Unit 7: 1890-1945
Outline
General Timelines
Timeline #1: Spanish-American War (1898)

Timeline #2: Other Territorial Acquisitions

Timeline #3: The Progressive Movement

Timeline #4: World War 1

Timeline #5: The New Era

Timeline #6: The Great Depression

Timeline #7: The 1st New Deal (1933-1934)

Timeline #8: The 2nd New Deal (1935-1938)

Timeline #9: Interwar Period Foreign Policy

Timeline #10: World War 2

General Maps
Map # 1: Spanish-American War in Cuba

Map # 2: Other Territorial Acquisitions

Map # 3: US in Progressive Era

Map # 4: US Involvement in Latin America

Map # 5: US in World War 1

Map # 6: Europe in World War 1

Map # 7: US in the New Era (1920s)

Map # 8: US in the Great Depression

Map # 9: US in the New Deal

Map # 10: Europe in the Interwar Period

Map # 11: The Pacific in the Interwar Period

Map # 12: Europe in World War 2

Map # 13: The Pacific in World War 2

Course Content
Spanish-American War:
Causes of the War
Situation in Cuba
-
Cuba & Puerto Rico were Spain's last colonies
-
In early 1800s, all of Spain's other colonies in America got independence
-
-
Cubans wanted independence from Spain
-
In 1895, Cuban revolutionary Jose Martí led a revolt against the Spanish
-
US sympathized with Cubans, but the Spanish hated the independence movement
-
-
Spanish General Valeriano Weyler instituted harsher policies in Cuba to suppress the revolutionaries
-
Put some Cubans in concentration camps where thousands died
-
US media covered this situation, causing Americans to sympathize with the Cubans
-
-
To help the Cubans, US called Spain to recall Weyler's brutal actions
-
Spain refused
-
-
In February 1898, American ship USS Maine sunk in Havana harbor due to an engine explosion
-
American media falsely blamed it on the Spanish, causing anti-Spanish sentiment in US
-
-
Spain again refused to end hostilities in Cuba, so US declared war on Spain

Battles of the War
Overview of War
-
A very short war (April - August 1898)
-
Only ~400 US troops died, but ~5000 died of disease
-
-
US had supply problems for its army
-
Had to rely on National Guard & volunteer regiments instead of actual military
-
Had little experience w/ large-scale war
-
-
Had shortage of rifles & ammunition
-
-
Many Blacks also served in the US army for the war
-
Mostly formed volunteer regiments or served in the 4 Black US regiments
-
War gave them a sense of freedom as many Cuban soldiers were also Black
-
.jpeg)
Battles in Cuba
Spanish Gen. Pascual Cervera slipped past the US navy & stationed himself at the port city of Santiago de Cuba (May 1898)
US needed to defeat Spanish forces at El Caney & San Juan Hill to retake Santiago de Cuba
US Gen. William Shafter was the main commander of troops to Cuba. His troops were very disorganized
After US forces had control of Spanish forts near Santiago de Cuba, Spanish troops tried leaving Santiago harbor but were attacked by US troops. US troops held Spanish Gen. Pascual captive (Jul 3, 1898)
Asst Sec of Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, led a regiment called "Rough Riders" as they were disorganized. He defeated the Spanish at El Caney & San Juan Hill (Jul 1, 1898)
Gen. Shafter employed Gen. Joseph Wheeler to attack the Spanish fort at Las Guasimas, but he lost (Jun 1898)
-
Yellow fever was spreading rapidly among US troops, so US withdrew its troops from Cuba
-
US only left one volunteer Black regiment in charge of Cuba
-
They were from the southern states, so they were more immune to yellow fever than other troops
-
Battles in Puerto Rico
US Navy Adm. William T Sampson attacked Puerto Rican capital, San Juan, & imposed naval blockade of it (May 12, 1898)
US Gen. Nelson A Miles arrived w/ 1300 soldiers to lead land campaigns. Battles of Yauco, Fajardo, and Guayama were all inconclusive as both parties retreated (Jul - Aug 1898)
US troops lost Battle of Coamo (Aug 9) & Battle of Asomante (Aug 12)
-
Because US forces were losing in Puerto Rico, they withdrew in Aug 1898
-
In Treaty of Paris (Dec 1898), Spain ceded Puerto Rico to the US
Battles in Philippines
US Navy Cmd. George Dewey led huge US victory at Battle of Manila Bay (May 1, 1898)
Emilio Aguinaldo gained support of other Filipinos in support of the US against Spanish rule. He declared independence of Philippines on Jul 12
On Aug 5, Spanish forces came to Manila to establish control. US forces defeated them at Battle of Manila (Aug 13, 1898), giving the Philippines to US
Battles in Guam
US fleet led by Capt. Henry Glass was on his way to Philippines & instead invaded Guam's Apra Harbor (Jun 20, 1898)
Local officials didn't know Spain & US were at war, so they didn't care to defend
Glass informed them that they were at war & forced them to surrender (Jun 21, 1898)
End of the War
Treaty of Paris (Dec 1898)
Cuba gets independence from Spain
US gets Puerto Rico and Guam
US pays $20 million to Spain for Philippines
Situation in Puerto Rico
-
Puerto Rico was a Spanish colony & long sought independence from Spain
-
In 1898, Luis Miñoz Rivera got some autonomy for Puerto Rico
-
-
However, in Dec 1898, Puerto Rico was in US's hands
-
Was under US military rule until 1900
-
-
In 1900, US passed Foraker Act
-
Created a government in Puerto Rico: US-appointed governor, 2 legislative assemblies, judicial system
-
-
In 1917, US passed Jones-Shafroth Act
-
Made all Puerto Ricans US citizens
-
-
Puerto Rico economically benefited from the US
-
It had a thriving sugar industry & could trade with US without tariffs
-

Philippine-American War (1899-1902)
-
After Treaty of Paris (Dec 1898), Filipinos felt betrayed as they wanted independence from US & Spain
-
Emilio Aguinaldo led the Filipinos to revolt against the US
-
In 1900, US Gen. Arthur MacArthur became the governor of US-occupied Philippines
-
Americans had brutal war tactics
-
Destroyed homes & plantations, forced people into concentration camps, etc.
-
In the end, over 200k Filipino civilians died while only about 6k US troops died
-
-
William Howard Taft (future US president) was Governor-General of Philippines (1901-1903)
-
Developed infrastructure in Philippines: Built roads, schools, bridges, sewers, etc.
-
Gave Filipinos some autonomy
-
-
Philippines was very dependent on US economy
-
US governors were actually preparing Philippines for independence
-
Philippines got independence from US in 1946

Development in Cuba
-
After Cuba got independence from Spain in 1898, US army was stationed there to help develop the nation
-
Gen. Leonard Wood was Governor of Cuba during that time
-
Build roads, schools, hospitals, etc. in Cuba
-
Set up Cuban government system
-
-
US then made Platt Amendment to Cuban constitution (1901)
-
Limited Cuba's ability to make treaties w/ other nations
-
Gave US the right to intervene in Cuba to preserve Cuban independence
-
Basically established US as the dominant power over Cuba
-
-
US then economically dominated Cuba
-
Bought many plantations, factories, railroads, etc.
-
Developed its thriving sugar economy
-
Known as "Yankee imperialism" where US is economically dominating Cuba
-

Imperialism:
Debates about Imperialism
-
As the US was developing into an imperial power during the Spanish-American, this sparked lots of debates about the ethics & benefits of imperialism
-
The viewpoints of both sides are highlighted below:
Imperialists:
-
Believed Filipinos are racially inferior & need US dominance
-
Believed Philippines brings economic opportunities to US
-
Wanted to compete with European colonial empires
-
Believed US has "closed" its frontier & needs to expand more
Anti-Imperialists:
-
Believed in self-determination (each nation chooses their own government)
-
Believed Filipinos are racially inferior & don't deserve to be part of US
-
Believed US had a tradition of isolation from foreign dominance
Acquiring New Territories
Alaska Purchase (1867)
Alaska was a Russian territory. Russia had little interest & not many settlers there. Russia didn't have resources to cater to Alaska
Russia was weakened by Crimean War & didn't have money to govern Alaska. US wanted Alaska to continue its Manifest Destiny & gain power in Asia-Pacific region
Russia agreed to sell Alaska to Pres. Andrew Johnson for $7.2 billion in Oct 1867
-
Alaska was purchased by William H Seward, the Secretary of State of Presidents Lincoln & Johnson
-
Many people opposed Alaska's purchase
-
Called it "Seward's Folly" as they thought the land was worthless
-
-
Eventually, valuable resources were found in Alaska, making it beneficial to the US
-
Gold was found in Yukon, near Alaska, in 1896
-
Lots of people went to Alaska & Yukon
-
-
Oil was discovered in Northern Alaska in 1968
-
Also has coal, timber, natural gas, fur, and lots of salmon & fishing
-
-
Alaska was ruled by the US military since 1867
-
Alaska got a civil government in 1884
-
Alaska became the 49th state in 1959
Annexation of Hawaii (1898)
In mid 1800s, many Americans came to Hawaii for its thriving sugar industry. Hawaii's sugar industry benefited from trade w/ the US
The McKinley Tariff (1890) imposed a tariff on imported sugar, which devastated the Hawaiian sugar industry as they couldn't sell in America
Americans in Hawaii believed that if they join the US, they won't have to pay the tariff anymore
The Spanish-American War (1898) spurred increased imperialism, allowing president McKinley to annex Hawaii (1898). He believed Hawaii was a good base to conquer Philippines
Dole went to DC to petition annexation, but Grover Cleveland was becoming president & he opposed annexation (1893)
Samuel Dole led other American planters in an uprising against Hawaiian Queen Liliuokalani (Jan 1893)
Open Door Policy in China (1899)
-
In late 1800s, many European nations were carving spheres of influence in China
-
US wanted to join, so the US also carved its own sphere of influence in China
-
-
Sec of State John Hay wrote the Open Door notes (1899), a set of rules for the spheres of influence:
-
Each nation should have free access to ports within its sphere & respect the spheres of other nations
-
Only the Chinese government should collect taxes
-
No nation should be exempt from paying taxes at harbors or railroads
-
-
The Open Door notes allowed the US to continue its trade with China

Annexation of American Samoa (1900)
US wanted to annex the Samoan islands (in South Pacific) as a naval base & as a gateway to Asian trade
In 1872, US agreed to help a Samoan tribe in the 2nd Samoan Civil War (1898-1899) in order to build a naval base. Germany & Britain also intervened in the war
In Tripartite Convention (1899), they divided Samoa: US got Eastern part, Germany got Western part, and Britain got other trade concessions
-
American Samoa was a strategic naval base for the US during World War 2
-
US Navy controlled American Samoa from 1900-1951
-
US Dept. of Interior controlled American Samoa from 1951-1977
-
Since 1977, governors of American Samoa have been elected by the people of American Samoa
The Progressive Movement:
Societal Progressive Movements
Muckrakers
-
Muckrakers were a group of journalists who wrote about societal problems
-
Lincoln Steffens published an article exposing political machines
-
His book was The Shame of Cities
-
Led to public outcry & reform of city governments
-
-
Ida Tarbell wrote about the bad and dangerous business practices of Rockefeller's Standard Oil Company & Trust
-
Upton Sinclair wrote The Jungle, exposing the dangerous working conditions in Chicago's meatpacking industry
-
His actions led to Pure Food and Drug Act & Meat Inspection Act (1906)
-

The Social Gospel
-
A movement within Christianity to bring social reform
-
Mostly within Protestantism, partially within Catholics & Jews as well
-
Used religious revival to bring social reform
-
Provided material aid & spiritual aid to the urban poor
-
-
Salvation Army was a famous example of this
-
Catholic priest John Ryan was a famous social reformer who used Catholicism for reform

The Settlement Houses
-
A group of houses to provide shelter & food to the urban poor
-
Jane Addams opened the Hull House in 1889, one of the 1st settlement houses in US
-
Led to the creation of hundreds of settlement houses nationwide
-
Many unmarried college women worked here
-
-
Led to the creation of the profession of social workers
-
Many universities now had classes for sociology
-

Professionalism
-
The rise of cities led to a need for more services in the cities (medical, legal, managerial, etc. services)
-
This led to the rise of a new middle class
-
-
This rise in the middle class professions led to the idea of professionalism
-
Before, anyone could pursue any job without any training
-
Now, governments and private groups made professional standards & licenses for jobs
-
-
In 1901, professional doctors created American Medical Association
-
Had strict educational requirements to obtain a license
-
Some states passed laws requiring licensing of all physicians
-
-
National Association of Manufacturers (est. 1895) was a professional group of manufacturing businessmen
-
US Chamber of Commerce (Est. 1912) was a group of professional businessmen
-
American Farm Bureau Federation (est. 1920) promoted rights for farmers & improved education on farming methods

Working Condition Reforms
-
Labor unions and the American Federation of Labor pressured states to pass labor laws
-
Some states passed child labor laws, workers' compensation, & limitation of women's working hours
-
-
In 1911, a fire in the Triangle Shirtwaist Company in NYC killed 146 workers
-
Led to a movement for better working conditions
-
Many city governments like Tammany Hall led working condition reforms
-

African-Americans & Reform
-
Booker T Washington sought to uplift the Black community by encouraging them to get an education
-
In his speech, the Atlanta Compromise (1895), he reasserted these views
-
-
W. E. B. DuBois disagreed w/ Washington. He believed Blacks should work on getting civil rights
-
He met w/ other Blacks in the Niagara Movement (1905) to work on getting civil rights
-
-
DuBois founded the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909
-
An organization to campaign for civil rights for Blacks
-
NAACP won many court cases to give some civil rights to Blacks
-
-
Many people also opposed lunching
-
Ida B Wells was a prominent anti-lynching activist
-

Temperance
-
Temperance was the anti-alcohol movement
-
Many women were active as they sought to limit the drunkenness of their husbands
-
Also wanted to limit the expenses their husbands spend on alcohol
-
-
-
Women's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) (est. 1873) used Christianity to promote temperance
-
Frances Willard was the president after 1879
-
-
Many states started to prohibit alcohol
-
After WW1, alcohol became a moral issue → 18th amendment (1919) banned alcohol consumption

Immigration Restriction & Eugenics
-
Many believed immigration was causing social problems, but they disagreed on how to solve this
-
Some wanted to assimilate immigrants into American society
-
Others wanted to slow immigration
-
-
This led to the eugenic movement
-
Forced the sterilization of the "racially inferior" and those w/ bad genetic qualities
-
Madison Grant wrote The Passing of the Great Race (1916) & was a famous eugenicist
-
Sen. William P Dillingham (R-VT) was the head of a committee that studied immigration
-
Concluded that these immigrants are less assimilable than the German/Irish immigrants from the early 1800s
-
-
-
Many factory owners liked immigration as it brings cheap labor

Women's Reform Movements
Women in Professions & New Image of Women
-
Many women went to colleges and entered into high-ranking professions themselves
-
Some were physicians, lawyers, managers, etc.
-
Women dominated the nursing industry
-
-
Many women had professions involving helping others (social workers, teachers, etc.)
-
Some Black women taught in Black schools
-
-
Husbands worked outside the home, children went to school, and domestic appliances could help w/ domestic chores, so women had more free time
-
Women could spend more time on their education & their job
-
-
Some women remained single & lived w/ other women to have time to pursue their education
-
Known as "Boston Marriages"
-

Clubwomen
-
Many women's clubs were arising for women to show their intellect & high social status
-
General Federation of Women's Clubs (GFWC) (est. 1892) had 1 million members by 1917
-
-
In early 1900s, clubs focused more on gaining women's rights
-
Black women joined separate Black women's clubs
-
Discussed racial issues like segregation & lynching
-
-
These clubs led to the passage of many laws to protect women's rights
-
Compensation for widows, food/drug regulations, workplace safety regulations, etc.
-
-
Women's Trade Union League (est. 1903) sought to campaign for women's rights in workplaces
-
Organized strikes & marches for women
-

Women's Suffrage
-
National American Women Suffrage Association (Est. 1890) sought to campaign for women's suffrage
-
Led by Anna Howard Shaw & Carrie Chapman Catt, Susan B Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Lucy Stone
-
-
Promoted the idea that women are the moral voice in society
-
Since women occupy a separate domestic sphere, they have a different perspective
-
Believed women could curb belligerence by men
-
Gained support after many soldiers returned home from WW1
-
-
-
In 1910s, many states gave women's suffrage
-
19th amendment to give women's suffrage was ratified in 1920

Governmental Reform
City & State-Level Governmental Reform
-
The first step to reforming political machines was decreasing the power of political parties
-
Before, parties gave their own ballots to their supporters
-
Now, election officials created their own general ballot, causing party loyalty to decline
-
Many illiterate people couldn't read the new ballots
-
This caused voter turnout to decline
-
-
-
There were also new forms of city governance
-
Commission Plan: City is led by a nonpartisan city council (about 400 cities adopted this)
-
Council-Manager Plan: Businessman from outside the city would run the city government
-
This person would be uninfluenced by political corruption in the city
-
-
-
Many state governments also had reforms
-
Initiative: The idea where people would submit legislation directly to the voters in the election
-
Referendum: The idea where a legislative policy could be returned to the voters in the election
-
Some states instituted a primary election
-
-
Robert La Follette was the Wisconsin governor & Senator who led many reforms in Wisconsin

The Rise of Socialism
-
Impoverished farmers led the socialist movement as they hated capitalism
-
Eugene V Debs was the leader of socialism & the socialist presidential candidate in 1912
-
Won over 1 million votes
-
-
-
Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) (known as "Wobblies") was a worldwide organization to promote socialism
-
Wanted one large union instead of multiple smaller unions
-
William "Big Bill" Haywood was one of the founders & leaders of the IWW
-
One of the leaders of the Socialist Party
-
-
-
IWW appealed especially to many miners and temporary workers in the West
-
IWW membership declined after 1917 when the gov outlawed the IWW due to an IWW-led strike

Theodore Roosevelt's Actions
Roosevelt's "Square Deal"
-
Theodore Roosevelt was William McKinley's VP & took over when McKinley was assassinated in 1901
-
Roosevelt was very young & was interested in lots of progressive reforms
-
-
Roosevelt's reform program was known as the "Square Deal"
-
Had 3 parts: Regulation of corporations, consumer protection, conservation of nature
-
-
To regulate corporations, Roosevelt filed many anti-trust cases against large corporations
-
Established Dept. of Commerce and Labor (est. 1903) to help with anti-trust cases
-
Filed a lawsuit against Northern Securities Company (1904), which was successful
-
Passed Hepburn Act (1906) to regulate railroads & strengthen Interstate Commerce Commission
-
-
For consumer protection, Roosevelt passed laws to regulate the food industry
-
Pure Food & Drug Act (1906) and Meat Inspection Act (1906) promoted safe food products
-
-
For conservation of nature, he passed laws to conserve forests & natural areas
-
Established National Forest Service (1905)
-
Gifford Pinchot was its first director
-
-
National Reclamation Act (1902) funded irrigation project in the West
-
Created 5 national parks & 18 nat'l monuments
-
John Muir, a prominent conservationist, encouraged him to do this
-
-
In Hetch Hetchy Controversy, residents of SF wanted to build a dam in Hetch Hetchy Valley of Yosemite to provide them water
-
John Muir opposed the project, but SF residents & Roosevelt promoted it
-
In 1913, the bill for the dam was signed
-
-

Panic of 1907
2 people borrowed lots of money to buy stocks in the US Copper Co., attempting to curb the stock price
These 2 people failed, which caused all the banks that lent them money to decline
This caused the Knickerbocker Trust, one of the largest banks to decline. This caused a huge financial crisis
Roosevelt allowed JP Morgan's US Steel Corp. to buy TC&I. This move was controversial as it allowed US Steel to somewhat monopolize the steel industry
There was still one more problem: Many people had who got loans used the Tennessee Coal, Iron, & Railroad Company's Stock (TC&I) as collateral, causing the TC&I's stock to fall
JP Morgan gave some of his funds & encouraged other NY Banks to give their funds to help restore the banking crisis. This allowed some banks to recover
William Howard Taft's Actions
Taft's Failed Actions & Ballinger-Pinchot Affair
-
Taft was also progressive but less progressive than Roosevelt, which made him controversial
-
Taft wanted to lower tariffs, so Congress passed the Payne-Aldrich Tariff (1909)
-
This was bad as it lowered some tariffs only slightly & put other taxes on certain goods
-
The failure of this bill caused many Progressives to hate him
-
-
Taft created the US Children's Bureau (est. 1912) to promote welfare for children
-
Meant to prevent child abuse & orphans
-
-
In the Ballinger-Pinchot Affair, Taft lost popularity
-
Taft put Richard Ballinger as Sec of Interior
-
Ballinger wanted to invalidate Roosevelt's order to protect a million acres of land
-
Louis Glavis (employee of dept. of interior) wanted to investigate into this issue
-
-
Glavis found that Ballinger wanted to use coal deposits in AK for profit
-
Glavis & Gifford Pinchot reported this to Taft
-
-
Taft fired Glavis and acquitted Ballinger
-
This was controversial as public opinion supported Pinchot & Glavis
-
-

The Return of Theodore Roosevelt
-
Roosevelt sought to reunite the Republican party after Taft's controversial actions
-
In a speech at Osawatomie, KS, (1910) he promoted the idea of "New Nationalism"
-
Promoted that the national gov should focus more on the welfare of its citizens
-
-
-
Democrats gained control of the House in 1910, so Roosevelt told Taft to become more progressive
-
In 1911, court ruled that US Steel Corp's acquisition of TC&I was illegal, so Roosevelt lost support
-
Roosevelt announced his candidacy for Republican nomination for presidency in Feb 1912
-
At the Republican Nat'l Convention (1912), there were disputed delegates, causing Taft to win
-
Roosevelt got mad, so he started his own party, the Progressive Party ("Bull Moose Party")
-
Wanted additional regulation of industries, social welfare, women suffrage, etc.
-
He didn't have as much support since many Republicans still supported Taft
-
-
-
In the 1912 election, Woodrow Wilson (D) won

Woodrow Wilson's Actions
-
Wilson was a political science professor at Princeton, then governor of NJ, then president in 1912
-
Wilson believed in "New Freedom"
-
Believed in destroying monopolies & large enterprises
-
Wanted small enterprises w/ individual opportunity
-
-
In contrast to "New Freedom," Roosevelt's "New Nationalism" wanted to regulate large enterprises, not destroy them
-
In Revenue Act (1913) (Underwood-Simmons Tariff), Wilson significantly lowered tariffs
-
Gave big businesses real foreign competition, preventing them from being super powerful
-
-
Federal Reserve Act (1913) created 12 regional banks
-
Each regional bank would control private banks in their region
-
Regional banks would control assets of private banks & give them low-interest loans
-
Implemented Federal Reserve Notes, which were not backed by gold & backed by the gov
-
Could quickly supply funds where necessary
-
-
-
Federal Trade Commission Act (1914) established Federal Trade Commission
-
This would identify if businesses are becoming monopolies or have unfair labor practices
-
-
Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) regulated monopolies
-
Smith-Lever Act (1914) created programs for land-grant universities to educate rural people about agricultural technologies
-
Democrats lost seats in 1914 Congressional elections, so Wilson became more progressive
-
Wanted to win 1916 election
-
Appointed Louis Brandeis to Supreme Court, the 1st progressive to serve there
-
Gave compensation to federal employees
-
Passed Keating-Owen Act (1916) to regulate the sale of goods produced by children
-
Declared unconstitutional later
-
-

World War 1:
US Neocolonialism in Latin America
Roosevelt & Roosevelt Corollary
-
Pres. Theodore Roosevelt expanded his navy as he believed US needed to protect other nations
-
Especially developed navy after Japan started developing its own navy
-
-
In 1906, Roosevelt was an arbitrator to end the Russo-Japanese War & won Nobel Peace Prize for it
-
Roosevelt added Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine
-
US can intervene in domestic affairs in Latin America if it was causing political instability
-
This would ensure US could protect its economic interests in Latin America
-
-
Intervened in Dominican Republic in 1903 after a revolutionary regime took over & was bad
-
Added Platt Amendment (1901) to Cuban Constitution to make US Cuba's dominant power
-
Intervened in Cuba in 1906 due to domestic issues
-

Panama Canal (1914)
US wanted to build a canal through Isthmus of Panama as the route was short & a French company already started construction
Colombia (who owned Panama at the time) refused to cede the land to the US, so US helped local Panamanians declare independence from Colombia (1903)
Panamanians allowed US to build the canal, completed in 1914
Taft's "Dollar Diplomacy" & Wilson's Intervention in Latin America
-
Pres. William Howard Taft adopted "dollar diplomacy"
-
US would invest money into Latin America in exchange for political influence
-
Invested in Nicaragua in 1909
-
Nicaraguans revolted against pro-American government, so US sent troops to stop it
-
-
Pres. Woodrow Wilson was more aggressive in Latin America
-
Established a military gov in Dominican Republic in 1916
-
US Marines occupied Haiti from 1915-1934
-
Bought Danish West Indies (fearing Germany might conquer it), named it Virgin Islands
-
-
Wilson also intervened in Mexican Revolution by supporting one revolutionary leader, Gen. Venustiano Carranza

The Battles of World War 1
Start of World War 1 in Europe
Europe had many alliances. Triple Alliance (Central Powers) were Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. Triple Entente (Allies) were Britain, France, Russia
Austro-Hungarian Archduke Franz Ferdinand was visiting Serbia. Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip killed Ferdinand
Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia
Britain declared war on Germany
Germany declared war on Russia & France
Russia wanted to protect Serbia, so it declared war on Austria-Hungary
US's Initial Neutrality
-
Initially, Pres. Wilson sought to remain neutral
-
US had many immigrants from both sides of war
-
US wanted to trade w/ both sides
-
Became complicated as Britain blockaded Germany
-
Also, German U-boats (submarines) would sink British merchant ships
-
-
US's economy was booming due to increased production of arms & trade w/ both sides
-
-
In 1915, Wilson prepared the army in case of war
-
In 1916, Wilson narrowly won re-election

US Joins the War
-
Germany started threatening US trade w/ Britain
-
In May 1915, Germany sunk British ship Lusitania, killing 128 Americans on board
-
Germany kept threatening British & French ships
-
-
In Jan 1917, Germany sent the Zimmerman Telegram to Mexico, but US intercepted it
-
Germany told Mexico to join the war against US in exchange for helping regain the territories ceded to US in Mexican-American War
-
US intercepted this & hated Germany more
-
-
In Mar 1917, a communist gov took over Russia & withdrew from the war
-
Now, Germany could focus all its efforts on Western front w/ Britain & France
-
-
Wilson also gave many loans to the Allies, especially to France
-
Made financial sense for US to help the Allies
-
-
French & British needed more ground troops to fight Germany
-
Needed troops from the US
-
After Russia's withdrawal, Germany had more troops to fight, so Allies needed more troops
-
-
Wilson thus told Congress to approve war declaration in Apr 1917, joining the Allies
-
Initially believed it to be a war on democracy
-
Wanted "Peace without Victory"
-

US in the War
-
Wilson & Sec of War Newton D Baker passed mandatory conscription laws
-
3 million men joined the war
-
This was called the American Expeditionary Force (AEF)
-
Led by Gen. John J Pershing
-
-
-
-
Women served auxiliary roles in the military
-
About 400k African-Americans served in the war
-
Many were in non-combat duties
-
Most were in segregated all-Black regiments
-
-
The war had many brutal weapons
-
Trench warfare became common, caused lots of disease spread
-
Airplanes were sometimes used, but were in early stage of development
-
Submarines (U-boats) were used to sink boats
-
-
Germany agreed to armistice in Nov 11, 1918
-
Millions of people died, but only 112k died from US

The Home Front
The US Economy during the War
-
US spent $32 billion on the war effort
-
Sold "Liberty bonds" to people to finance it
-
Raised taxes
-
-
US needed to mobilize its economy to support war
-
In 1917, Wilson created War Industries Board (WIB)
-
Meant to coordinate government purchase of military supplies
-
Had some management problems
-
-
War caused US economy to boom
-
Industry boomed due to increased exports
-
Shipbuilding grew in West due to Panama Canal
-
Farming grew due to higher demand for food
-

US Economy's Labor Sources During the War
-
Because many men were at war, women & minorities got job opportunities in factories
-
National War Labor Board (est. 1918) sought to resolve labor disputes in industry
-
Imposed 8-hour workday, equal pay for men & women, right for unions to bargain collectively
-
Workers got some other gains
-
-
Still, there were some strikes
-
A miner strike in Ludlow, CO led to the Ludlow Massacre (1914), killing 39 strikers
-
-
100,000s of African-Americans migrated from Jim Crow South to the North ("Great Migration")
-
Found many job opportunities in industrial cities of the North
-
Caused many riots by whites against Blacks
-
-
Many Women also joined industrial jobs
-
Unfortunately, they were fired or quit after the war when men returned
-
-
Many other minorities (Mexicans, Japanese, etc.) got industrial jobs
-
When white male soldiers returned from the war, they retook these jobs from these minorities
-

Suppressing Dissent & Promoting Wartime Propaganda
-
Many people supported WW1
-
Churches prayed for soldiers
-
Led to anti-German sentiment throughout US
-
-
Committee on Public Information (CPI) sought to promote pro-war propaganda
-
Promoted pro-war literature & propaganda
-
Depicted crude images of Germans
-
-
Government passed acts to ban anti-war propaganda
-
Espionage Act of 1917 gave penalties for obstructing or sabotaging war effort
-
Post Office banned seditious stuff (including all socialist stuff) from its mail
-
Sedition Act (1918) banned any public criticism of the war
-
Some vigilantes organized mobs to spy on people for signs of disloyalty to war effort
-
-
Many Germans were targets of violence
-
Lots of people opposed the war
-
Socialists opposed the war
-
Socialist leaders were jailed
-
-
Many immigrants opposed the war
-

Post-War Peace
Wilson's 14 Points
-
Pres. Wilson drafted the 14 points in the war, a set of peace agreements meant for after the war
-
The general agreements are described below:
Readjust borders within Europe
Free trade in the seas & open diplomacy (no secret treaties)
International body of nations (the League of Nations)
-
The main theme of these points is the idea of self-determination
-
The idea where each nation chooses its own type of government
-
-
There were other flaws
-
Didn't mention economic rivalries and how they can affect free trade in the seas
-
The international organization had some flaws
-
The Paris Peace Conference
-
A conference at Palace of Versailles (France) to discuss the post-WW1 peace agreement
-
David Lloyd George (UK), Georges Clemenceau (France), Wilson (US), and Vittorio Orlando (Italy) were the "Big Four" delegates
-
-
Wilson presented his 14 points, but many ideas failed
-
Freedom of trade in the seas failed
-
Self-determination failed
-
-
Wilson also opposed charging the Central Powers for the war, but that failed
-
Britain & France wanted reparations from Germany ($32 billion) for war damage
-
-
One thing in which Wilson succeeded was the creation of the League of Nations
-
In Jan 1919, they accepted the Covenant of the League of Nations
-
Established an international body to resolve disputes
-
It was flawed as it relied on collective security
-
If one nation is invaded, all other nations must come to its defense
-
-
-
-
All the agreements were passed in the Treaty of Versailles (1919)

Ratification of the Treaty of Versailles
-
The next obstacle was to get Congress to ratify the Treaty of Versailles
-
In 1918, Republicans won control of both houses, making ratification hard
-
-
Congress opposed the League of Nations
-
Believed joining an international organization limits US sovereignty
-
Believed it allows other nations to intervene in Americas, voiding the Monroe Doctrine
-
-
Sen. Henry Cabot Lodge led the opposition to the League of Nations
-
Proposed some modifications to the treaty, but Wilson never approved them
-
-
-
Wilson decided to travel throughout the country to gain support for the Treaty of Versailles
-
This failed
-
-
In the end, US never joined the League of Nations

Post-War Problems
Situation in Industry
-
War ended sooner than people expected
-
People produced more goods than needed, causing inflation
-
This led to a small recession in 1920-1921
-
-
As soldiers came back from the war, they retook their industrial jobs
-
All the women, Blacks, & other minorities that got industrial jobs had to give them back to the White men who came back from war
-
-
Also, as economy shifted back to normal, employers rescinded previous benefits
-
Rescinded the 8-hour workday, etc.
-
-
There were many strikes in 1919
-
A shipyard strike in Seattle in Jan 1919 put the city at standstill until US Marines came
-
In Sep 1919, Boston Police Force went on strike
-
Gov. Calvin Coolidge (future President) called National Guard to quell it
-
-
In Sep 1919, 350k steelworkers from midwest went on a huge strike
-
Lasted until January
-
-
.png)
Situation for African-Americans
-
Many African-Americans felt a feeling of liberty after the war
-
Fighting in the War encouraged them to fight for their civil rights
-
This still didn't change Whites' attitudes toward them
-
-
There were many Race Riots, and hostility toward Blacks increased
-
Lynchings increased in the South
-
Black industrial workers had to give up their jobs to White men returning from war
-
Chicago Race Riot of 1919 killed 38
-
-
Marcus Garvey, a Jamaican, advocated for Black Nationalism & promoting of Black culture
-
Believed Blacks should be proud of their heritage & promote Black culture
-
United Negro Improvement Association (UNIA)
-
Wanted Blacks to go back to Africa
-
-

The Red Scare
-
Communism was common among American farmers & industrial workers since late 1800s
-
Remained a small movement w/ little potential
-
-
In 1917, Bolshevik Communist revolution in Russia showed that a communist gov is possible
-
Led many to believe that communists could take over the US eventually
-
-
Russia formed Communist International (Comintern) to promote communism worldwide
-
Communist Party USA (est. 1919) promoted communism
-
Many states suppressed communism & enacted sedition laws
-
There were also mobs & other violence against communist revolutionaries
-
-
American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU, est. 1920) promoted that communism was free speech
-
Opposed anti-communist suppression & publicized the actions of anti-communist mobs
-

The New Era:
Developments in the Economy
Economic & Technological Innovations
-
European industry was down at this time, so US industry boomed
-
Automobile industry boomed
-
This caused steel, iron, glass, tool, oil, and road construction industries to also boom
-
-
Radios became popular as they could transmit speech & music via radio signals
-
Almost all families had one by end of 1920s
-
-
-
There were many more technological innovations
-
Commercial planes were starting out
-
Trains became faster & more efficient
-
Home appliances were developed
-
Telephones became somewhat common
-
Early computers were developed
-

Welfare Capitalism & Decline of Labor Unions
-
Many employers adopted "welfare capitalism" where they give welfare benefits to employees
-
Shorter workweeks, higher wages, paid vacation
-
-
Unemployment was high because new tech was rapidly expanding, & old jobs become obsolete
-
Standard of living was increasing
-
Labor Unions started to decline
-
Much harder to organize unions since jobs were less of manufacturing/unskilled & more of craft and contract labor
-
Widespread anti-union sentiment as well
-
The spread of Welfare Capitalism prevented the need for labor unions & strikes
-
-
Some adopted the "American Plan," the idea that no employee should be required to join a labor union
-
This was also the idea that many employers would refuse to negotiate with a union
-
Caused labor unions to decline as well
-

Women & Minorities in the Workforce
-
Many women had "pink collar" jobs
-
Service jobs, clerks, telephone operators, teachers, etc.
-
-
African-Americans migrated north in the Great Migration & many held low-class jobs
-
After Whites retook their industrial jobs after WW1, Blacks resorted to low-class jobs
-
Janitors, domestic servants, etc.
-
Excluded from most labor unions
-
Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters (est. 1925) was a Black labor union that got some benefits for Blacks
-
-
Many Asians were in the West & were discriminated
-
After Chinese Exclusion Act (1882), Japanese immigrants took their place
-
Some Japanese actually built their own successful businesses
-
CA passed Alien Land Laws of 1913 & 1920 to restrict land sales to Japanese
-
-
Filipinos also took unskilled industrial jobs, causing anti-Filipino riots
-
Led to Filipino Repatriation Act (1935) to limit Filipino immigration
-
-
-
Many Mexicans held low-income agricultural jobs in the Southwest
-
Less hostility toward them as most Whites actually needed their agricultural services
-

Agricultural Technology
-
More agricultural technology was developing
-
Tractors became common & efficient
-
Chemical fertilizers, pesticides, etc. were created
-
This led to production of more crops w/ fewer workers
-
-
Many farmers left agriculture as there was too little demand for food due to high supply, causing crop prices to fall
-
Farmers promoted the idea of parity
-
Prices for goods are increased such as farmers can at least regain their production costs
-
Wanted the gov to purchase surplus goods & sell to international market
-
McNary-Haugen Bill promoted parity & was debated, but eventually vetoed by president
-

Development of a New Culture
Consumerism
-
As people now generated extra wages, they could use those to buy extra things
-
Bought kitchen appliances (vacuums, refrigerators, irons, etc;)
-
Women bought makeup & cosmetics
-
-
Companies were now able to advertise their products to promote their glamor & appeal
-
Advertising became a whole industry
-
-
Many people also were able to buy cars
-
Rural people could now escape isolation & drive to the cities
-
City dwellers could escape city congestion & drive to the countryside
-
Many middle-class city-dwellers moved to the suburbs as they could drive to the city for work
-
-
More people had access to vacations
-
Many middle-class & even working-class people had access to vacations
-
Companies gave paid vacation days
-
-
Young people could use cars & move away from their parents, creating a new youth culture

Movies & Broadcasting Networks
-
Movies were becoming common as they had sound
-
The Jazz Singer (1927) was the 1st movie w/ sound
-
Made movies more appealing
-
People went to the movie theaters really often
-
Sometimes, the gov would ban any offensive movies
-
-
Radio broadcasting also became common
-
Networks like the National Broadcasting Company (NBC) (est. 1926) emerged
-
These were rarely supervised & somewhat had freedom to broadcast what they wanted
-

Modernist Religion
-
Many people abandoned strict religion & followed a more modern life
-
Due to the rise of movies & a consumer culture, they cared more about modern society
-
-
Less people cared about religion, assumed it as a secondary role in life
-
Caused a decline in Church attendance
-
-
This religious decline led to a religious revival (described in a below section)
-
Harry Emerson Fosdick was an important modernist

Changing Ideas of Women
-
People now had different views of mothers
-
Believed mothers should rely on guidance of doctors & nurses to raise their children
-
Believed marriage is more for love and pleasure
-
-
Margaret Sanger led the birth control movement
-
Many states had banned birth control
-
Now, women engaged in sexual relationships for pleasure, not for procreation, so they needed birth control
-
-
Women also started to depart from their traditional role & were more active in modern society
-
They were allowed to smoke, drink, attend parties, etc.
-
Women wrote the "flapper" image of clothing: They wore short skirts
-
This demonstrated that they could choose their own clothing
-
-
-
Women also sought to campaign for equal rights
-
National Women's Party (est. 1916) wanted the Equal Rights Amendment
-
Believed 19th amendment wasn't enough
-
Wanted equal rights for men & women in all circumstances
-
Was never implemented
-
-
Sheppard-Towner Act (1921) established prenatal & child care programs
-
Was terminated as women hated that it classified women as mothers, not normal people
-
-

Rise of Education & Youth Culture
-
High school & college enrollment increased
-
Colleges now provided training in technical skills (engineering, management, economics, etc.)
-
Some colleges were vocational schools
-
-
This caused a rise in youth culture
-
This was a time when people enjoyed & celebrated the adolescent age
-
Adolescents had their own social patterns, hobbies, interests, activities, etc.
-
Schools now also had athletics, clubs, fraternities, etc. causing a rise in youth culture
-

The Harlem Renaissance
-
In Harlem in NYC, a group of Black artists & writers created a new Black culture
-
Many jazz musicians became common
-
Many theaters had musicals & vaudevilles
-
-
Black art, poetry, and literature flourished
-
Black artists depicted the richness of their culture
-
Langston Hughes was a famous Black poet
-
Aaron Douglas painted murals in many important buildings
-
Alain LeRoy Locke is known as the "Father of the Harlem Renaissance"
-
Wrote a collection of writings in The New Negro (1925)
-
-

Conflict with Traditional Culture
Feeling of Disenchantment
-
Many people felt disenchanted & alienated after WW1 and believed 1920s to be a lost generation
-
Felt personal alienation
-
Ernest Hemingway: A Farewell to Arms (1929)
-
An American officer is fighting in Europe but returns home as there is no point in fighting
-
-
-
Many people also critiqued modern society & rejected their successes
-
F Scott Fitzgerald wrote The Great Gatsby about a rejection of wealth
-

Alcohol Prohibition
-
The 18th amendment (banning alcohol) wasn't really enforced
-
Very few police officers actually enforced this
-
Government couldn't get local police to enforce this
-
-
Many people organized an illegal alcohol trade
-
Many progressives who supported prohibition later changed their minds
-
18th amendment was repealed in 1933
.jpeg)
Nativism and the 2nd Ku Klux Klan
-
Many progressives sought to limit immigration
-
Believed immigration causes radicalism
-
-
Congress passed Emergency Immigration Act (1921), limiting immigration severely
-
National Origins Act of 1924 made these restrictions even more severe
-
Banned immigration from East Asia entirely (Japanese people hated this)
-
-
-
This renewed nativism allowed the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) to gain more support
-
The first Klan died in the 1870s
-
Nativists met in Stone Mountain (GA) to create the 2nd KKK in 1915
-
Had 4 million members by 1924
-
-
-
This Klan persecuted Blacks and other minorities and also sought to impose traditional values
-
Persecuted White protestants who drank too much or had sexual promiscuity
-
Promoted prohibition of alcohol
-
-
Declined after 1925 due to scandals involving its leaders

Religious Revival & Fundamentalism
-
A group of people called Fundamentalists sought to promote traditional religion
-
Opposed the Modernists, who wanted to adapt religion to modern society (described earlier)
-
-
Many Fundamentalists were evangelists who promoted religious revival
-
Billy Sunday was a famous revivalist
-
Opposed Charles Darwin's evolutionary theory b/c they believed all humans came from god
-
Got some local governments to ban Darwin's teachings in school
-
State of Tennessee did this in 1925
-
-
-
Tennessee's banning Darwin's teachings led to the Scopes Trial ("Monkey Trial")
-
American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) opposed the law & employed a teacher to break the law
-
The case was very long, and William Jennings Bryan even came as a witness
-
Fundamentalists won, but the victory was long & embarrassing, causing them to decline
-

Political Developments
Warren G Harding
-
Democrats lost power due to internal divisions
-
Divided among those who favored traditional values vs modern values of society
-
-
Warren G Harding became president in 1920
-
He became unpopular due to the Teapot Dome scandal
-
His Sec. of Interior, Albert B Fall, leased the oil reserves of Teapot Dome, WY, to businessmen
-
Fall received money in return, which he used to pay off personal debts
-
Fall was convicted of bribery
-
-
Harding went on a tour of the US West, and he died in San Francisco in 1923
-

Calvin Coolidge
-
Calvin Coolidge was very calm & passive
-
Was Harding's VP, became president after his death in 1923
-
Reelected in 1924
-
-
Coolidge tried to help the US's economy
-
Wanted isolation in foreign policy
-
Gave huge tax cuts
-
Limited his aid to farmers
-

The Great Depression:
Causes of the Great Depression
Reasons for the Great Depression
Lack of Diversity in US economy
US industry was mostly automobiles & construction. These 2 started to decline in late 1920s, and other industries (chemicals, petrol, etc.) couldn't grow fast enough
Poverty in America
More than half of families lived near subsistence level & were too poor to buy industrial goods
Problems in Credit Structure
Farmers struggled to pay off mortgages due to low crop prices. Small banks failed as their customers couldn't pay back loans. Big banks invested massively into stock market
Int'l Debt Structure, Declining Int'l Trade
Allies had war debts to US, and German reparations would pay them off. Germany couldn't pay them off, causing a problem for Allies. This also caused European economy to suffer, causing decline in int'l trade
The Stock Market Crash (Oct 1929)
In early & mid 1920s, stock prices were rising. This caused speculative fever as people kept investing so much in the stock market and were taking loans from banks to invest in stock market
In Oct 1929, stock prices were falling. Everyone tried to withdraw their investments from the market. Many people were unable to withdraw funds from the market in time
On Oct 24, 1929 ("Black Thursday"), stock market crashed. This was mostly due to people investing too much. People couldn't pay back their loans to the banks, causing banks to fail
Progression of the Great Depression
-
The crisis worsened after the Stock Market crash
-
Banking system collapsed as many large banks invested in Stock Market
-
This caused small banks to collapse
-
Depositors lost $2.5 billion in deposits
-
-
Nation's money supply fell, causing severe deflation
-
Merchants had to reduce prices, cut off production and lay off workers
-
Due to declining purchasing power of people, less people could buy stuff, causing merchants to cut production more & lay off more people
-
This cycle repeats
-
-
GDP declined almost 25% from 1929-1932
-
-
Federal Reserve raised interest rates in 1931 to protect itself, worsening the problem
-
The crisis spread to Europe as Europe depended on American banks
-
Due to int'l debt structure (described earlier)
-

The Struggles of the Americans
Widespread Unemployment
-
The crisis caused widespread unemployment
-
This was due to the cycle below:
-
People lost money in stocks & had less purchasing power
Less workers were needed (to produce less goods), so more workers were fired
Less people had the money to buy industrial goods
Less goods were produced in factories (b/c less people could afford them)
-
Unemployment was super high
-
Almost 60% unemployment in industrial cities
-
-
Public & private relief systems collapsed due to high demand for relief
-
Pubic relief systems relied on tax revenue, but people now paid less taxes due to less income
-
Private relief systems also didn't have enough money to supply relief to so many people
-
-
Many people were homeless or nomads
-
Waited in long bread lines, lined outside the Salvation army, rode trains from city to city
-
Tried looking for jobs, but failed
-
-
Farming also fared worse
-
Farm income declined almost 60% (1929-32)
-
1/3 of Farmers lost their land
-
Arable land in the Plains had a drought, called the "Dust Bowl"
-
Decline in rainfall, increase in heat, worsened effects of the Depression
-
Many had to migrate west
-
-
Still, due to agricultural surplus, crop prices fell, causing farm income to decline
-
Many farmers had to leave their land
-
-
-
Many people died of malnutrition & starvation
-
Many lived in makeshift shacks outside cities
-
Many families also declined in status
-
Less money → Less children → Lower divorce rate
-
Many families retreated from consumerism & made goods at home
-
Distant relatives often moved in together
-
Women During the Depression
-
Many women were initially unemployed
-
It was believed that married women whose husbands work don't need a job
-
-
Due to widespread unemployment of their husbands, many women were forced to work
-
Many "pink collar" jobs held by women were unaffected by the Depression
-
Teaching, social work, clerks, etc.
-
Allowed women to somewhat retain their jobs
-
-
In industrial jobs, though, women fared worse than men
-
More likely to be laid off or have wage cuts
-
-
20% more women worked by the end of the Depression than by the beginning
-
-
Black women fared worse since their domestic service jobs were mostly gone
-
Overall, the Depression was bad for women b/c by going to work, it eroded the idea that women are independent (won by feminists in the 1920s)

African-Americans During the Depression
-
African-Americans in the South fared badly
-
Many Black sharecroppers suffered, causing them to lose their land & be unemployed
-
-
Many Whites also lost their jobs and took formerly Black jobs like janitors, street cleaners, etc.
-
Unemployed Whites sought to remove Blacks from their jobs until all Whites were employed
-
Caused > 1/2 of Blacks in the South to be unemployed
-
-
Many Blacks migrated to the North, where there was less discrimination, but most were still unemployed
-
Segregation continued in the South
-
In the Scottsboro Case (1931), 9 Black teens were falsely accused of rape & sentenced tp death
-
Supreme Court over turned this, setting a precedent for more protection for criminal defendants
-
-
-
NAACP tried to encourage Blacks to join the workforce & prevent workplace segregation
-
Some Blacks actually were able to get jobs
-

Mexican-Americans During the Depression
-
Many Mexican-Americans were did low-class jobs in Southwest US
-
Most were in agriculture, some were in industrial jobs or other unskilled jobs
-
Unemployed Whites forced Mexicans out of their jobs to give the jobs to Whites
-
-
Many Mexicans were denied relief or hospital admission
-
Some were even deported to Mexico
-
-
Organized a union of farmworkers, but that failed
-
Forced to migrate to cities (such as LA) where they lived in poverty

Asian-Americans During the Depression
-
California had largest Chinese/Japanese populations
-
Many Japanese were well educated but still had low-class jobs
-
Worked in fruit stands, agriculture, industry
-
Lost jobs to unemployed Whites in the Depression
-
Farmers lost their jobs due to competition from White farmers migrating west from "Dust Bowl"
-
-
Organized the Japanese American Citizens League (est. 1930) to assimilate them to American society
-
Believed this was the best way to get civil rights
-
-
Many Chinese people fared no better than Japanese
-
Many worked in laundromats or restaurants
-

American Culture during the Depression
Feelings during the Depression
-
Many people reasserted their devotion to traditional ideas & opposed modern society
-
Didn't want to participate in modern society and emphasized individualism & spirituality
-
-
Many felt shamed for not being able to get a job
-
Many men left the family as they felt ashamed of not having a job
-
Many didn't want to leave their homes due as they felt shameful
-
-
Many undermined the success ethic & believed they cannot be successful
-
Blamed large corporations for the Depression
-
-

Art & Literature during the Depression
-
Many photographers & documentaries depicted rural poverty during the Depression
-
Literature reflected the hardships of the depression
-
Erskine Caldwell wrote Tobacco Road (1932)
-
Nathanael West wrote Miss Lonelyhearts (1933)
-
John Steinbeck wrote The Grapes of Wrath (1939)
-
Richard Wright wrote Native Son (1940)
-
-
Other literature did not depict the hardships of the Depression but was escapist: It sought to escape the hardships of the Depression w/ a romantic image
-
Margaret Mitchell: Gone with the Wind (1936)
-
-
The Life Magazine also depicted the hardships of the Depression as well as escapist themes
_.jpg)
Radios & Movies during the Depression
-
Radios became super popular b/c almost every family had one
-
Listening to radios was a community experience
-
-
Radios had many escapist comedies
-
Had fun content to help people escape the hardships of the Depression
-
Soap operas were also broadcasted, & they generally targeted women
-
-
Radios also had live broadcasts of many events
-
Bands, comedies, dramas were performed in front of an audience & also broadcast via radio
-
Important events (presidential inauguration, sports games, etc.) were broadcast
-
-
Radios drew the nation together during this difficult time
-
Movies also became popular & were a cheap entertainment option
-
Became appealing due to the addition of sound & color to movies
-
Walt Disney emerged & created the Disney movies for children
-
Made movies really popular
-
-

Political Developments & Hoover's Fails
Rise of Communism & the Popular Front
-
During the Depression, many communist & anti-fascist groups gained power
-
Hated the capitalists & blamed the Depression on them
-
American Communist Party gained power
-
Supported Franklin D Roosevelt (FDR)
-
Were supported by Comintern (Communist International) in Russia
-
-
Socialist Party of America also gained power
-
Southern Tenant Farmers' Union (STFU) was supported by Socialists
-
Sought economic reform for tenant farmers
-
-
-
Many governments sought to suppress all communist activities

Herbert Hoover's Failures
-
Hoover helped the economy, but not enough
-
He sought to boost the economy through volunteerism
-
Wanted local charities & support groups to help those who were suffering
-
Wanted employers to raise wages & not lay off their workers
-
This failed b/c the government itself did little to the economy
-
-
Wanted Congress to fund $423 million in public works programs, but it wasn't enough
-
Hoover sought to protect the agriculture industry, but still his help wasn't enough
-
Agricultural Marketing Act (1929): Established Federal Farm board
-
Helped give loans & buy surpluses to stabilize crop prices
-
-
Tariff Act of 1930 (Smoot-Hawley Tariff) increased tariffs for some crops, limiting foreign competition
-
-
Democrats won majority in House in 1930 as they hated Hoover's very little gov assistance to economy
-
He established Reconstruction Finance Corporation (1932) to provide loans to banks & businesses
-
Failed as it only helped larger banks that had enough collateral
-
-
Overall, Hoover's administration was a fail as it didn't provide enough gov assistance to economy

Anti-Hoover Protests & Rise of FDR
-
Many people (especially farmers) started to protest against Hoover's administration
-
Farmers established Farmers' Holiday Association (1932) to create a farmers' strike
-
Withheld their crops from local markets, but this failed eventually
-
-
-
In 1924, Congress approved an act to give $1k to all WW1 veterans by 1945, but many veterans wanted that bonus immediately
-
In 1932, Veterans formed Bonus Expeditionary Force ("Bonus Army") & marched to DC to protest
-
Congress rejected their proposal & police violently suppressed them
-
-
Hoover's Administration's violent suppression of the Bonus Army gave it a bad public image
-
New York governor, Franklin D Roosevelt (FDR), was Democratic nominee for 1932 election
-
Promoted an economic relief program called the "New Deal"
-
Wanted to build public works projects
-
This gave him lots of popularity
-
-
Incumbent Hoover was Republican nomination
-
FDR won in a landslide
-

The New Deal:
The 3 R's of the New Deal
Relief
Recovery
Reform
The 1st New Deal (1933-34)
Overview of the 1st New Deal
-
Mostly a short-term top-down approach
-
Wanted to fix everything at the top: banking, industry, corporations, gov agencies, etc.
-
Its legislative actions & reform agencies allowed it to focus more on social welfare for the unemployed later on (in 2nd New Deal, 1935-36)
-
-
The beginning of the program was known as "The First Hundred Days"
-
From Mar - Jun 1933, Congress passed legislation to combat banking crisis, industrial downfall, etc.
-
Franklin D Roosevelt (FDR) created many agencies to carry out this reform
-
-
5 main aspects: Banking & monetary reform, agricultural reform, industrial recovery, public works, federal relief

Banking Reform
-
1st step to solving Great Depression was fixing the banking crisis
-
FDR closed all banks for 4 days in March ("Banking Holiday") to give Congress time to pass banking reform legislation
-
-
Emergency Banking Act (1933): Meant to restore confidence in national banking system & make the banking system more stable
-
Treasury Department would inspect each bank for financial stability before allowing it to reopen
-
Would provide assistance & money to banks in financial trouble
-
-
Within 3 days, about 75% of Federal Reserve banks reopened
-
FDR encouraged the American people to deposit their money into these banks
-
-
Economy Act (1933): Cut salaries of federal employees & reduced benefits to veterans to lower the federal budget
-
21st Amendment (1933): Repealed alcohol prohibition
-
Meant to restore faith in national gov for the Americans
-

Agricultural Adjustment Acts
-
Agricultural Adjustment Act (1933): Gives subsidies to farmers to limit their production
-
Sought to end agricultural surpluses by limiting production, to prevent fall of crop prices
-
Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) would tell farmers how much to produce
-
Gave some money to farmers in exchange for keeping part of their land idle
-
-
Supreme Court declared the AAA unconstitutional → Soil Conservation & Domestic Allotment Act (1936) replaced it
-
Basically the same thing
-
It would pay farmers to keep their land idle to conserve the soil & prevent land erosion
-
-
Resettlement Administration (1935-37) & Farm Security Administration (est. 1937): Gave loans to help relocate farmers to better lands
-
Rural Electrification Administration (1936): Created projects to give electric supply to the rural south

Industrial Recovery
National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA)
-
Sought to boost industry by regulating prices of industrial goods & workers' wages
-
Allowed workers to organize into labor unions
-
Created the NRA & PWA (described to the right)
National Recovery Administration (NRA)
-
An agency created by the NIRA to establish law codes to regulate industry
-
"Blanket Codes": Set minimum wage, maximum workweek, abolished child labor
-
Other codes regulated minimum prices to prevent monopolies
Public Works Administration (PWA)
-
Large-scale public works agency to bring jobs to revive the economy
-
By giving people jobs, it allowed those people to buy industrial goods, which helped the industrial economy as well
-
In 1935, Supreme Court ruled against the NRA codes
-
This was the Schechter Case (1935)
-
It was unconstitutional to give legislative power to the president to draft NRA codes
-
It was also illegal for NRA codes to regulate non-interstate commerce
-
-
In the end, NRA codes failed in the short-term, but led to the 2nd New Deal
Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA)
-
FDR signed Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) Act (May 1933) to create the TVA
-
A regional agency overseen by federal gov
-
Sought to build dams in the Tennessee Valley to prevent flooding & provide electricity
-
Also helped rebuild the local economy
-
-
-
TVA built a dam at Muscle Shoals (AL) in 1918, and was officially incorporated in 1933
-
Brought cheap electricity to thousands of people in rural areas
-
-
TVA did more projects to bring electricity to rural areas, while helping rebuild the local economy

Monetary Reform
Gold Standard Abolition (Apr 1933)
-
FDR abolished the gold standard
-
Finally defeated the biggest obstacle to economic recovery
-
Money was now set to a government-manipulated value
Glass-Steagall Act (Jun 1933)
-
Created separate rules for commercial & investment banks, preventing commercial banks from investing in stocks
-
Boosted confidence in the banking system
-
Established the FDIC
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) (Jun 1933)
-
Created insurance to compensate people who lose their deposits if their bank collapses
-
Made people less hesitant to invest in banks
Banking Act of 1935 (Aug 1935)
-
Reorganized Federal Reserve leadership structure
-
Gave more authority of banks to Federal Reserve Board in DC
Truth in Securities Act (May 1933)
-
Required companies to give truthful info to investors about their stocks
-
Meant to boost confidence in investing in stocks
Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) (Jun 1934)
-
Sought to regulate the stock market for any fraud or unlawful actions
-
Meant to boost confidence in investing in stocks
Federal Relief
Federal Emergency Relief Administration (FERA) (May 1933)
-
Gave money to states to create relief agencies
-
Funded salaries for gov workers
-
Funded relief programs (such as soup kitchens)
Farm Credit Administration (Mar 1933)
-
Provided safe sources to credit to farmers & people in rural areas
-
Mostly meant to help farmers pay off mortgages
Home Owners' Loan Corporation (HOLC) (Jun 1933)
-
Refinanced mortgages of urban homes
-
Federal Housing Administration (Jun 1934) provided insurance for mortgages to protect the money lenders
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC)
-
Civilian Conservation Corps (Est. Apr 1933): Provided unemployed young men w/ public works projects in rural areas
-
Created camps in rural areas for people to work
-
People worked on planting trees, building reservoirs, creating parks, making irrigation, etc.
-
-
This is different from the PWA & WPA
-
Public Works Agency (PWA) & Works Progress Administration (WPA) are mostly urban projects, while CCC is rural
-
PWA is large-scale projects, while WPA is small-scale unskilled projects
-
PWA was also sometimes managed by private firms, while WPA was all public
-
[WPA is described in a section below]
-
-

Opposition to the 1st New Deal
-
Many people opposed the 1st New Deal, both on the right & the left
-
Far-right conservatives hated FDR's dictatorial policies
-
Far-left communists believed FDR wasn't doing enough to help the unemployed people
-
-
Dr. Francis E Townsend was one critic & created the Townsend Plan
-
Believed all Americans over age 60 should get monthly pensions to spend in the economy
-
-
Father Charles E Coughlin believed in monetary reform
-
Wanted to remonetize silver & bring more prosperity in the banking system
-
He had one of the widest radio audiences in US
-
-
Sen. Huey Long (D-LA) promoted the Share-Our-Wealth Plan
-
Believed in taxing the rich & redistributing the money to the poor
-
Wanted to guarantee each family a minimum homestead & annual wage
-
-
These critical ideas led to the ideas in the 2nd New Deal

The 2nd New Deal (1935-38)
Overview of the 2nd New Deal
-
Mostly along-term bottom-up approach
-
Dealt most closely with the unemployed people to help bring them back into the economy
-
-
Focused mostly on social justice & social welfare
-
Established the social security system to provide benefits to retirees
-
Provided temporary public works jobs to millions of unemployed people to rebuild the economy
-
Also gave workers more rights by allowing them to form labor unions & giving them good wages
-
This was a legacy of the NIRA from the 1st New Deal
-
-

National Labor Relations Act (1935)
Supreme Court declared the National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA) unconstitutional in the Schechter Poultry Case (1935)
Sen. Robert F Wagner (D-NY) created National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act) (1935). Meant to replace Section 7a of the NIRA, giving workers the right to form unions
The Wagner Act led to the creation of the National Labor Relations Board (est. 1935) to enforce the right for workers to form unions
Legacy of National Labor Relations Act
-
Many labor unions gained power as the National Labor Relations Act gave them a legal basis to exist
-
Most labor unions initially (like the AFL) were for skilled or craft-based workers
-
The idea of industrial unionism emerged: People were organized based on their industry, rather than their specific craft within the industry
-
Helped organize unskilled workers
-
-
John L Lewis founded the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO), a group of industrial unions
-
Was more open to women & minorities than other craft unions
-
This became more a militant union, which had to fight & campaign w/ employers to gain recognition
-
-
-
United Auto Workers (UAW) organized a 2-month sit-down strike at the GM plant to gain recognition
-
Dec 1936 - Feb 1937
-
Eventually, GM was forced to recognize UAW
-
-
US Steel was forced to recognize the Steel Workers' Organizing Committee (SWOC) after a strike in 1936
-
On Memorial Day 1937, SWOC went on strike to try to gain recognition from Little Steel (which refers to all of the smaller steel companies besides US Steel)
-
Police opened fire & killed 10 strikers
-
Memorial Day Massacre (May 1937)
-

Social Security Act
-
Social Security Act (Aug 1935) created the system of social security
- 1st part of social security was pensions for the elderly
- The poor elderly would get $15 a month
- Other Americans would have a payroll tax which would be paid to them after their retirement
- Retirement benefits
- 2nd part were unemployment benefits
- People laid off from jobs could get temporary wages
- People w/ disabilities or dependent children could also get some benefits
- One of the most important parts of the New Deal as it has a long-lasting effect & still in use today

Works Progress Administration (WPA)
-
The biggest problem was unemployment
-
Millions were unemployed & needed a temporary job to get back on their feet
-
-
FDR established the Works Progress Administration (WPA) to provide temporary employment
-
A public works agency for unskilled workers
-
Different from CCC & PWA as the WPA was more small-scale & for unskilled workers
-
-
WPA was a huge project
-
$5 billion budget
-
Built/renovated 110k public buildings, 600 airpots, 500k miles of roads, 100k bridges, etc.
-
Kept 8.5 million people employed, allowing them to earn money & spend it on goods, which also boosted the industrial sector
-
-
WPA was mostly helping men, not women
-
The main aid women received was the social security pensions for single mothers
-

End of the New Deal
Situation in Court
-
To make his plans successful, FDR needed to eliminate all conservative judges from court
-
Court had previously struck down many of his acts in the 1st New Deal, and he didn't want the same situation in 2nd New Deal
-
-
In Feb 1937, FDR proposed the Judicial Procedures Reform Bill of 1937
-
Sought to replace all Supreme Court justices over age of 70
-
Claimed he was adding fresh ideas to Court, but he was actually replacing conservative justices w/ liberal ones
-
-
Managed to replace 6 justices
-
This actually led to a 5-4 vote in court for many of FDR's legislation
-
-
Although FDR was successful, public opinion largely opposed FDR's moves

Recession of 1937-1938
In 1937, FDR wanted to lower the federal budget as the economy was improving
FDR cut the budget if the WPA in half, laying off 1.5 million workers
This caused a huge recession, similar to the Great Depression. 4 million workers lost their jobs
-
Many call this recession "Roosevelt's Recession" as FDR's decision to cut the budget caused this
Resolving the Recession of 1937-1938
-
FDR gave $5 billion to the economy, causing economic recovery to begin again
-
FDR created Temporary National Economic Committee (TNEC) (est. 1938) to promote antitrust laws
-
Meant to stop monopolies from dominating the economy
-
-
FDR passed Fair Labor Standards Act (1938)
-
Established national minimum wage, created overtime pay, and limited child labor
-
-
At the end of 1938, the New Deal basically ended
-
Congressional opposition made it difficult for FDR to pass any legislation
-
FDR was more concerned w/ the upcoming World War 2 then with the New Deal
-

Legacy of the New Deal
African-Americans in the New Deal
-
New Deal did little to help African-Americans although FDR did more to help Blacks than other presidents
-
FDR put some African-Americans in the "Black Cabinet," a group of informal advisors to the president
-
-
In mid 1930s, most African-Americans switched political parties (Rep to Dem)
-
In 1932, most Blacks voted Republican
-
In 1936, >90% of Black electorate voted Democratic
-
This political shift was significant & helped Democrats gain significant power later on
-
-
Still, FDR did little to change race relations
-
All New Deal programs still had racial segregation & discriminated toward Blacks
-

Indian Reorganization Act (1934)
-
New Deal initially sought to suppress the Indians
-
John Collier, a social worker who worked w/ Indians in New Mexico sought to promote Native American culture
-
Collier promoted & got Congress to pass Indian Reorganization Act (1934)
-
Allowed Indians to own land collectively
-
Increased Indian self-government & responsibility for themselves
-
Somewhat replaced the Dawes Act (1887)
-

Women in the New Deal
-
New Deal did very little to help women
-
Women actually held some government positions
-
FDR appointed Frances Perkins as Sec of Labor in 1933
-
Many other women had lower-level positions
-
-
Many disagreed on the proper role of women: Some believed women should be equal to men, others believed women should have special place in society
-
Social Security Act gave aid to dependent children to help single mothers
-
New Deal generally believed women should free up the workplace for men
-
New Deal relief agencies had little employment opportunities for women
-

Economic Development in West & South
-
West & South received a lot more funds from the New Deal than other regions
-
The West had many public works projects
-
Agricultural projects were done b/c agriculture was important to the Western economy
-
Dams, power plants, etc. were built in the West
-
Grand Coulee Dam (WA) was largest public works project at the time
-
-
Allowed the West's economy to develop & gave the federal gov a strong presence in the West
-
-
Some projects were also in the South
-
South was least economically developed, so it needed more help
-
However, it was less important to the US's economy than the West, so it was given less help
-
-
Rural electrification projects were really helpful & provided electricity to the Southern countryside
-

Overall Legacy of the New Deal on the US
-
The US economy only fully recovered after WW2
-
New Deal led to economic development of the South & West
-
Increased control of federal gov over the stock market & banking system
-
-
New Deal established the welfare system (Social Security), which is still in use today
-
New Deal ended the gov's traditional reluctance to help its poorest & lowest-ranking citizens
-
I.e. the farmers & unskilled workers
-
-
The New Deal gave the federal gov more power than it had before
- Federal gov now had more authority over states & local govs than they did before
- Established the president as the main power within the federal government
- New Deal allowed the Democratic Party to gain lots of power
- Most African-Americans switched from Republican to Democratic
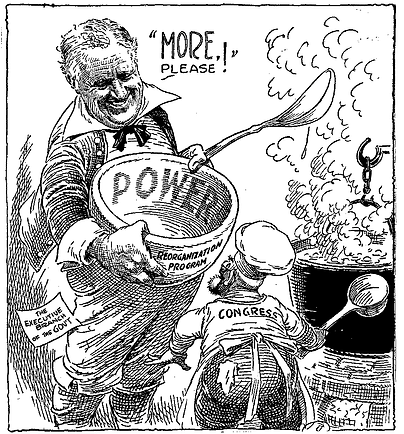
Interwar Period Foreign Policy:
Isolationism in the 1920s
International Treaties
-
US didn't join the League of Nations as it would give US a responsibility to help other nations
-
US wanted to remain isolationist & not be involved w/ affairs of other nations
-
-
However, US wanted peace w/ other nations, so US signed many peace treaties w/ other nations:
Washington Naval Treaty (1922)
-
Limited construction of warships by US, UK, Italy, France, & Japan
-
Prevented Japan from dominating East Asia
-
Meant to prevent a nation from becoming super dominant in their region
Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928)
-
An agreement between 62 nations to not use war to resolve any conflict
-
Relied on a moral agreement, did not have any method of enforcing it
-
Ultimately failed as it couldn't be enforced
Other Treaties
-
Four-Power Treaty (1921): Signed by US, UK, France, Japan, meant to prevent aggression in East Asia
-
Nine-Power Treaty (1922): Allowed for the continuation of Open Door Policy in China
-
Many of these treaties failed as they had no method of enforcement & couldn't combat aggression by Japan, Germany, or Italy
International Debts & Diplomacy
-
US wanted to stay isolationist, but it had to resolve its loan problems first
-
Europeans had many loans to the US, & US wanted to resolve these
-
Allies (France, UK) owed $11 billion to US
-
Germany owed $32 billion as reparations to Allies
-
Dawes Plan (1924) allowed US to give loans to Germany & cut down German reparations
-
This created a circular debt structure, which was problematic
-
-
European economy was suffering, so US invested a lot there
-
American banks invested in businesses there as most other businesses were in decline
-
Because European industry was unstable, American banks became unstable
-
-
Pres. Coolidge then passed Fordney-McCumber Act (1922) to raise tariffs
-
Caused European industry to decline more as they couldn't export goods to US
-
-
US also had loans to Latin America
-
US invested a lot into Latin America to gain access to its rich natural resources
-
Latin America also struggled to pay back the US, causing economic problems there
-
-
Overall, the US struggled to stay isolationist due to its investments overseas

Diplomatic Crisis in Great Depression
-
The Great Depression (1929) undid the int'l treaties of the 1920s as nations wanted more nationalism & isolationism to solve the economic crisis
-
This would eventually lead to war
-
-
Hoover wanted to remove all US troops from Latin America
-
Agreed to accept any current gov in Latin America; removed his troops from there
-
-
Hoover proposed a moratorium on loan payments from Europe, but his assistants opposed it
-
This worsened the economic crisis in Europe
-
-
The ineffectiveness of diplomacy in Europe was problematic & allowed new regimes to take power
-
Hitler in Germany & Mussolini in Italy could consolidate power easily & US couldn't do anything about it
-
A similar situation happened with Japan:
-
Pro-military people took control of Japanese government. Japan then invaded Manchuria (Northeast China) in an event known as the Mukden Incident (1931).
The League of Nations told Japan to stop, but Japan withdrew from the League.
US Sec of State Henry Stimson could not engage in any sanction or activity against Japan. The most he could do was not recognize Japanese control of Manchuria
-
The Mukden Incident (1931) showed how the US could not do anything to combat threats to combat world peace
-
Similar thing happened with Germany & Italy, causing WW2 in 1939
-
FDR's Initial Diplomacy
FDR's Diplomacy to Combat Great Depression
-
In Jun 1933, FDR released a "bombshell" message to end the gold standard for currency
-
FDR took the US off the gold standard in Jul 1933
-
-
FDR passed Johnson Debt Default Act (1934) to prevent American banks from giving loans to Europe until European nations pay back all existing loans
-
Boosted the US's stance of isolationism from European issues
-
-
FDR signed Reciprocal Tariff Act (1934): Allowed FDR to reduce tariffs significantly if other nations also reduce tariffs by the same amount
-
Allowed international trade to increase
-
However, European goods struggled to compete w/ American goods, causing European economy to suffer
-
-
Overall, FDR wanted to help European economies while maintaining his stance of isolationism

Good Neighbor Policy in Latin America
-
FDR wanted to have better relations w/ Latin America by emphasizing economic cooperation rather than military intervention
-
US had lots of trade w/ Latin America & FDR wanted to increase them
-
-
Sec of State Cordell Hull signed an agreement to prevent nations in the Americas from interfering w/ the affairs of other nations
-
Known as the Good Neighbor Policy
-
Allowed US to economically dominate Latin American nations & get them to repay debts
-

US's Relationship with USSR
-
US initially didn't recognize the USSR (Communist Russia) after Bolshevik Revolution (1917)
-
Didn't want to be allied w/ Communist nation
-
-
Later, in 1930s, US engaged in relations w/ USSR
-
US believed forming an economic alliance w/ USSR would be really beneficial
-
US & USSR could work together to combat Japanese aggression
-
-
FDR signed a treaty w/ Russia to mutually recognize each other & support each other
-
Eventually, due to isolationist sentiment & lack of mutual help, this relationship started to fall apart

FDR's Isolationism
Causes of Isolationism
-
As other nations became isolated, US had to adhere to isolationism:
-
Geneva Disarmament Conference (1932) collapsed in 1934
-
Hitler & Mussolini withdrew from this agreement
-
-
Japan withdrew from the treaties meant to reduce naval warfare
-
-
Because other international treaties failed, US was forced to adhere to isolationism

Nye Committee (1934-1936)
Sen. Gerald Nye (R-ND) led an investigation into why US joined WW1
Figured out that many bankers & financial institutions pressured Woodrow Wilson to join WW1 to protect their loans abroad
This led to widespread isolationist sentiment in US as they hated that banks pressured US to join WW1
Neutrality Acts (1936-1939)
Neutrality Act of 1936
-
Forbade US from exporting war supplies (guns, munitions, etc.) to any nation currently in war
-
Also forbade US from giving loans to any nation currently in war
Neutrality Act of 1937
-
Prevented US citizens from traveling on ships of nations currently in war
-
Created cash-and-carry system: Nations could get anything (except military supplies) from US if they pay in cash & transport it home themselves
Neutrality Act of 1939
-
Extended cash-and-carry system to military supplies as well
-
Still forbade US from giving loans to warring nations & from traveling themselves to deliver supplies to warring nations
World War 2:
Start of World War 2
Threats to Isolationism
-
US remained very isolationist since around 1935, but many totalitarian regimes in Europe threatened US's position
-
Mussolini (Italy) invaded Ethiopia in 1935 & withdrew from the League of Nations
-
Signed Axis agreement w/ Hitler in 1936
-
-
Adolf Hitler (Germany) invaded Rhineland (1936) & Austria (1938)
-
Japan invaded Manchuria (1931)
-
Spain had a civil war between Fascists & Republicans, and Fascists won
-
Japan bombed USS Panay (1937) in China
-
-
All of the above events threatened US's isolationist position, but US still remained isolationist

German Aggression & Start of WW2 (1938-1939)
Hitler wanted to create an "anschluss" (union) of all German-speaking lands. He conquered Rhineland (1936) & Austria (1938)
Hitler wanted to invade Sudetenland, but France & Britain didn't want him to
France & Britain didn't want war w/ Hitler, so they signed the Munich Agreement (Sep 1938) w/ Hitler, allowing Hitler to invade Sudetenland but nothing else
Responding to Hitler's invasion of Poland, Britain & France declared war on Germany (Sep 1939)
Hitler went even further & invaded Poland in Sep 1939
Hitler invaded Sudetenland in Oct 1938. He broke the Munich Agreement & invaded rest of Czechoslovakia in Mar 1939
FDR's Aid to Allies at Start of War
-
Responding to the start of war, FDR created the Neutrality Act of 1939
-
Extended cash-and-carry system to military supplies: Warring nations could buy war supplies from US if they could transport it themselves
-
-
US's ally, France, was defeated by Germany in Jun 1940 → All British & French troops retreated to Dunkirk
-
This significantly strained France & Britain
-
If Germany occupies Britain & France, they are literally a few days away from attacking US
-
-
Also, in Sep 1940 - May 1941, Germany bombed London, making Britain more in need of help
-
FDR decided to help Britain & France even more to prevent Germany from attacking US
-
FDR created a new fleet of warplanes
-
Winston Churchill (British PM) asked FDR for help, FDR sent war materials, ships, planes, etc. to Britain
-
In exchange, US can build military bases on some British lands
-
-
-
Congress also passed Burke-Wadsworth Act (1940), creating a military draft in case of war
-
Within US, there was lots of disagreement over whether to join the war or not:
Committee to Defend America by Aiding the Allies (CDAAA)
-
Wanted to keep US out of war by providing financial & material aid to the Allies (France & Britain)
Fight for Freedom Committee
-
Wanted US to actually join the war & repeal Neutrality Acts
America First Committee
-
Wanted US to remain isolationist & not enter WW2
-
Had strong support of many Republicans
-
These 3 committees created lots of tension in US
-
Eventually, FDR won re-election (3rd term) in 1940
Lend-Lease System & Further Threats to US
-
After FDR's re-election in 1940, US was moving more toward war
-
In Mar 1941, Congress replaced cash-and-carry system w/ lend-lease system: Britain could borrow military supplies from US & pay back later
-
US did this b/c Britain was nearly bankrupt
-
-
Germany started threatening British ships in Atlantic as they'd travel to US to pick up military supplies → US would now escort supplies halfway across Atlantic
-
-
Hitler invaded USSR in fall 1941 → USSR needed help from US → US extended lend-lease to USSR & created formal US-USSR alliance
- German U-boats started to threaten US ships, so FDR ordered US ships to fire at German submarines
- In fall 1941, USS Greer was shot by German U-boats → FDR ordered US ships to "shoot-on-sight" at German U-boats
- In Oct 1941, USS Reuben James was sunk by German U-boats
- In Aug 1941, US met w/ Britain to create the Atlantic Charter, a set of principles to maintain post-war peace & prosperity
- This failed as US joined the war soon after

Pearl Harbor Attack (Dec 1941) & US Joins the War
Japan also had a fascist militarist gov & signed Tripartite Pact w/ Hitler & Mussolini (Sep 1940)
Inspired by German success in Europe, Japan wanted to take over parts of East Asia
Japan invaded French Indochina in Sep 1940
Japan thus bombed Pearl Harbor (Dec 7, 1941). US declared war on Japan after that. Then Germany & Italy declared war on US
Japanese militants didn't want to compromise or negotiate w/ US
US imposed an oil embargo on Japan as US wanted to protect its ally, France, and its colony, French Indochina
Containing the Axis Powers
Containing the Japanese
Japan took over US & British territories in the Pacific (Philippines, Hong Kong, Singapore, etc.)
Allies (US & Britain) had many victories against Japan: Defeated Japan at Midway Islands (May 1942) & Guadalcanal (Feb 1943)
Now, Allies had stopped Japan from advancing forward, setting the stage to defeat Japan later on
Containing the Germans
Germany sought to invade USSR in a campaign called Operation Barbarossa (Jun-Dec 1941)
USSR's winter weather & vast landscape caused Germany to fail & was forced to retreat
Allies (US & Britain) defeated Germans at Battle of El Alamein in Egypt (Oct-Nov 1942)
Allies then launched air force & naval raids to remove Germany from the rest of North Africa
Allies captured Sicily (part of Italy) in Jul 1943, causing Mussolini to escape to Germany
Hitler then extended his rule to Italy, which stalled a potential Allied invasion of the rest of Italy
Allied invasion resumed later on, and the Allies took Rome in Jun 1944
The Holocaust
-
One major element to WW2 was the Holocaust
-
Germans blamed all "racially inferior" people for Germany's economic troubles
-
Including Jews, Poles, gypsies, homosexuals, etc.
-
-
Nazi Germany would send these people to concentration camps
-
At the camps, they'd be killed in gas chambers or used to test deadly weapons
-
-
-
Although US public opinion was against Holocaust, the gov wasn't doing much to stop it
-
US gov believed best way to stop Holocaust was to just win the war, not to bomb concentration camps or railroads leading to them
-
US rejected many Jewish refugees
-

Defeating the Axis Powers
Victory in Europe (Against Germany)
Allies (US & Britain) bombed major industrial centers in Germany (Dresden, Berlin, etc.)
USSR was pushing westward from the USSR into Germany
On D-day (Jun 6, 1944), Allies landed in Normandy, France & prepared to liberate France from Nazi rule and push eastward until Germany
USSR could conquer the land in its path, including Czechoslovakia & East Germany
In Apr 1945, the Nazis in Berlin were surrounded by USSR on the East & US/Britain on the West. Nazis surrendered in May 1945
The Creation of the Atomic Bomb
-
Scientists warned the US gov that Germans were creating an atomic bomb → US gov now wanted to create one as well
-
Scientist Albert Einstein fled Germany & was living in US; He warned FDR about a potential German atomic bomb
-
Atomic physicists now began experimenting to create an atomic bomb as soon as possible
-
-
Enrico Fermi discovered radioactivity of uranium in 1930s, and this concept was used in atomic bombs
-
Gen. Leslie Groves of the US Army organized the atomic bomb project under a single initiative, the Manhattan Project
-
Worked w/ university labs to create the atomic bomb
-
-
In Jul 1945, the 1st atomic bomb, Trinity, was tested in a desert in New Mexico & was successful
-
In Aug 1945, atomic bombs were dropped in Japan

Victory in Pacific (Against Japan)
US defeated Japan at Marshall Islands, Mariana Islands, Guam, Saipan, Tinian, and many other islands (early-mid 1944)
In Oct 1944, US defeated Japan at Battle of Leyte Gulf in Philippines, the largest naval battle in WW2
US got 2 islands: Iwo Jima & Okinawa from Japan (mid 1945)
Japan surrendered to US in Sep 1945
US dropped 2 atomic bombs: One in Hiroshima, one in Nagasaki (Aug 1945)
Japan refused to unconditionally surrender to US
American Society During the War
Economic Development During the War
-
Due to significant economic development, the war officially ended the Great Depression
-
US economy was finally restored to pre-Depression levels
-
Incomes increased, GDP increased, federal budget increased
-
This was due to high wartime product demands
-
-
Most gov spending went to the West as that's where the US military got supplies to fight Japan
-
Pacific Coast became a center for shipbuilding & aircraft building industry
-
-
Due to economic development & rise of Republicans in Congress, the New Deal ended
-
Most New Deal programs (like CCC & WPA) ended b/c unemployment wasn't really a problem anymore
-
New Deal wasn't necessary anymore since economy fully recovered
-

Economic Mobilization For the War
-
Due to high prices, there was a fear of inflation during WW2
-
Office of Price Administration (OPA) would regulate prices, wages, & salaries to prevent inflation
-
OPA was somewhat successful
-
-
-
In 1942, FDR established War Production Board (WPB) (counterpart to WW1's WIB) to coordinate the US economy for WW2
-
Regulated the economy, gave contracts to certain businesses to make things for the war
-
-
Factory & industrial production was super high during the war
-
Industrial output of US was higher than that of all Axis forces combined
-

Labor Sources & Labor Unions
-
WW2 created a labor shortage as 15 million people were taken into the war effort
-
Many more people were needed in the US economy → Women, children, etc. all joined the industrial workforce
-
-
Labor unions got more power, but they had to give up some economic demands
-
Gov created a max 15% wage increase rule during wartime & a "no strike" pledge for all workers
-
This was b/c the gov wanted production to run smoothly
-
-
In exchange, the gov would allow unions to continue operating & recognize their existence
-
-
FDR passed the War Labor Disputes Act (Smith-Connally Act) (1943): Allowed FDR to seize any private factory that threatens to strike

Technological Developments
-
National Defense Research Committee led research efforts into new technologies to help win WW2
-
Axis powers had many advances in tech
-
Germans had tanks, mechanized armor, and submarines
-
Japanese had some naval tech & aircraft carriers
-
-
US used its strong assembly line to make military tech like planes, ships, tanks, etc. in large numbers, outnumbering the Axis powers
-
US & Britain developed sonar technology
-
Underwater radio signals that could detect German U-boats & naval mines
-
-
US & Britain developed 4-engine bomber planes which were much faster than Axis planes
-
US & Britain developed GEE navigation system: More accurate than other navigation systems, used for bomb raids
-
US & Britain developed many intelligence projects
-
Britain developed a project called Ultra: A cryptology project to decipher German & Japanese army movements
-
Britain developed a computer called Colossus II, used to decipher German army movements
-
-
US developed a cryptology project called Magic to decipher Japanese movements in Pacific
-

African-Americans & the War
-
African-Americans wanted to use the opportunity to fight in the war to try to get civil rights → Didn't fully happen
-
A Philip Randolph, pres. of Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters (African-American labor union), organized a march in DC against segregation
-
Believed that companies in the war industry should integrate Blacks & Whites
-
FDR canceled the march as he feared violence → Created Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) to ban discrimination in war industries
-
-
Due to openings in industrial jobs, many African-Americans migrated from South to North
-
Much bigger than "Great Migration" of WW1
-
-
Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) (est. 1942) organized mass resistance to discrimination
-
Organized sit-ins in segregated places
-
-
Military had less segregation than before
-
More African-Americans served as fighters in the army, marines, etc.
-

Native Americans & the War
-
About 25k Native Americans served in war
-
Some men served in combat (one notable person is Ira Hayes)
-
Other Natives served in military communications as "code-talkers"
-
Would converse w/ each other in their native language → Axis powers wouldn't understand
-
-
-
Many natives started to leave reservations
-
Many young natives joined the industrial workforce
-
Many realized that opportunities in the reservations were limited → moved out of them
-
This created more pressure to assimilate Indians to White society → Opposition to Indian Reorganization Act (1934)
-

Mexican-Americans & the War
-
Many Mexicans entered the US to join the workforce due to labor shortages in Pacific Coast
-
Contract laborers (known as braceros) would temporarily live in US to work in industrial jobs
-
-
Mexican-Americans gained many more job opportunities in industrial workforce
-
Many left agriculture to join industrial workforce
-
-
Over 300k Mexicans joined the army
-
This created lots of tensions between Mexicans & Americas
-
In LA, Whites hated Mexican street gangs, known as "zoot-suits" → Organized "zoot-suit" riots (Jun 1943) against them
-

Women & the War
-
Because many men served in the military, many women had to join the workforce to replace them
-
Number of women in workforce increased 60%
-
-
"Rosie the Riveter" was a popular image that encouraged women to join the workforce
-
Many joined industrial workforce → eliminated prejudice against them for doing men's jobs
-
Many women even joined labor unions
-
-
Some women did service work in gov or military
-
Many were clerks, secretaries, typists, etc.
-
.jpeg)
Internment of Japanese-Americans
-
A lot of Japanese-Americans lived on the West Coast & US gov believed they may interfere w/ the military's campaigns against Japan
-
Thus, the US gov sought to relocate all Japanese from the West Coast to internment camps
-
War Relocation Authority (WRA) relocated 100k Japanese-Americans to internment camps
-
Meant to assimilate them to American culture
-
Would provide some education to them, make some of them work, etc.
-
Conditions were somewhat harsh & uncomfortable
-
-
-
Some Japanese left the camps, but many of their homes on the West Coast were gone
-
Weren't allowed to return to West Coast during the war → Went to East Coast to study or work
-
-
Korematsu v US (1944) case ruled that internment of Japanese was constitutional
-
In 1945 (when war ended), they were finally permitted to return home
-
Many of them found their home taken way
-

Chinese-Americans & the War
-
US gov enhanced its relation w/ Chinese government since it allied w/ China in the war
-
Repealed Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) in 1943 → Many Chinese people migrated to US
-
-
US gov started portraying Chinese people as good
-
Generally wanted to differentiate Chinese people from Japanese people
-
Many Chinese joined industrial war plants
-
Some Chinese even joined the military
-

Flashcards
Link to flashcards: https://quizlet.com/583124070/apush-unit-7-flash-cards/
Summary
Spanish-American War:
After the Latin American revolutions of the early 1800s, Spain only had control of Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. Cuba started revolting against Spain, and the US came to Cuba's aid. In February 1898, an American ship called USS Maine sunk in Havana's harbor, causing outrage agains Spain, even though Spain didn't sink the ship. This caused a war between US and Spain, where the US fought against Spain to give Cuba independence. However, as the US realized that Spain was weakened, the focus of the war shifted to conquering all of Spain's colonies, which is why in the end, the US got control of Puerto Rico, Guam, and Philippines in addition to getting Cuba its independence. After this, the US economically developed each of its newly-acquired territories.
Imperialism:
The Spanish-American War (1898) generated lots of debates about imperialism. Many opposed imperialism and believed the US had a long-standing tradition of isolation from foreign affairs. However, others embraced imperialism for its economic advantages. After the Spanish-American war, the US became an imperial power and conquered Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. In addition, the US acquired Alaska, Hawaii, and American Samoa. Also, the US carved a sphere of influence in China, gaining economic power in China.
The Progressive Movement:
The societal problems created by the Gilded Age led to a series of reform movements, known as the Progressive Movement. Many progressive movements, such as the Social Gospel and the Settlement House movement, dealt with combating urban poverty. Others sought to expose the corruption of political machines and monopolistic businesses. The main progressive movement is the suffrage movement, which promoted the idea that women are more moral and men and that women should get the right to vote, culminating in the 19th amendment (1920), giving women the right to vote.
World War 1:
In Europe, a huge war broke out, known as the Great War (or World War 1). The US initially stayed neutral due to economic and political interests, but it later joined the war in 1917 due to threats to its neutrality, such as threats by German U-boats and the need for more troops on the side of the Allies. Woodrow Wilson mainly joined the war to maintain postwar peace, and he drafted a peace agreement called the Fourteen Points, but at the Paris Peace Conference (1919), many of those were rejected. In the end, an association of nations called the League of Nations was created, but the US did not join due to Republican opposition in Congress. Furthermore, the Treaty of Versailles (1919) forced Germany to pay reparations, something Wilson was staunchly against. During the war, the US mobilized its economy and its industry for the war, opening up employment opportunities for women & minorities. However, the US also suppressed any anti-war propaganda through its Sedition & Espionage Acts.
The New Era:
The postwar era, known as the New Era or the 1920s, was an age of lots of innovation and in tech and culture. New technologies like home appliances allowed people, especially women, to engage more with modern society. Women gained more freedom and they were able to engage more with modern society rather than staying at home, and this idea was known as the "flapper image" of women. Women also got "pink collar" service jobs as teachers, clerks, phone operators, etc. There was also a rise in American culture where Americans used radios and watched movies often, and they somewhat ignored religion and assumed it as a secondary role. This created lots of conflict between these modernists and traditionalists, people who still wanted to embrace traditional values of society. This led to the rise of the 2nd KKK, a group of people who wanted to suppress all minorities and promote traditional values like alcohol prohibition. Furthermore, a disagreement between traditionalists & modernists over the evolutionary theory led to the Scopes Trial, an event which emphasized the conflict between the 2 groups. Finally, another element of the New Era is a rise in consumer culture, where the middle class would use their extra wages to buy extra consumer-type goods.
The Great Depression:
Although the economy was successful in the New Era, it was vey fragile. There was lots of poverty, and people heavily depended on the banks. People had a lot of credit in the banks, so any failure of the banks would cause a huge financial panic. People started to invest a lot into the stock market and were taking out loans from the banks in order to invest, but in October 1929, the stock market crashed, and people tried to put money back into the banks, but they couldn't as they lost all their life savings in the stock market, which caused the banks to fail. This caused a huge chain reaction, and eventually millions of people were unemployed. Women actually fared better than men because their pink collar jobs weren't really affected by the depression, but other minorities faced worse because unemployed White people took their jobs.
The New Deal:
The New Deal was an attempt by President FDR to revive the economy after the Great Depression. The First New Deal was a program that sought to revive everything from the top, like banking, industry, agriculture, etc. and then focus on reviving unemployment at the bottom. Its legislation focused on boosting confidence in banks and reviving the industrial economy as well as agriculture. Many people criticized it for not doing much to resolve unemployment, so in 1935, FDR enacted a new series of reforms, called the 2nd New Deal. The main 2 things are the Social Security Act and the Works Progress Administration. The Social Security act was significant in that it established the modern-day social security system. The Works Progress Administration employed millions of people and helped economically develop the West and the South. This helped revive the economy slightly, and it only fully recovered after World War 2. Overall, the New Deal was significant in that it gave the government a stronger and a more interventionist role in the US, and it encouraged many African-Americans to switch from Republican to Democratic.
Interwar Period Foreign Policy:
The US took a very isolationist stance in the interwar period. It signed many treaties such as the Washington Naval Treaty (1922) & Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928), but those did not really do much. When FDR came into power, other totalitarian regimes were threatening America's neutrality by invading other regions, but FDR still remained neutral. He signed the Neutrality Acts (1936-1939) to remain neutral. When WW2 broke out in Europe, FDR had to economically help Britain through the cash-and-carry system and later the lend-lease system so that Germany does not invade Britain and later take over the US. Meanwhile, Japan was becoming powerful in the Pacific, so the US imposed an oil embargo on Japan after Japan invaded French Indochina, so Japan then bombed Pearl Harbor (Dec 1941), bringing US into the war.
World War 2:
World War 2 started in Europe in 1939, and the US was brought into the war in 1941. The first step to winning was containing the Allies. The US & Britain contained Germany by defeating Germany in North Africa & Italy. The US contained Japan in the Pacific by defeating Japan at Midway Islands and Marshall Islands. Then, the Allies liberated France and won the war in Europe. Later, the US bombed Japan, winning the war in the Pacific as well. During the war, the American economy boomed, which brought more people into the workforce, including many women, African-Americans, and Mexican contract workers (braceros). Also, the US viewed the Japanese-Americans on the West Coast as a threat to their military plans, so they started to send them to internment camps during the war. This was not done to Chinese-Americans as the US allied with China.
