Many US college students protested US involvement in the war as they feared being drafted into war
Life in the East Bloc
-
Stalin was very cruel in his governance
-
Put down all uprisings & revolts
-
Imprisoned political dissidents
-
Gave no civil liberties
-
Censored all anti-Soviet & Western press, literature, art, etc.
-
-
Stalin used force to establish & maintain communist dictatorships in East Bloc nations
-
Sometimes arrested disloyal communist leaders
-
Yugoslavia resisted USSR domination as there was no USSR army present there
-
Yugoslavia still had a communist dictatorship
-
-
-
East Bloc nations used five-year plans to boost their economies
-
Promoted heavy industry (iron, steel) over consumer goods
-
Promoted collectivization of agriculture
-
Stalin only allowed Poland to have private agricultural plots as Poland often rebelled, compromising USSR's stability
-
Neglected consumer goods as they promote individualism (bad for communist state)
-
-
Working conditions were very bad in East Bloc
-
People lacked household necessities as the state only promoted heavy industry
-
People worked long hours for little pay
-

De-Stalinization & Khrushchev's Reforms
-
After Stalin died in 1953, there were debates as to who should succeed him
-
Everyone wanted to reduce the cruelty of Stalin's rule
-
Conservatives wanted a gradual transition to a less cruel regime
-
Nikita Khrushchev wanted a radical transition to a less cruel regime
-
-
Khrushchev took power in 1955 & began program of de-Stalinization (removal of Stalin's cruelties)
-
Promoted agriculture & consumer goods more than heavy industry
-
Allowed more people to buy consumer goods (cars, TVs, radios, etc.)
-
Relaxed workplace rules, allowing people to live more freely
-
This all led to a higher standard of living
-
Many authors wrote about life during de-Stalinization as censorship was eased
-
-
Khrushchev sought to ease relations with the West (known as detente)
-
Gave independence to Austria (which was neutral in Cold War) after 10 years of Allied control (1955)
-
Provided economic aid to Africa & Asia
-
-
Other East Bloc nations responded differently to Khrushchev's de-Stalinization
-
Poland didn't want de-Stalinization & followed initial Warsaw Pact, giving it more autonomy from USSR
-
In Hungary, Imre Nagy became new PM & promoted a democratic government (1956)
-
USSR crushed this & restored communism there
-
-
-
As Khrushchev's stability was decreasing due to de-Stalinization, he sought to tighten control of his subjects
-
After many people crossed from East to West Berlin, he built the Berlin Wall (1961)
-
Secretly put nuclear missile test sites in Communist Cuba, led by Fidel Castro (1962)
-
US president JFK found out & ordered USSR to remove them, so Khrushchev agreed
-
US also agreed to remove its missiles from Turkey
-
-
-
Many hated Khrushchev's lenient policies, so Leonid Brezhnev mounted a coup & took over in 1964
-
Began re-Stalinization, launched massive arms buildings, suppressed all dissidents, etc.
-

Decline in East Bloc
Detente & Student Protests
-
In 1960s, many Western European nations became more left-wing, bringing them closer to socialism
-
This allowed for more peace between Western Europe & East Bloc
-
In 1970, former West German chancellor Willy Brandt went to Poland to sign peace agreements
-
Apologized for poor treatment of Jews
-
Negotiated with some East Bloc nations to accept existing national borders
-
Agreed that force cannot be used to change national borders
-
-
-
-
US & USSR also agreed to limit nuclear arms race
-
This relaxation of Cold War tensions was known as detente
-
US, USSR, Canada, & most European Nations signed Helsinki Accord (1975)
-
Agreed that existing national borders cannot be changed by force
-
Decreased Cold War tensions & gave some civil liberties to its citizens
-
-
Meanwhile, many people (especially students) protested involvement in the Cold War
-
Believed the war was useless & costly
-
In France, a protest in May 1968 coincided with a strike
-
Known as "May Events," caused economy to slow down significantly
-
Protestors took over factories but police clashed with protestors
-
President Charles de Gaulle initiated some workplace reforms, but the needs of student protestors still weren't fully met
-
Majority conservative members were elected to French Parliament, furthering the conflict
-
-

Protests in East Bloc & Brezhnev Doctrine (1968)
-
East Bloc economies always lagged behind the West
-
In 1960s, some East Bloc nations initiated reforms to slightly privatize the economy
-
Hungary & East Germany initiated some reforms, allowing their economies to be a bit successful
-
Nations diverted resources to consumer goods instead of heavy industry, allowing more people to have TVs
-
-
Some authors in communist nations published works criticizing the communist regime
-
This was allowed as nations relaxed censorship
-
Still, states suppressed these works, so authors created a secret network of books passed among dissidents
-
-
Leonid Brezhnev created Brezhnev Doctrine (1968), allowing him to intervene if any nation abolishes communism
-
Many communist nations protested against the communist regime
-
In Czechoslovakia, the Communist party outvoted the Stalinist leader in favor of liberal communist leader Alexander Dubcek
-
Dubcek initiated liberal reforms, relaxing censorship and slightly privatizing industry
-
Brezhnev ordered USSR army to crush the liberal regime in Prague (Prague Spring, 1968)
-
After this, Brezhnev created Brezhnev Doctrine (1968), stating that he can intervene if any East Bloc nation threatens communism
-
-

Crisis in East Bloc & Repeal of Detente
-
Energy crisis of 1970s hurt East Bloc economies, causing dissent in East Bloc
-
East Bloc nations required lots of cheap energy as industrial factories needed energy to function
-
West Bloc nations developed into post-industrial & advanced tech societies that evaded the energy crisis
-
East Bloc nations couldn't adopt post-industrial tech economy without compromising communist principles, so East Bloc nations struggled during the energy crisis
-
-
In Czechoslovakia & Poland, people revolted against communist regime
-
In Czechoslovakia, Vaclav Havel criticized the Czech communist regime for not giving the civil liberties outlined in the Helsinki Accord
-
In Poland, after many worker strikes due to stagnating economy, gov adopted Gdansk Agreement (1980)
-
Stated that communist gov would rule on behalf of proletariat & support the workers
-
-
-
Polish reformer Lech Walesa organized anti-communist movement called Solidarity
-
Practiced idea of moderation, only giving the civil liberties outlined in Gdansk Agreement (1980)
-
Solidarity gained lots of power, so he got many concessions from Polish gov
-
Later, economic crisis undermined support for Solidarity as people believed Solidarity movement caused the crisis
-
In 1981, some Solidarity leaders were arrested, but the movement grew again in late 1980s as the Polish gov was unwilling to launch full campaigns against the movement
-
-
Later, US believed Brezhnev violated peace agreements in Helsinki Accord & started rebuilding his military power
-
Soviets invaded Afghanistan to save a communist regime there, which alarmed the US (1979)
-
US believed Soviets would spread communism to Afghanistan & later to oil-rich nations of Middle East
-
US later started rebuilding its own military power & rebuilt its alliances with Western Europe
-

Gorbachev's Reforms
-
East Bloc economy was stagnating, so Mikhail Gorbachev (new USSR leader who took power in 1983) initiated reforms
-
Arms race was straining East Bloc's economy, wanted more peaceful relations with west
-
-
First reform program was perestroika
-
Privatized some industries, eased government control on industry and prices
-
This failed because it was closer to capitalism, where people had to accumulate more wealth to gain higher social status
-
Many didn't like this because of the new social order
-
-
-
Second reform was glasnost
-
This was a relaxation of censorship, giving more openness to the government & media
-
He even allowed free speech
-
-
Many authors with banned works could now publish their works
-
This led may people to openly criticize the Soviet regime
-
-
Gorbachev also created a small congress with free elections
-
Known of Congress of People's Deputies, created in 1989
-
Many anti-communist people were elected, promoting anti-communist ideas
-
-
Gorbachev also withdrew troops from Afghanistan & halted the arms race
-
Replaced Brezhnev Doctrine with Sinatra Doctrine (1989), allowing East Bloc nations to govern themselves & reform their own government

End of Cold War
Collapse of Communism in East Bloc
-
East Bloc nations never fully recovered from economic crisis of 1970s, so anti-communist movements were inevitable
-
In Poland, Solidarity movement gained momentum again
-
In 1988, Polish economy was collapsing because many workers (who were Solidarity members) were on strike
-
In 1989, Poland legalized Solidarity, allowed some representatives to be chosen with free elections
-
Still, communists would be guaranteed a majority
-
-
Lech Walesa (Solidarity leader) made alliances with other communist parties, thus winning a majority
-
In 1989, Tadeusz Mazowiecki (member of Solidarity) became Polish Prime Minister
-
Mazowiecki made radical democratic changes to Poland
-
-
Hungary also abolished communism after revolts
-
In 1956, Hungarian communist leader allowed privatized economies after an uprising
-
In 1988, as there were more uprisings due to bad economy, Hungarian Communist party put a reform-minded man as the leader so the Communist party could maintain power
-
Many hated this leader, so the Hungarian Communist party agreed to hold free elections in 1989
-
Communists thought they could easily win the majority of seats here, but that wasn't true later on
-
-
To strengthen the support for Hungarian Communist party, they opened the border w/ East Germany & Austria
-
Many East Germans crossed to West Germany via Hungary & Austria
-
-
-
In Czechoslovakia, protests forced Communist party to resign, put Vaclav Havel as president in 1990 (Velvet Revolution)
-
Split into Czech Republic & Slovakia (Velvet Divorce) (1993)
-
-
In Romania, dictator Nicolau Ceausescu ordered secret polish to crush the anti-communist protests
-
His own court killed him and his wife, putting a democratic government in place
-

Fall of East Germany & Reunification of West Germany
-
Reform-minded communists took power in East Germany in Oct 1989, wanting democratic socialism
-
After anti-communist protests, East Germany was in turmoil
-
East German communist leaders that the only way to stabilize the situation would be to tear the Berlin Wall
-
Thus, many people crossed from East to West Germany
-
Also, as Hungary opened its borders, many crossed into West Germany via Hungary & Austria
-
-
-
Germans knew unification was inevitable as the Berlin wall was torn down & many crossed into West Germany
-
West German chancellor Helmut Kohl created a plan for unification
-
Offered economic opportunities & social welfare benefits for East German citizens
-
Created Alliance (political party) in East Germany to favor unification
-
Alliance won majority of East German parliamentary seats & supported unification
-
-
Germany was fully reunified in Oct 1990
-
-
Since unified Germany would be most powerful state in Central Europe, Kohl signed agreement with Gorbachev to limit German military power
-
Reunification led to decrease in Cold War tensions
-
US, USSR, European nations signed Paris Accord (Nov 1990), agreeing to scale down arms race & accepting that existing European borders couldn't change
-

Collapse of USSR
Gorbachev's reform programs led to decreased economic production, so many nations declared independence
Baltic Nations (Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia) started in Aug 1991. 12 other nations declared independence afterward
Gorbachev then abolished Communist party's monopoly on political power & gave some sovereignty to the Congress of People's Deputies

Gorbachev's popularity was basically gone due to his failed reforms, so Yeltsin just took control & created Russian Federation. Former USSR nations formed Commonwealth of Independent States (1991)
A group of conspirators attacked Gorbachev while in Crimea. Yeltsin crushed the rebellion
Boris Yeltsin created Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic (Russia)
Post-Cold War Developments in Eastern Europe
Economic Shock of Russia & Russia under Vladimir Putin
-
After 1991, Boris Yeltsin made rapid economic reforms
-
Decreased government control of prices
-
Made rapid privatization of industry
-
Gave people money so they could buy stocks in these new privatized industry
-
-
Yeltsin's reforms failed as a group of wealthy people (Oligarchs) concentrated all the wealth
-
Since USSR previously had a few giant factories that specialized in heavy industry, the owners of those factories had all the power now
-
These factory owners could raise prices & limit production to maximize profits
-
Overall, prices increased & production decreased
-
-
Yeltsin's reforms led to a lower standard of living
-
Life expectancy declined, many fell into poverty
-
Social welfare benefits lost their value
-
-
In 2000, Vladimir Putin became Russian president
-
He reinstated little government control of prices
-
Removed some privileges of the Oligarchs
-
He ruled somewhat autocratically, allowing for economic reform
-
He put high prices on important exports (oil, natural gas), allowing for economic prosperity
-
-
Putin also ruled very aggressively
-
Gave civil liberties, but arrested those who oppose the state
-
Mostly just suppressed the independent media & supported pro-government media
-
When Chechnya (a Southern Russian region with high Muslim population) declared independence, Putin's troops invaded it
-
When South Ossetia (part of Georgia) declared independence from Georgia, Putin supporting South Ossetian troops
-
-
In 2008, Putin became Prime Minister, but he became president again in 2012

Postwar Life in the Former East Bloc
-
Most East Bloc nations privatized their economies for economic growth
-
Poland rapidly privatized everything (known as "shock therapy"), causing severe inflation
-
The International Monetary Fund provided aid, allowing for Polish economy to be successful
-
-
Other nations were more gradual & often gave vouchers to people to buy stocks
-
-
Poland, Czech Republic, and Hungary were the most successful economies
-
They created new civic institutions, legal systems, media outlets all in favor of business
-
Had new entrepreneurial classes
-
Romania & Bulgaria lagged behind as they were much poorer initially
-
-
Economic growth had similar consequences to Russia
-
Capital cities got larger, provincial centers & industrial centers declined
-
Elderly & workers got poorer
-
Young people, former communists, and investors got wealthier
-
-
Many people liked the new economic system, but others liked communism better
-
They liked that communism guarantees everyone a job and didn't like competitive nature of capitalism
-

Breakup of Yugoslavia
After death of Yugoslavian leader in 1980, power passed to individual provinces. Also, Revolutions of 1989 in East Bloc increased the ethnic conflict
Serbian president Slobodan Milosevic wanted Greater Serbia, a land where all Serbians live, strengthening the nationalist movement in Serbia
Croatia & Slovenia declared independence from Yugoslavia
In Jul 1995, Bosnian Serbs (Christian) took over Srebrenica (a Muslim Bosnian city) & killed many Muslim Bosnians, so NATO bombed the Bosnian Serbs
In 1992, Bosnia-Herzegovina declared independence. Christian Serbs made up 30% of the population & didn't want rule under Muslim Bosniaks. Bosnia-Herzegovina ordered "ethnic cleansing" (genocide) of all its Serbs
Serbian army occupied 30% of Croatia but failed to attack Slovenia
In Nov 1995, NATO agreed to give Muslim Bosnians 49% of Bosnia and Christian Bosnian Serbs the rest
Kosovo gained nothing, so it fought against Serbia for independence. Milosevic gave it self-rule but not independence, so NATO bombed Serbia. NATO put peacekeeping force in Kosovo
The Yugoslavian conflict was over: 6 new nations were created. In 2001, Milosevic was voted out of Serbian presidency as his war destroyed part of Serbian economy
Post-WW2 Conflicts & Developments:
Postwar Social Transformations
Changing Class Structures & Role of Women
-
After WW2, white collar workers had high position in society instead of people with wealthy familial connections
-
White collar workers refer to managers and people with desk jobs
-
Important in managing large businesses
-
-
People with inherited property & familial connections declined as their family-owned businesses went out of business
-
Larger corporations took over
-
-
-
In East Bloc, all classes were roughly the same
-
Mostly everyone worked & received roughly the same benefits
-
-
Structure for lower classes became more flexible & open as many poor people could become wealthier more easily
-
Rural-urban migration was common, and many former factory workers became white-collar workers
-
Social welfare benefits also helped the lower classes
-
-
Women often had more freedom & played a more important role in society
-
Male-dominated industries (iron, steel, etc.) declined, and many women became white-collar workers
-
Many women received an education
-
Women still faced workplace discrimination
-
Often had lower pay & lower positions
-
Often could only find part-time jobs
-
Many married women still had housekeeping & childbreading responsibilities
-
-

Post-WW2 Migration Patterns & Youth Culture
-
Post-WW2 internal migration was common
-
Many people migrated from rural to urban centers as less jobs were available in rural places
-
Many in Spain, Portugal, Italy migrated from poorer to richer regions
-
In East Bloc, due to collectivization of agriculture & promotion of heavy industry, rural-urban migration was common
-
Before Berlin wall was built, many crossed from East Germany to West Germany
-
-
West Germany implemented the guest worker program to get temporary workers as West Germany lost many people during WW2
-
People would migrate to West Germany for a short amount of time & work there
-
Often sent their pay back home to their families
-
Mostly unskilled laborers who worked for low wages
-
Were supposed to return home after a while, but many just stayed in West Germany
-
-
Many colonial subjects migrated to their colonizers' countries
-
Many Algerians migrated to France
-
Many Indians migrated to India
-
These migrants did labor that helped with economic recovery
-
Often were separated into immigrant communities as some Europeans didn't want them in Europe
-
-
Furthermore, a new youth culture developed
-
These were known as "baby boomers" & were born in the years following WW2
-
These people enjoyed trendy clothing, music, etc.
-

Postwar Developments in Europe
Economic Recovery in Western Europe
-
Social Democratic parties emerged throughout Europe, promoting economic recovery
-
Offered a center-right political view
-
Focused on liberalism & democracy instead of nationalism & authoritarianism
-
Spain & Portugal didn't have Christian Democratic regimes (they had authoritarian regimes), causing them to fall slightly behind economically
-
Britain, France, etc. had Christian Democratic regimes, explaining their economic growth
-
-
Offered welfare benefits, nationalized important industries, etc.
-
-
Many nations also wanted political & economic unity within Europe
-
Belgium, France, Luxembourg, Italy, Germany, Netherlands signed Treaty of Rome (1957), creating European Economic Community (Common Market)
-
Reduced tariffs among themselves
-
-
Many sought a common Parliament among Europe, but many larger nations didn't want to give up their sovereignty to the Parliament
-
-
The Consumer Revolution occurred as more people bought consumer goods
-
Wages were rising and people spend less on basic necessities, allowing them to spend more on extra products
-
People had retirement benefits, allowing them to spend more now as they'd have money later on
-
People often payed in installments with credit unions, allowing them to take on more debt
-
Things like radios, automobiles, TVs, etc. became popular
-
Consumer revolution was more successful in West Bloc than in East Bloc because capitalism (west) allowed more people to buy expensive goods as opposed to class leveling (East)
-
Tourism also became more common
-
Some nations mandated month-long vacations
-
Packaged tours were offered by some companies
-
-
Household appliances made housekeeping & cooking easier
-
Consumerism weakened family ties as divorce rates increased and more people lived alone
-
-
Many criticized the inequality of wealth
-
Wanted something in between capitalism and socialism (known as New Left)
-
Believed capitalism leads to wealth gaps that degrade society
-
-
In sexual revolution, birth control pills became more common

Economic Crisis & Political Change in Western Europe
-
West entered economic decline in 1970s
-
Most European money was based on US dollar, but as US dollar declined due to high American spending, European currencies declined, causing inflation
-
OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) imposed oil embargo on US, increasing oil prices
-
Caused economic decline & increase in wealth gap
-
-
Conservative leaders rose to power at this time to bring the west out of economic crisis
-
Believed in having no government intervention in economics at all (free-market or laissez-faire economics)
-
Believed in cutting spending on social welfare benefits
-
Margaret Thatcher led Britain out of economic crisis
-
These conservative policies weren't always super successful
-
-
Many feminist movements arose during this period
-
Sought equality to men
-
Most were successful but not fully complete
-
-
Many environmental movements also arose
-
Sought to limit the effects of environmental degradation
-
Some collaborated with governments, others made non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to support their cause
-
-
Many separatist movements also occurred
-
Some ethnic minorities wanted separation from larger nations
-
The Basque province of Spain wanted autonomy from Spanish rule
-
In 1975, after the death of dictator Francisco Franco, the new constitution gave Basque some autonomy
-
-
Similarly, people in Northern Ireland (under British control) wanted independence from the British
-
On Bloody Sunday in Jan 1972, British troops killed many Northern Irish independence protestors
-
Peace was achieved in 1998
-
-
Others hated European integration and wanted separate customs checks & policies for each individual nation
-
These people often hated immigrants and viewed them as stealing jobs
-
-

Decolonization
Reasons for Decolonization & Decolonization of Africa
-
After WW2, many European nations supported decolonization to focus on internal reforms
-
Japanese conquest of Pacific islands decreased European importance there
-
Western armies were devastated after the war
-
Often gave independence to colonies to avoid a costly war like WW2
-
Cold War politics affected decolonization as Western powers wanted to promote capitalism while China & Soviets promoted communism in colonies
-
Sought to give aid to colonies on their side of the Cold War immediately after independence
-
Many African nations sought nonalignment (not allying with US or USSR)
-
-
-
Starting in 1957, most British colonies got independence
-
Ghana, Nigeria, Tanzania got independence easily & became part of British Commonwealth
-
Kenya got independence in 1963 after short war
-
South Africa got independence in 1961 but was racially segregated among blacks & whites
-
-
Decolonization of Belgian Congo was a major Cold War conflict
-
Congolese announced independence would come soon & Patrice Lumumba would be Prime Minister
-
Later, Lumumba became PM, so Belgian army attacked Congo, but Congo army held them off & partially defeated them
-
Lumumba asked USSR for aid, which feared the US as US & Western Europe had many financial investments in Congo
-
US organized a coup against Lumumba, put US-backed Joseph Mobutu in power in Congo
-
-
French put all of its colonies in a French Commonwealth, but Algeria wanted complete independence, leading to war
-
Algerians in Algeria created National Liberation Front (NLF), attacked French armies & French in Algeria
-
War lasted from 1954-1962, and Algerians won independence
-
-
Still, after independence, Europeans still maintained ties with former colonies & gave them funding
-
Known as neocolonialism
-

Decolonization of Asia
-
Indonesia achieved independence from Dutch in 1949
-
After Japanese took Dutch East Indies (Indonesia) from the Dutch, Dutch took it back in 1945
-
Dutch wanted to take advantage of its rubber to support economic recovery in Netherlands
-
Indonesians later sought independence & won in 1949 after a guerilla war
-
-
France also retook French Indochina after Japanese lost control of them
-
Vietnam declared independence & was divided into communist north & nationalist south
-
US provided aid to nationalist south
-
After Vietnam War, communist government reunified Vietnam
-
-
Laos & Cambodia got independence under non-communist governments
-
-
In British India, Hindus & Muslims didn't want to live in the same country
-
Muslims feared that a unified India would still give them repression from Hindus
-
Muslims created Pakistan, a muslim state
-
Present-day India became a secular state, mostly Hindus
-
-
China had a civil war between nationalists & communists
-
Nationalists organized Guomindang (led by Sun Yatsen & later by Jiang Jeishi)
-
Communists were led by Mao Zedong
-
Communists were more organized & more powerful & forced Guomindang into exile to Taiwan
-
Communists initiated Stalin-style repressions & had economic policies in favor of industry
-

Decolonization in Middle East & Crisis in Israel (1948)
Former British & French mandates in Middle East got independence. Britain had earlier promised a Jewish homeland in Palestine, so British gave Palestine to the UN to decide
The UN decided to divide Palestine into Jewish & Muslim lands. In 1948, Jews proclaimed nation of Israel
Palestinians & Arabs hated this agreement & attacked the Jews. Jews were backed by the US & won even more territory
Suez Canal Crisis (1956)
Gamal Abdel Nasser mounted a coup in Egypt in 1952, promoted pan-Arab nationalism. Nationalized the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company
British, French, & Israeli armies attacked Suez Canal because Western powers actually owned the Suez Canal, not Egypt
US ordered British, French, & Israeli armies to stop. US believed Egypt might align with USSR against the West
Globalization:
Global Economy & Technology
European Union & Other International Organizations
-
In 1993, the Common Market was renamed to the European Union (EU)
-
Sought free movement of capital & labor throughout the EU
-
Maastricht Treaty (1991) set requirements for EU membership
-
Most were financial requirements
-
-
Some nations hated giving up their sovereignty to the EU
-
Other nations hated the financial requirements of EU membership
-
It involved cutting social welfare benefits, setting specific prices on basic products
-
-
Euro currency was created in 2002, a common currency among many EU members
-
South to ratify EU constitution in 2004 with a common president, etc.
-
This failed as not all nations wanted to give up their sovereignty to the EU
-
-
Treaty of Lisbon (2009) was a new constitution that was less extreme & actually became ratified
-
-
United Nations (UN) was established in 1945 after WW2
-
5 victories Allies powers (US, UK, France, Russia, China) were permanent member with veto power in the Security Council of UN
-
Other committees of the UN are very powerful
-
-
World Bank & International Monetary Fund are global banks that provide economic aid to nations
-
World Trade Organization (WTO) regulates international trade & sets tariffs for its >150 member nations

Economic Globalization & Global Technologies
-
More multinational corporations emerged due to free-market trade
-
Would conduct business easily in multiple nations
-
Often would outsource production & manufacturing to places with low labor costs (especially China)
-
Global communications networks & the internet helped with international business
-
-
More economic globalization made the entire world vulnerable to small-scale economic crises
-
In 1997, Thai banking crisis eventually spread throughout the world
-
-
Created huge wealth inequalities
-
Top business executives were wealthy, while middle-class & poor had stagnating incomes
-
Former industrial nations were poor, and post-industrial (tech) societies were richer
-
Russia & East Bloc were poor as they relied on heavy industry
-
-
Many people protested against wealth inequality, global dominance of specific companies, exploitation of labor, environmental effects of globalization, etc.
-
-
More people organized their lives around tech devices
-
Audio files replaced CDs, which replaced cassettes
-
Streaming networks allowed people to watch movies at home
-
Digital cameras replaced film cameras
-
Internet & communication networks allowed for more efficient communication
-
Online shopping & online bookstores largely replaced in-store shopping
-
Many people questioned privacy as governments & other sites can store/monitor our data
-
%20(1).jpeg)
Immigration to Europe
Reasons for Immigration
-
Population within Europe was declining
-
Women wanted to finish education & get a stable job before having kids
-
Wealthy women didn't have time to raise multiple kids as they were busy at work
-
Poor women didn't have the money to raise multiple kids
-
Women raised on average 1.2-1.8 children each, causing population of Europeans to decline
-
Population only grew became of immigration
-
-
Lots of people also immigrated to Europe at this time
-
Many former colonial subjects migrated to their colonizer's capital cities
-
Many refugees came from the East Bloc or from Yugoslavia during its civil war
-
Wanted the high wages that European jobs offered
-
Illegal immigration was a problem
-
Due to open borders in EU, illegal immigrants could easily travel throughout Europe
-
Many people smuggled prostitutes
-
-

Effects of Immigration
-
Immigration created multicultural communities in Europe & played an important role in society
-
Some immigrants were skilled & could speak European languages
-
Other immigrants were unskilled & couldn't speak European languages
-
These often lived in poor housing
-
-
Immigrants brought their food & culture to Europe
-
Sometimes, immigrants blended their indigenous culture with European culture
-
Reggae & Rai are examples
-
-
-
Growth of immigration led to controversy about them
-
Many Europeans believed immigrants are stealing their jobs
-
Many despised the gov for providing aid to illegal immigrants (especially during economic crisis)
-
French politician Jean-Marie Le Pen believed in removing all immigrants from France
-
-
European Muslim population also created controversy
-
Muslims made up 2nd largest religion in Europe
-
Many feared Muslims, especially after 9/11 attacks
-
Sometimes, Europeans banned hijabs in public schools, causing Muslims to protest
-
Many 2nd & 3rd generation Muslims protested & wanted less discrimination
-
These Muslims were outcasts in their home country as they were born in Europe
-
-
-

Global Problems
US-EU Tensions & Recession of 2008
-
US & EU initially collaborated together as they fought together against Iraq in Gulf War (1990-1991)
-
Later, US refused to sign Kyoto Protocol (1991) & refused to join International Criminal Court
-
EU hated this as US doesn't care about climate change & supports crimes against humanity
-
EU also hated that US has death penalty & gun ownership is allowed
-
-
Former East Bloc nations got admitted into NATO, so US couldn't convince them to get rid of communism anymore
-
EU also hated that US wanted to use terrorism to attack Iraq & Afghanistan after 9/11 attacks
-
EU wanted to use intelligence & security to attack them
-
-
After Obama got elected in 2008, tensions decreased as US withdrew troops from Iraq & Afghanistan
-
Also, US removed missiles from central Europe
-
-
Later, in 2008, US had a recession due to housing boom & bank failure
-
Spread to Europe & first to Iceland
-
Wealthier nations had to help the smaller nations
-
IMF would only provide aid if these nations cut social welfare spending, which was bad for some poorer nations
-
Wealthier nations didn't always want to help poorer nations, leading to anti-EU sentiment
-
This is one cause of the Brexit (2020)
-
-
This shows that the Eurozone (group of countries that use currency Euro) isn't stable as it contains many different economies
-
.png)
Turmoil in Muslim World
-
Anti-Western sentiment appeared in the Islamic world mostly by force
-
Started to hate Europeans since the mandate system established after WW1
-
When Europeans left after mandate system, US intervened in the Middle East
-
US supported an Iranian president, but the Iranians overthrew him & put an anti-US man in charge
-
US also supported Israel
-
-
After 9/11 attacks, US wanted to attack Afghanistan & Iraq
-
US killed Osama bin Laden in 2011, the leader of the 9/11 terrorist attacks
-
US also wanted to kill Saddam Hussein, Iraqi president
-
Believed he was developing nuclear weapons after agreeing not to in 1991
-
Many doubted this fear as UN inspectors found no such weapons, but US & UK still invaded Iraq in 2003
-
Caused Hussein's regime to collapse
-
-
Arab Spring of 2011 also caused turmoil in Middle East
-
Started as a Tunisian fruit vendor put himself to fire to protest harassment from government
-
Protests arose throughout the Middle East
-
Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, Yemen, Syria, Bahrain ended authoritarian regimes
-
After the Arab Spring, no stable government existed due to ethnic conflict
-
-
.jpg)
Climate Change & Human Rights
-
As nations needed more energy, they increased their reliance on fossil fuels
-
These release lots of carbon emissions, causing climate change
-
Also, fossil fuels could run out soon
-
Also, controlling oil was important as Russia surpassed Saudi Arabia as largest oil producer
-
Oil could also run out soon
-
-
-
Climate change is a big problem
-
Causes habitat destruction, rising sea levels, etc.
-
Many nations imposed restrictions on carbon emissions, but not all nations have followed it
-
India & China struggle to balance carbon emissions with economic growth
-
NGOs also helped with combating climate change
-
In 2012, 192 nations met in Doha, Qatar, to discuss climate change goals
-
Still, the success of these goals is uncertain as it would require radical changes
-
-
-
European nations also sought to promote human rights throughout the world
-
Believed in abolishing death penalty, legalizing same-sex marriage
-
Wanted to stop civil wars & prevent tyrannical governments from killing their people
-
Also wanted to provide healthcare to combat AIDS
-
Wanted to spread individual freedom
-

Summary
World War 1:
World War 1 began with many nationalist rivalries. Due to international alliances, small conflicts allowed whole alliances to turn against other alliances, causing huge destruction. This is what happened in WW1, where a small conflict between Austria-Hungary and its Slavic province led to Germany declaring war on Britain, France, and Russia. The war was a stalemate due to trench warfare & new battle techniques. The home front was completely mobilized for the war as they all had to work & had production quotas. Germany defeated Russia, which allowed for Vladimir Lenin's communist government to take over & win popular support due to its desire to withdraw from the war. Russia later withdrew from the war and established communism as the main government. Meanwhile, US joined the war as it made financial sense to do so and defeated Germany. US, Britain, and France drafted the Treaty of Versailles (1920), making Germany pay for the war. The ottoman state collapsed, and a secular nation of Turkey was founded. In the former Ottoman-held Arab states, Britain & France established mandates. Austria-Hungary also broke apart. 15-20 million lives were lost, and 20 million more were lost in the influenza pandemic of 1918 following the war.
Interwar Period:
The interwar period allowed nations to rebuild themselves after the war and brace for another war. The Great Depression started with the US Stock Market crash of 1929 and spread throughout Europe & the world as US gave many loans to Europe. Britain & Scandinavian countries successfully combated the crisis, while France couldn't due to internal political rivalries. Additionally, people were more pessimistic and believed god & humanity had abandoned them. Abstract art became common as it involved making random lines. Furthermore, totalitarian regimes gained power in Italy, Germany, and Russia. In Italy & Germany, fascist regimes took power. Mussolini led Italian fascism & gained support because Italians believed Mussolini would bring economic recovery after WW1. Hitler gained power for roughly the same reason as many opposed the existing German Weimar republic. Hitler believed Germany was not responsible for WW1 & promised economic recovery. Hitler emphasized anti-Semitism & German superiority. In Russia, as Lenin died, Stalin took over & ruled very cruelly. He suppressed all dissidents, promoted heavy industry, and forced all peasants to live on collectivitized farms.
World War 2:
World War 2 started as Hitler believed Germany was not responsible for WW1's reparations and wanted more living space for the Germans. Hitler sought to create a union of the lands with all ethnic Germans, so he first invaded Sudetenland, a part of Czechoslovakia with majority Germans. Britain & France let him as they feared war with Germany. Hitler then sought to invade the rest of Europe & eventually conquered most of Europe using his lightning war (blitzkrieg) techniques. He trapped the French army at Dunkirk & used his air force to attack London. British air force successfully fought back, but London was devastated. Italy also joined the war with Germany. Japan also had a fascist regime and attacked the US at Pearl Harbor after US opposed Japanese aggression in Southeast Asia. As you can see, the Axis powers (Germany, Japan, Italy) had many early victories. However, the Allies powers (US, Britain, France, Russia, China) later took over and removed Germany from North Africa & from Italy. On D-Day (6/6/1944), Britain & US troops landed in Normandy, France, and for a year, they kept pushing the German front lines toward Germany. Meanwhile, Germany failed to attack Moscow & lost at Stalingrad, so the Russian army was pushing westward into Germany. In May 1945, the US, UK, & Russian armies met in Germany and Germany surrendered. Later, US bombed Japan & caused Japan to surrender.
Cold War:
After WW2, US & USSR didn't agree on the peace settlement. US wanted to spread capitalism throughout the world, while USSR wanted to spread communism, leading to the Cold War, an indirect war between US & USSR in which no actual fighting took place. US created NATO among its capitalist members in the West Bloc (Western Europe), and the USSR created the Warsaw Pact among its communist members in the East Bloc (Eastern Europe). US & USSR then had the nuclear arms race in which they both developed complex nuclear arms in case of nuclear war but never actually used them. Furthermore, West Bloc & USSR occupied Germany to prevent another war caused by Germany. US & USSR sought to prevent the spread of communism & capitalism, respectively, leading to the Korean War & Vietnam War, in which they supported opposite sides of the conflict. When Stalin died, Khrushchev took over, and he was less cruel & initiated de-Stalinization and detente (slight peace) with the US. However, this slightly caused the USSR to collapse, so he made his rule a bit stricter. Many East Bloc nations revolted, most notably the Prague Spring (1968), so Brezhnev, the next ruler, created the Brezhnev Doctrine (1968), allowing him to intervene in the East Bloc wherever communism is threatened. Later, economic crisis of 1970s caused many East Bloc nations to suffer, leading to more anti-communist protests. Finally, the next leader, Gorbachev, initiated failed economic reforms and allowed East Bloc nations to outvote their communist regimes to maintain stability in the USSR. Eventually, all nations of East Bloc & part of USSR declared independence. After the Cold War, Russian economy fell due to a sudden transition to capitalism, but under Putin, it grew again. Other East Bloc nations also made economic & political reforms after abolishing communism. In Yugoslavia, ethnic conflicts caused it to breakup into 6 individual nations.
Post-WW2 Conflicts & Developments:
In Europe, white collar jobs replaced industrial jobs, and women were allowed to play a prominent role in society due to this change. Furthermore, due to the consumer revolution, a new youth culture developed (baby boomers). Many people (especially from former European colonies) migrated to Europe, adding to Europe's ethnic diversity. Furthermore, center-right politicians promoted liberal values & led European economic recovery by stimulating the consumer revolution. 6 European nations created the Common Market in 1957, which eventually became the EU in 1993. In the economic crisis of 1970s, conservative leaders led economic recovery. More feminist & environmentalist movements also arose. Later, due to European economic crisis & self-determination movements, the former European colonies declared independence. Most European nations still maintained ties with their colonies. France put all of its African colonies into a larger French Commonwealth, but since Algeria wanted complete independence, Algeria caused an 8-year war, which it won.
Globalization:
In the modern period, the world has globalized to such a great extent due to modern technology. International organizations like the European Union (formed in 1993 from the Common Market), United Nations, World Trade Organizations, etc. lead international cooperation and allow for transnational businesses & organizations to exist. More technologies like CDs, computers, TVs, etc. have allowed people to communicate with people and watch/listen to things easily right from their home. Due to easy transportation, more migration has occurred, which has created multicultural communities in the migrant destinations. Furthermore, many people question migration & often despise immigrants for stealing their nation's jobs. As always, there are still many global problems. US & EU have disagreed on many things, causing tensions between them. A recession in 2008 caused the European economy to also collapse, creating tension among the EU as the wealthier nations didn't always want to help the poorer nations. US & Europe also had problems with the Arab world, especially after the 9/11 attacks, because Islamist groups in Afghanistan were responsible were responsible for the attacks. In 2003, US & UK invaded Iraq, thinking they were hiding weapons. In 2011, the Arab Spring caused the overthrow of many authoritarian regimes in the Middle East. Furthermore, issues like climate change & human rights are really important as many industries pollute the environment, and many authoritarian regimes restrict the rights of their humans.
