Unit 5: 1844-1877
Outline
General Timelines
Timeline #1: Mexican-American War & Pre-Civil War Developments (1836-1861)

Timeline #2: Civil War (1861-1865)

Timeline #3: Reconstruction (1863-1877)

General Maps
Map # 1: Conflict over Texas Boundary

Map # 2: Mexican-American War

Map # 3: End of Mexican-American War

Map # 4: Manifest Destiny pre-1850

Map # 5: Post-1850 Compromises & Developments

Map # 6: Secession Timeline
Map # 7: Battles in Eastern Theater (1861-1863)
Map # 8: Battles in Western Theater (1861-1863)
Map # 9: Battles in Kansas-Missouri Region
Map # 10: Final Union Attack & Confederate Surrender (1864-1865)

Map # 11: Timeline of Readmission to Union





Course Content
Manifest Destiny:
Situation in Texas
Background Situation in Texas
-
Mexico inherited Texas after receiving independence from Spain in 1821
-
When US purchased Louisiana from France in 1803, US tried to claim TX but gave up in 1819 as Mexico refused to give it up
-
-
Mexico called for Americans to settle in Texas so they could help boost its economy
-
Passed a law in 1824 to give cheap land to Americans & 4-year tax exemption
-
Believed American presence in TX would create a buffer between Mexico & US
-
Didn't happen as the Americans remained loyal to the US & not Mexico
-
-
Thousands of Americans migrated there
-
Many Southerners migrated w/ their slaves to grow cotton
-
-
-
Americans sought to declare autonomy of TX
-
Stephen Austin established first government in TX in 1822
-
Austin and others created governments that tried to claim autonomy of Texas
-
In the Fredonian Rebellion (1826-1827), one gov tried to claim independence of TX, but the Mexican gov crushed the rebellion
-
-
Mexico thus passed laws to prevent more immigration from the US
-
This failed, so they lifted the ban in 1833
-
-
30,000 Americans (including slaves) were in TX by 1835
-

Independence of Texas (1836)
In 1830, Mexico made slavery illegal. Also, in 1833, Gen. Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna became Mexican dictator & passed laws to limit state power & promote national power
Texans hated the ban on slavery & hated the autocratic rule of Santa Anna, so they got mad
Santa Anna imprisoned Stephen Austin for planning a revolt and Mexican troops came to Texas, so Texas declared independence in 1836
Gen. Sam Houston defeated the Mexican Army at the Battle of San Jacinto (in Houston). He killed some Mexican army members & imprisoned Santa Anna (Apr 1836)
Mexican army attacked a Texan garrison at the Alamo in San Antonio (Mar 1836)
Mexican army attacked a Texan garrison at Goliad & killed its members (Oct 1835)
Santa Anna signed a treaty to give independence to Texas (1836)
Annexation of Texas (1845)
-
First Texan president, Sam Houston, sent agents to DC to petition for annexation
-
Northerners opposed it as they didn't want such a large slave state to join
-
Jackson didn't want more sectional conflict, and the next 2 presidents delayed looking into it
-
-
As it failed to get annexed by US, it sought to develop itself as a powerful independent nation
-
Negotiated trade treaties w/ Britain & France
-
-
Question about Texas's annexation became important in election of 1844
-
Election of 1844 was Henry Clay vs James K Polk
-
Polk supported annexation; Clay didn't
-
-
However, before leaving office, John Tyler (previous president) already presented to Congress a bill annexing Texas
-
Thus, Texas became a state in Feb 1845
-
-

Situation in Oregon, California, New Mexico
Situation in Oregon Region
-
Oregon territory includes present-day Oregon, Washington, parts of Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, and British Columbia (Canada)
-
US & Britain both claimed this land, agreed to "joint occupation" for 20 years starting 1818
-
-
Population of the territory was small, mostly fur traders settled there
-
In 1831, 4 Nez Perce & Flathead Indians mysteriously appeared in St. Louis
-
Americans believed it was an invitation to expand westward into Oregon territory
-
-
Interest grew in the region for missionaries
-
Marcus Whitman & his wife Narcissa created an unsuccessful mission among Cayuse Indians
-
In 1840, more Americans settled in the region, causing a measles pandemic among the Indians
-
Pandemic killed many Cayuse Indians
-
-
Cayuse Indians blamed Whitman for it, so they killed him, Narcissa, and other whites (1847)
-
-
Many Americans settled in the region, along the Pacific Coast
-
Polk wanted to annex Oregon Territory (1846)
-
Proposed a compromise to Britain: 49th parallel would divide US & British territory
-
British minister initially rejected it but later accepted it as he didn't want war
-
This border of 49th parallel exists today
-

Westward Migration
-
Many people migrated from the Midwest region to the West
-
Most were adventurous young men to migrated for new opportunities
-
Sometimes whole families migrated to settle as laborers in the West
-
Some speculators came to take advantage of federal land grants
-
Some people (especially Mormons) went on religious missions
-
-
About 300,000 people migrated from 1840-1860
-
Most gathered in depots in Missouri or Iowa & loaded their stuff on chartered wagons
-
Traveled mostly via Oregon Trail
-
-
Migration was often slow
-
Wagons were really slow
-
Snow in the Rockies could delay the journey
-
Indians were helpful as guides, but some died in conflict with them
-
Some had conflict with travelmates
-

Situation in California & Gold Rush of 1849
-
US initially had some interests in annexing California
-
Many Mexicans & Indians lived there
-
Americans went there as whalers along the coast & as merchants to trade w/ Mexicans & Indians
-
Later, many Americans settled in Sacramento Valley (a rich agricultural region)
-
-
In Jan 1848, James Marshall found gold while working in John Sutter's sawmill in Sierra Nevadas
-
Wanted to prevent the news from spreading to prevent gold rush, but the news somehow spread
-
100,000s of people came to find gold (these were known as the 49ers as it was 1849)
-
-
Many Chinese people migrated during the Gold Rush
-
Most got loans to migrate
-
Some came to find gold, others came to work in auxiliary tasks to support the gold miners
-
-
Some gold miners exploited the local Indians & made them perform indentured labor
-
Few people actually found gold, so most returned home unhappy, but others settled in California

Situation in New Mexico
-
Spanish had long lived closely with the Pueblo Indians of New Mexico
-
After Mexican independence, Mexico invited Americans to settle in NM to develop its economy
-
Same situation as Texas
-
Many Americans settled in New Mexico, so it became more American than Mexican
-
There was a thriving commerce between Independence, MO, and Santa Fe, NM
-
This was called the Santa Fe Trail
-
-
-
Polk wanted to annex Mexico along with California

Mexican-American War (1846-1848)
Causes of Mexican-American War
-
Mexico challenged the border with Texas
-
Mexico believed the border was the Nueces river, but US believed it to be Rio Grande River
-
Nueces river was far north of Rio Grande
-
Rio Grande River border would add New Mexico territory to the US (which was what US wanted)
-
[Map is shown below]
-

President Polk dispatched Zachary Taylor to guard Nueces River. He also sent John Slidell to buy NM and CA from Mexico
Mexico refused Slidell's offer. Thus, Polk told Taylor to advance from Nueces river toward Rio Grande River
One Mexican army attacked Taylor's army, which marked the start of the war (Apr 1846)
-
When Polk sent Taylor to Texas, he also told the US Pacific naval squadron to occupy the ports in California in case Mexico declares war
-
The naval squadron also told American farmers in California to prepare for war
-
-
After the Mexican army attacked Taylor's army, Polk really quickly asked Congress to approve war
-
Lots of people opposed the war effort
-
Polk supported war as he wanted expansion
-
So many northerners didn't want to expand southward into potential slave territory
-
Many believed the war effort was useless & straining resources
-
Some believed it gave Polk too much power to invade any country he wants for no reason
-
Transcendentalist thinker Thoreau was briefly jailed for refusing to pay taxes
-
He hated that his taxes will finance the war
-
-
-
Those who supported war were really enthusiastic about it
-
Believed in gaining "All Mexico!"
-
Wanted to annex the entire Mexico
-
-
Battles of Mexican-American War
President Polk wanted Taylor to take over Northeast Mexico
Taylor took over Monterrey in Sep 1846
Mexicans negotiated an armistice & retreated. Polk believed Taylor couldn't take over Mexico City due to this armistice
Polk told Col. Stephen W Kearny to take over NM and CA. Kearny easily conquered Santa Fe in Summer of 1846
US navy in CA helped a group of US explorers in California (led by John C Frémont) lead the Bear Flag Revolt against Mexico (Jun 1846). American settlers in CA helped with this revolt
Kearny came to CA and joined the Bear Flag Revolt. He finished conquest of CA by Fall of 1846

End of Mexican-American War
Mexico refused to concede after losing CA and NM, so Gen. Winfield Scott launched a final campaign
Scott assembled an army of 14k soldiers and the navy transported it to Veracruz (in Mexico)
The army marched 260 miles to Mexico City (Sep 1847). Before seizing it, Mexico agreed to peace
Here is a map of this part of the war:

-
Polk send diplomat Nicholas Trist to Mexico City to negotiate peace treaty w/ Mexico (Feb 1848)
-
Known as Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
-
Mexico gave California, New Mexico, and Rio Grande Texas boundary to the US
-
US paid $15 million to Mexico for war reparations
-
-
Annexation of "All Mexico!" had failed
This map shows the Mexican cession of land as well as the state of Texas:

Post-War Sectional Conflict
Sectional Conflict over Former Mexican Territories
-
Rep David Wilmot (D-PA) created a bill called the Wilmot Proviso (Aug 1846)
-
Believed slavery should be prohibited in former Mexican territories
-
Passed in House but not Senate
-
Debated on for years, a really important bill in the sectional conflict
-
-
Polk wanted to extend Missouri Compromise line to the West Coast
-
Also debated on, but not that popular
-
This issue was unresolved when Polk left office in 1849
-
-
Sectional conflict was an important issue in Election of 1848
-
Democrats had Lewis Cass (MI), Whigs had Zachary Taylor (LA) (the war hero)
-
Liberty Party (now called the Free-Soil party) had Martin van Buren
-
Taylor narrowly won, and Free-Soil party elected 10 seats to Congress
-
-
In Dec 1849, Taylor asked Congress to admit CA and NM as states
-
Believed the 2 states would choose to be either free or slave states after gaining statehood
-
Congress didn't to pass it as it feared both states might oppose slavery
-
-
The North had many more anti-slavery developments that the South hated
-
North passed laws that prohibit gov officials from returning runaway slaves to the South
-
Known as Fugitive Slave Law
-
-
South also hated that territory of Washington DC might abolish slavery
-
South hated that admission of the new territories as states would upset the 15/15 balance of free & slave states
-

Compromise of 1850
California is admitted as a free state
The remainder of the former Mexican territories would be divided into Utah & New Mexico territories. They can choose whether slavery is allowed
Fugitive slave law reinstated in the North: Officials must return runaway slaves in the north to their masters in the South
Slave trade would be banned in DC, but slavery itself wouldn't be banned there
New border between New Mexico & Texas would be made
This map shows the state of CA, territories of NM and UT, and the new TX border as part of the Compromise of 1850:

Debate over Compromise of 1850
-
During winter of 1849-1850, Henry Clay led efforts to craft a Compromise
-
He created the Compromise in Jan 1850, with the 5 terms expressed in the section above
-
-
This was debated on extensively, in 2 phases
-
First phase: Clay, Calhoun, and Webster debated on it
-
These were the 3 old people in Congress
-
All 3 shared broad ideals of nationalism and sectionalism in support of Compromise
-
Calhoun even had more radical ideas
-
Wanted 2 presidents: one each for the South and the North
-
Believed North should stop attacking Southern slavery
-
Believed North & South should exist peacefully w/o attacking each other
-
-
Congress disapproved the compromise, which led to the 2nd phase of debate
-
Clay got sick, Calhoun died, and Webster was promoted, so all 3 were out of Congress
-
-
Second phase: Younger senators debated
-
Believed more in boosting the economy than supporting personal liberty
-

Passing of Compromise of 1850
-
Pres. Taylor died in Jul 1850, so Millard Fillmore became president
-
He was more flexible in compromises
-
-
Senator Stephen Douglas (D-IL) wanted to break up the "omnibus bill" (a bill with multiple parts)
-
Wanted Congress to vote on each part separately
-
-
In Sept 1850, Congress approved all 5 components, and Fillmore signed it

Post-1850 Sectional Conflicts:
Developments in Franklin Pierce's Presidency
-
Election of 1852 was between Franklin Pierce (D) and Gen. Winfield Scott (W)
-
Whigs were divided among themselves as they struggled over the issue of slavery
-
Pierce won because Whigs were divided
-
-
Pierce struggled to enforce the fugitive slave law
-
Many northerners opposed it, so they organized mobs to prevent its enforcement
-
White southerners had to come to the north to recapture runaway slaves
-
-
Pierce was inspired by European liberal revolutions of 1848 to promote the "Young America Movement"
-
It was an artistic, cultural, and political movement to expand US influence
-
Pierce sought to conquer more territory
-
His envoys wrote the Ostend Manifesto, a document explaining how to seize Cuba
-
When this was leaked to the public, northerners hated it as they didn't want another slave state
-
-
Hawaii & Canada had also petitioned to join US, but that failed due to slavery issues
-
It would mess up North/South balance
-
-
-
Pierce also encountered sectional conflict w/ transcontinental railroad
-
To settle in the unorganized territory, there needs to be communication between East & West
-
A transcontinental railroad was needed
-
-
Location of transcontinental railroad provoked sectional conflict
-
Northerners wanted it to connect w/ Chicago
-
Southerners wanted it to connect Southern cities
-
-
His Sec. of War, Jefferson Davis, sent James Gadsden to buy a narrow strip of land from Mexico (just south of New Mexico)
-
This would allow for railroad construction between the Southern cities
-
-

Situation in Kansas & Nebraska
Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)
-
Sen. Stephan A Douglas (D-IL) wanted to organize the territory west of Illinois
-
This was west of IL, MO, and IA, but east of the new Utah territory
-
Wanted to clear up the Indians from the area so he could build a railroad there
-
-
He proposed the territory of Nebraska (comprising present-day Nebraska & Kansas)
-
Southerners hated this they thought Nebraska would become a free state
-
-
In response to those concerns, Douglas divided the territory into 2
-
Lower part (Kansas) and Upper part (Nebraska)
-
Both territories would choose to be free or slave with popular sovereignty
-
Popular sovereignty: the residents vote on it
-
Nebraska would likely be free, Kansas would likely be slave
-
-
This would repeal the Missouri Compromise line
-
-
This act, the Kansas-Nebraska Act, passed in 1854
-
The Republican party was created in 1854 for those who hated the Kansas-Nebraska Act
-
Both Democrats & Whigs who hated the bill joined the Republicans
-
The Whigs became super divided & ceased to exist by 1856
-
This map shows the Kansas & Nebraska territories (in the center of the map) after the Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854):

Post-1854 Turmoil in Kansas
-
In 1855, people in Kansas elected the territorial legislature
-
Lots of pro-slavery people from Missouri settled in Kansas
-
This increased the pro-slavery votes
-
-
Thus, the legislature became majority pro-slavery
-
-
Anti-slavery people were outraged & set up their own constitutional convention
-
Created an anti-slavery government
-
Failed to achieve statehood as President Pierce denounced them
-
-
Pro-slavery people organized an army & sacked the anti-slavery buildings in Lawrence, KS
-
John Brown, an anti-slavery man, killed 5 pro-slavery people in one night (May 1856)
-
Known as Pottawatomie Massacre (1856)
-
He put their bodies on display to discourage pro-slavery people from entering Kansas
-
-
There continued to be lots of violence in Kansas
-
Kansas was known as "Bleeding Kansas"
-

Final Decision in Kansas
-
President James Buchanan (elected in 1856) sought to deal with the Kansas situation
-
Kansas residents organized a constitutional convention to write their final state constitution
-
This convention would determine whether Kansas would be free or slave
-
Pro-slavery people were the majority because of gerrymandering
-
In 1857, at Lecompton, KS, the convention wrote a pro-slavery constitution
-
-
However, when territorial legislature (different from constitutional convention) was elected, anti-slavery people were the majority
-
Submitted pro-slavery Lecompton constitution to the Kansas residents, who voted against it
-
-
Buchanan still persuaded Congress to admit Kansas as a slave state, but it failed in the House
-
Congress approved a Compromise in April 1858
-
Pro-slavery Lecompton constitution would be presented again to Kansas voters
-
If approved, KS becomes slave state
-
If not, statehood would be postponed
-
-
-
In the end, the pro-slavery constitution was voted against, and KS became free state in 1861

Developments in Buchanan's Presidency
Election of 1856 & Panic of 1857
-
In election of 1856, the issue of settlement in the unorganized territory was really important
-
Democrats chose James Buchanan
-
Republican party (a new party created in 1854) chose John C Fremont
-
Native American Party (Know-Nothings) chose Millard Fillmore
-
-
Buchanan narrowly won
-
Buchanan was the 2nd oldest president (after William Henry Harrison)
-
He was a bit indecisive & timid
-
-
-
There was a financial panic in 1857
-
Many lower class workers were affected; they switched to Republican party
-

Arguments For & Against Slavery
-
Northerners largely opposed slavery
-
Believed in "free soil" ideology
-
Believed in stopping the westward expansion of slavery
-
-
Also believed South promoted the "slave power conspiracy"
-
Believed South wanted to extend slavery north & threaten North's capitalism
-
-
-
As North sought to attack slavery, the South sought to protect it
-
Believed the growing cotton economy was crucial to economic success
-
Believed slavery was good because slaves had a better life than industrial workers in north
-
Believed slavery allowed whites to live a refined life
-
Believed blacks were biologically inferior
-

Dred Scott v Sandford (1857)
-
One of the most controversial court decisions in history
-
Dred Scott was a Missouri slave who traveled to Wisconsin & Illinois (free territories) w/ his owner
-
When he returned to Missouri, he believed he was freed as he traveled through free territories
-
When his owner died, he sued the owner's widow for freedom
-
Lower courts made Scott free
-
However, the widow's brother, John Sanford, appealed to state courts, who reversed the decision
-
-
Scott then appealed to Supreme Court
-
Court misspelled Sanford as Sandford
-
Court was super divided on this issue
-
Roger Taney (chief justice) believed slaves were property & technically couldn't file a court case
-
He also believed slaveowners can't be deprived of their property when entering a free state
-
Thus, Missouri Compromise was technically unconstitutional
-
-
Court ruled that Scott remains in slavery as blacks weren't citizens & don't have the same privileges as whites
-
-
This shows that the federal court doesn't have the power to deal with such intimate issues
-
Republicans sought to reverse this decision

John Brown's Raid at Harper's Ferry
John Brown (same person who sparked the uprising in Kansas) sought to invade the South
In 1859, he led a group of armed men to invade mountain fortress at Harpers Ferry, VA. Sought to initiate a slave uprising from there
He seized an arsenal, but US troops seized him & sentenced him to death. White southerners feared they wouldn't be safe due to constant uprisings
Emergence of Abraham Lincoln
Lincoln's Unsuccessful Senate Run (1858)
-
1858 Senate election of IL was Stephen A Douglas (D) vs Abraham Lincoln (R)
-
Through Lincoln-Douglas debates, Lincoln gained lots of fame & prominence
-
Their viewpoints are described below
-
Douglas:
Each state could decide its own fate for slavery (popular sovereignty)
US will be dominated by whites, and blacks won't be allowed citizenship
Lincoln:
Slavery should be confined to the South & shouldn't spread westward
Westward expansion of slavery decreases opportunities for white immigrants
-
In the end, Douglas was elected to Senate
-
Over the next few years, Democrats lost support in Northern cities & Republicans gained support
-
Lincoln became popular in IL and throughout the nation
Presidential Election of 1860
-
Democrats were divided by those who supported slavery & those who wanted popular sovereignty for slavery
Democrats who believed in popular sovereignty nominated Stephen Douglas
Southern Democrats who wanted expansion of slavery nominated John C Breckinridge
Conservative ex-Whigs formed Constitutional Union Party, nominated John Bell
Republicans nominated Lincoln, promoted economic nationalism, believed slavery shouldn't expand
-
Lincoln appealed to the north by promoting economic nationalism
-
Believed the south was blocking the north's economic aspirations
-
Promoted Whig-like ideas: American system, internal improvements, transcontinental railroad
-
-
Lincoln wanted no slavery in the West, but he believed he doesn't have the power to regulate slavery in the territories
-
In the end, Lincoln was elected
-
Whites in the south believed their position in the US was hopeless as Lincoln was elected
-
They believed Lincoln was a sectional president & only served the interests of the North
-
Believed that if Lincoln wanted to stop westward expansion of slavery, pro-slavery South would be a minority in Congress
-
-
For these reasons, the South seceded soon after
-
Civil War:
Secession of the South & Start of War
Election of 1860 & Secession of Southern States
-
Election of 1860 had Abraham Lincoln as Republican candidate
-
Believed slavery should be confined to the South, didn't want slavery to expand westward
-
-
Southern slave states hated Lincoln's vision of America
-
Since Lincoln opposed slavery in the west, Southern states wouldn't get much influence
-
Southern states planned to secede if Lincoln would win
-
-
In the end, Lincoln (R) won
-
Thus, Southern states sought to secede
-
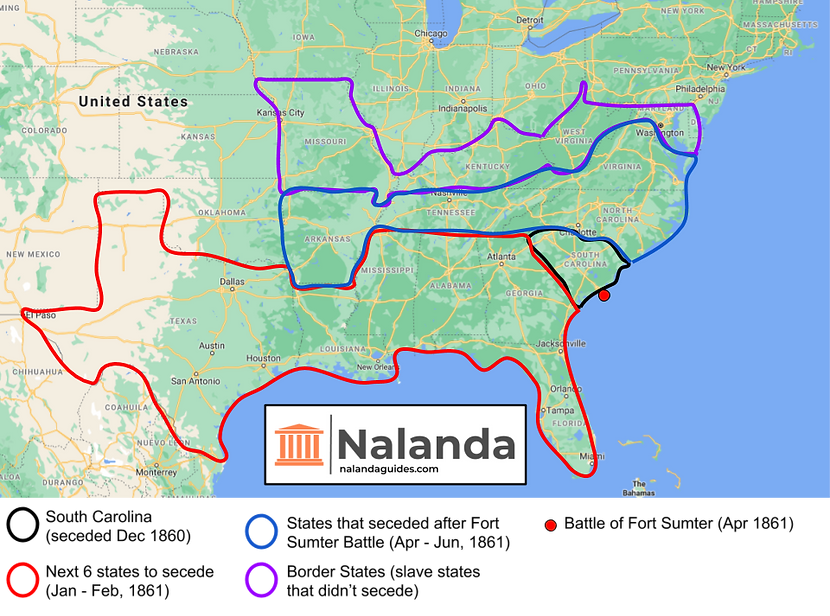
South Carolina seceded first in Dec 1860; 6 other states seceded by Feb 1861
-
AL, FL, GA, LA, MS, TX (as well as SC) seceded
-
Met in Montgomery, AL, to form Confederate States of America (Feb 1861)
-
-
-
Response from the North was confused
-
President Buchanan said no state can secede, but there was nothing stopping them
-

Initial Clashes with Confederacy & Failure of Compromise
-
Confederacy sought to get weapons from all arsenals in their region
-
Sought to conquer Fort Sumter & Fort Pickens, 2 offshore forts in the Confederacy
-
Buchanan refused to surrender Fort Sumter to the Confederacy & sent an army there
-
Confederacy fired at Buchanan's army
-
-
-
Sen. John J Crittenden (KY) proposed the Crittenden Compromise:
Fugitive slave law reinstated: Runaway slaves would be returned to south
Missouri Compromise line would expand to West Coast (slavery would be allowed south of the line)
All places with slavery currently can keep slavery
-
This compromise failed:
-
Republicans in Congress didn't want westward expansion of slavery
-
-
In 1861, when Lincoln was inaugurated, he promoted the vision that the Union can't separate
-
Believed more in keeping the nation together than in preventing expansion of slavery
-
Battle of Fort Sumter (Apr 1861)
Major Robert Anderson (Union) was stationed at Fort Sumter. He was running low on supplies, so Lincoln quickly sent supplies to him
Gen. P G T Beauregard (Confederate) bombarded Fort Sumter (Apr 12-13, 1861)
Anderson (Union) surrendered on Apr 14. This was the start of the Civil War
Post-Fort Sumter Secession & Situation in Border States
-
After the Battle of Fort Sumter, 4 more slave states seceded & joined the Confederacy
-
VA, NC, TN, AR joined Confederacy
-
-
Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware, (& later West Virginia) were border states
-
They had slavery but supported the Union
-
Lincoln convinced these states not to secede
-
They had a high population, so the Union needed them
-
If Maryland joined Confederacy, Washington DC would be completely surrounded by Confederacy
-
-
Here is a map depicting the secession timeline:
Differences in Advantages in North & South
North:
Much larger population
More industrial capacity & weapons
Better transportation & communications systems
Divided opinions about war effort
South:
Much smaller population
Home field advantage (war was mostly fought in south)
More popular support for the war effort
Battles of the Civil War
First Battle of Bull Run (Jul 1861)
Union Gen. Irvin McDowell was stationed in Washington DC w/ 30k soldiers
Confederate Gen. P G T Beauregard was in Manassas (30 miles from DC)
Both armies went to creek of Bull Run & fought. Union forces dispersed the Confederacy, but Confederacy counterattacked
Union forces retreated as Gen. McDowell couldn't reorganize them. Showed that the Civil War would be much longer & not an easy Union victory
Creation of West Virginia
Union Gen. George McClellan went to Western Virginia to gain support of the people there
The people in western Virginia opposed secession & supported Gen. George McClellan
The people in this region created a new state called West Virginia, admitted to Union in 1863. It was a border state
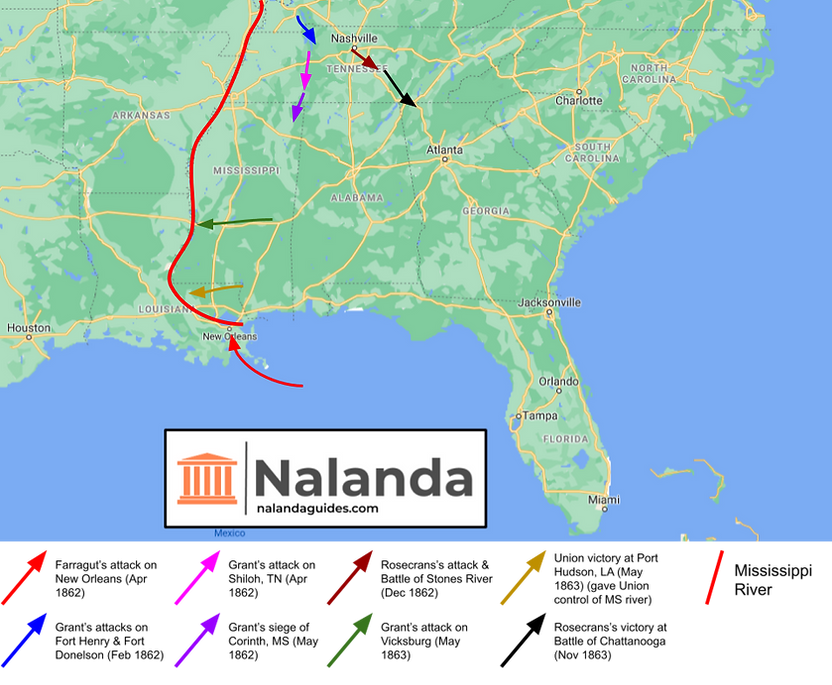
Union Successes in the West in 1862
Union forces sought to seize control of Mississippi River
Union forces under David G Farragut went to Gulf of Mexico. They defeated Confederate fortifications at Mississippi River's mouth
They did a surprise attack on New Orleans from the south. Gained control of Port of New Orleans, closed it to Confederate trade (April 1862)
Confederates under Gen. Albert Sidney Johnston made a defensive line from Fort Henry to Fort Donelson in Tennessee
Union Gen. Ulysses S Grant used ironclad ships to take Fort Henry via Tennessee River. He then took over Fort Donelson (Feb 1862)
He gained control of Tennessee River, forcing Confederates out of Kentucky & western half of Tennessee
Union Gen. Ulysses S Grant sought to conquer Shiloh, TN, so he could destroy Confederate railroad infrastructure
Grant marched w/ 40k men (after winning battles in Tennessee) to Shiloh. Confederate Gen. Johnston & Beauregard surprised him & forced him to retreat
Grant got 25k fresh troops and counterattacked, taking over Shiloh, TN, and Corinth, MS, a major railroad hub
Gen. Braxton Bragg replaced Johnston as Confederate General in West. He gathered forces in Chattanooga, TN, wanted to take over rest of Tennessee
Union forces led by Gen. William Rosecrans sought to take over Chattanooga
Both forces met in Dec 1862 - Jan 1863 at Battle of Stones River. Confederates withdrew, so Union forces won
Union Failures in the East in 1862
Gen. George McClellan (Union) was commander of Northern forces. Brought 100k men via a roundabout to Richmond by sea
Gen. Thomas J (Stonewall) Jackson (Confederate) marched through Shenandoah Valley in Virginia, was coming toward DC
Lincoln sent 30k troops from DC to face off Stonewall Jackson. Jackson defeated Union army in Valley Campaigns of 1862
Gen. Joseph E Johnston led Confederacy to attack Gen. McClellan's Army outside Richmond
Union forces (under McClellan) partially lost in the Battle of Seven Pines (May 1862)
Robert E Lee replaced Johnston & Stonewall Jackson. He attacked McClellan's army in the Seven Days Battle (Jun 1862)
Robert E Lee attacked Pope's Army in 2nd Battle of Bull Run (Aug 1862) before McClellan got there. Lincoln recalled Pope & put McClellan in charge of all Union forces in north
Pres. Lincoln told McClellan to go to Northern VA and combine with Gen. John Pope's army. From there, they'd do a direct attack on RIchmond
Union forces (under McClellan) retreated to the East
Battle of Antietam (Sep 1862)
-
After Gen. Robert E Lee defeated Gen. Pope at 2nd Battle of Bull Run, we went offensive in Maryland
-
He was going to assemble at Antietam Creek, near Sharpesburg
-
Gen. McClellan (Union) somehow found out that Lee would assemble at Antietam
-
-
Both sides fought at Battle of Antietam
-
The Bloodiest battle in Civil War
-
About 6,000 died
-
Additional 16,000 wounded or missing
-
-
Stopped potential Confederate invasion of Washington DC
-
Union technically won, but both sides were significantly wounded & weakened
-
McClellan allowed Confederacy to retreat instead of attacking them, so Lincoln recalled McClellan
-
-
Emancipation proclamation was drafted a week after the battle

Battles of 1863
Gen. Joseph Hooker (Union) was in charge of northern forces. He sought to attack Richmond
Gen. Hooker became nervous and retreated to forest area. Gen. Lee & Stonewall Jackson attacked him, so Hooker retreated
Huge Confederate victory, stopped invasion of Richmond. Stonewall Jackson was wounded & died of pneumonia. Battle of Chancellorsville (May 1863)
Gen. Ulysses S Grant (Union) attacked Vicksburg, MS. Conquered it after 6 weeks of siege (May-Jul 1863)
Another Union army conquered Port Hudson, LA (May-Jul 1863)
Union forces controlled the entire Mississippi River. They split the Confederacy into 2 pieces
Gen. William Rosecrans (Union) sought to pursue Gen. Braxton Bragg's forces (Confederate) after taking Chattanooga.
Unions lost Battle of Chickamauga (Sep 1863) & retreated back to Chattanooga
Gen. Bragg (Confederate) later sought to seize Chattanooga
Union forces now had control of most of eastern Tennessee & entire Tennessee River (in addition to Mississippi river from earlier)
Gen. Ulysses S Grant (Union) came to help Rosecrans. At Battle of Chattanooga (Nov 1863), Union forces took Chattanooga
Battle of Gettysburg (Jul 1863)
-
Robert E Lee sought to attack Pennsylvania to divert Union troops from the South
-
Met at Gettysburg, PA
-
-
Gen. George C Meade commanded Union troops
-
They fought at Battle of Gettysburg (Jul 1863)
-
Meade made a stronghold on the hills near the town, notably Cemetery Ridge
-
Confederates failed to attack Union forces on the nearby hills
-
Lee ordered an offensive assault the next day called Pickett's Charge
-
15k Confederate soldiers charged up the hills while Union forces kept shooting at them
-
Only 5k made it up the hill & were weakened
-
-
-
Confederacy lost & retreated
-
This is significant because it showed that Confederacy failed to invade the North
-
One of the only battles fought in the North
-
-
Lincoln made Gettysburg Address in Nov 1863
-
Only 2 minutes, super important speech
-
Contains lots of important ideas about freedom
-
Mentions that the soldiers fought to preserve the unity & freedom of the nation's people
-
-
Here is a map depicting the Battles in the East from 1861-1863:

Here is a map depicting the Battles in the West from 1861-1863:
End of the Civil War
Grant's Final Push in Virginia
Ulysses S Grant became general in chief of all Union armies. Finally Union had a smart & trustworthy general
Grant sought to take Richmond by land. He brought his 115k men into VA & won Battle of Spotsylvania Court House (May 1864)
Grant kept pushing to Richmond & lost more of his soldiers at Battle of Cold Harbor (Jun 1864) near Richmond
Grant sieged Petersburg for 9 months (Jun 1864 - Mar 1865)
Grant changed his plan & sought to attack Petersburg, a railroad junction south of Richmond. This would cut off communications from Richmond to rest of Confederacy
Sherman's Final Push in the South
Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman commanded Union troops in the South. Gen. Joseph E Johnston was commander of Confederate troops there
Gen. Sherman kept on advancing toward Atlanta. Gen. Johnston kept trying to maneuver & delay him
Gen. Johnston was replaced with Gen. John B Hood. Hood attacked Union army twice, but he weakened himself
Took Savannah in Dec 1864. Continued to march northward into South & North Carolina to pursue Gen. Johnston (Confederate)
Gen. Sherman & Union forces began "March to the Sea." Marched from Atlanta to Savannah, burned all plantations & towns in their path
In Sep 1864, Gen. Sherman took Atlanta. The Union forces & northerners got really happy & started to support the war more
Final Surrender
After 9 months of battle, Gen. Grant (Union) finally sieged an important railroad junction near Petersburg (Mar 1865)
Gen. Lee (Confederate) lost railroad access to the South. Couldn't get more troops without the railroad
Gen. Lee realized he lost. He met Grant at his home in Appomattox Court House, VA, & surrendered (Apr 1865)
President Davis (Confederate) thought war wasn't over yet. He went to south where he was captured. Some white southerners continued to fight but failed
Gen. Johnston (Confederate) surrendered to Gen. Sherman (Union) 9 days later in Durham, North Carolina
Here is a map depicting the final pushes of Grant & Sherman and the Confederate surrender (1864-1865):

Mobilization of the North
Boosting the Northern Economy
-
Southerners were mostly gone from Congress, so Northern Republicans passed economic bills to promote the war effort
-
Homestead Act of 1862: People could claim 160 acres of public land & buy it after 5 years
-
Morrill Land Grant Act (1862). Federal gov gives land to the states to sell to individual people
-
This money from the land sales is used to finance public schools & colleges
-
-
-
Built transcontinental railroad
-
Union Pacific & Central Pacific Railroad Co build a line from Omaha to San Francisco in 1869
-
Finished at Promontory, UT, in 1869
-
-
Passed National Bank Acts of 1863-1864
-
Any bank could join national banking system if they had enough capital
-
Provided banknotes to these banks
-
-
Collected income taxes
-
Created a uniform system of paper money & issued lots of paper money
-
Fluctuated in price
-
-
Encouraged people to invest in bonds to give the government more money
-
Promoted industrial & economic development
-
Boosted production of coal, railroads, etc.
-
-
Many workers formed labor unions as they hated new working conditions & lower wages

Raising the Union Army
-
Union army was very small & weak
-
Lincoln sought to increase its size
-
Most soldiers were in state militias & volunteer armies
-
-
Congress passed national draft law in Mar 1863
-
Any young adult male could be drafted
-
Draftees could escape service by hiring someone else or paying $300 to gov
-
-
Many people rioted against the draft law
-
Immigrants, poor laborers, & most Democrats opposed this
-
Peace Democrats opposed the war, were known as "Copperheads"
-
-
Most famous were July 1863 New York Draft Riots
-
People burned black businesses, blamed them for the war
-
Irish immigrants believed blacks would replace them as low-income laborers
-
-

Opposition to the War & Wartime Politics
-
Lincoln hired a cabinet to represent every possible faction & viewpoint of Republican party
-
Many people opposed the war
-
Many Democrats (called Peace Democrats) opposed it
-
Some believed the national gov had too much power & states should get the power to secede
-
-
Lincoln used authoritarian methods in his presidency, mostly to suppress opposition
-
Raised an army & declared war on the South w/o Congress's approval
-
Believed it was a domestic insurrection, not a real war against another country
-
-
Ordered naval blockade of the South w/o Congress's approval
-
Ordered the military arrest of those who opposed the war
-
Suspended habeas corpus, the right to report an unlawful detention
-
Arrested more than 13k dissidents
-
-
Even defied Supreme Court orders
-
In a case called Ex Parte Merryman, Court ruled Lincoln must free a MD secessionist leader who was imprisoned
-
Lincoln ignored this
-
-
In another case (Ex Parte Milligan), Court ruled that military arrests were unconstitutional
-
-
-
Lincoln sought to boost popular support for the war
-
Made pro-war speeches pamphlets, etc.
-
Told people to take photos of the war to show the sacrifices being made to preserve the Union
-

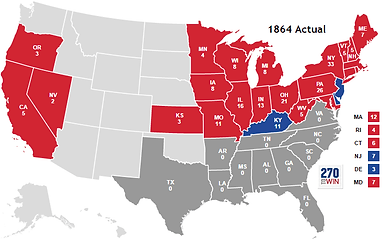
Election of 1864
-
Union party was created
-
Combined Republicans with pro-war Democrats
-
Had Lincoln as president, Andrew Johnson of Tennessee as running mate
-
Johnson was formerly a Democrat, he was meant to gain support of Democrats
-
-
-
Democrats had George McClellan (former Union military general)
-
Wanted peace & truce in the war
-
-
Since the US was in a bad military position in 1863, most supported Democrats (which were anti-war)
-
After capture of Atlanta (Sep 1864), people realized the Union was in a good military position
-
More people supported the Republicans / Union party
-
-
In the end, Lincoln won, Andrew Johnson was VP
Women's Involvement in the War
-
As men went to battlefield, many women took their places
-
Often teachers, office clerks, mill & factory workers, etc.
-
-
Dorothea Dix was in the US Sanitary Commission, sought to bring women into nursing
-
Same person in the mentally ill reform movement
-
By 1900, nursing became almost all female
-
Many resented having women in the nursing field
-
Believed women to be incompetent to care for complete strangers
-
-
Many women helped care for soldiers at the battlefield
-
Helped decrease mortality of soldiers
-
-
-
Many women believed helping in the war was a liberating experience for themselves
-
Elizabeth Cady Stanton & Susan B Anthony founded National Woman's Loyal League (1863)
-
Wanted suffrage for themselves in addition to blacks
-
-
Clara Barton founded American Red Cross, promoted women in nursing profession
-
.png)
Emancipation Proclamation
-
Radical Republicans wanted immediate emancipation for slaves
-
Conservatives wanted gradual emancipation
-
At first, Lincoln just wanted to preserve the Union, didn't care much about emancipation
-
Later, he passed 1st Confiscation Act (1861)
-
Hated that many slaves were forced to fight for Confederacy
-
Freed all slaves who fought for the Confederacy
-
-
Passed 2nd Confiscation Act (1862)
-
All slaves whose masters were in Confederate military were free
-
Lincoln used these slaves in the Union army
-
-
Now, northerners learned that emancipation was the general goal of the war
-
In Sep 1862, Lincoln signed Emancipation Proclamation
-
Signed after Union victory at Antietam, needed more blacks to serve in his army
-
All slaves in Confederacy were free
-
Didn't apply to border states
-
Gave moral purpose to war: Showed that war was for emancipation, not just preservation of Union
-
Allowed European nations to support the Union as they opposed slavery
-
-
-
After Emancipation Proclamation (1863), Union army worked to liberate all slaves in its path

Role of Blacks in the Union War Effort
-
About 180k former slaves joined Union army
-
Often faced discrimination from generals as there were few black regiments
-
Gained popularity after Emancipation Proclamation
-
Often did behind-the-scenes work like digging trenches, transporting resources
-
Had unsanitary conditions
-
Had lower pay than whites (until Congress changed this in 1864)
-
-
Robert Gould Shaw was a white man who commanded the 54th Massachusetts regiment
-
A very famous all-black regiment
-
The movie Glory is based on this regiment
-
-
They risk being caught by Confederacy at battle & being returned to their masters
.jpg)
Mobilization of the South
Confederate Government
-
Confederate constitution gave more rights to the states (much more decentralized)
-
Jefferson Davis was president
-
Alexander H Stephens was VP
-
Limited the power of national government
-
States had lots of power
-
Pres. Davis couldn't declare martial law
-
-
-
Had very strong governmental support for the war
-
Almost all whites supported war
-
-
Still, not everyone supported war
-
All blacks opposed war (obviously)
-
Some whites in the poor backcountry opposed war & didn't recognize Confederacy
-
Most notably West Virginia, which became a separate state in 1863
-
-

Raising the Army & Revenue for Confederacy
-
Generating revenue was hard since they didn't have stable banking system
-
Most money was invested in slaves → little money left for war
-
Didn't want to tax the citizens → encouraged them. to invest in bonds
-
These bonds fluctuated in value
-
-
-
Thus, Confederacy issued lots of paper money
-
There was widespread inflation as there was no centralized currency system
-
-
To raise the army, Confederacy enacted draft law for white males (18-35 y/o)
-
Like the north, they could hire a substitute
-
Many slaves would perform auxiliary tasks (laundry, chores, etc.)
-
Thus, whites were free to serve in front lines
-
-
Sometimes, they took slaves from plantations w/o their masters' approval to work in the military
-
-
Confederacy enacted "food draft" where soldiers can feed on any crops from any plantation in their path
-
Many people opposed this
-
.jpeg)
Effects of the War on the Confederacy
-
Economy declined significantly in the South
-
Cotton lost its markets as it couldn't trade w/ industrial north
-
Plantation owners w/o slaves lost their workforce since many whites went to battle
-
-
Most fighting was in the South → Southern infrastructure, crops, etc. were destroyed
-
US imposed a naval blockade in the South in 1862 → Food shortage in the South
-
South had less food as most of its crops were cotton (which wasn't edible)
-
Many white men served in military → less workforce to harvest food crops at plantations
-
Naval blockade made this worse → food riots
-
-
Many rioted against draft law, food shortage, etc.
-
Many men were away at war → Women had important managerial roles at home
-
Some were in charge of plantations
-
-
Masters imposed stricter restrictions on slaves as they were scared of slave revolts
-
Still, many slaves managed to escape to the Union w/ the help of Union troops
-

Other Wartime Developments
Untrustworthy Military Commanders
-
Lincoln struggled to find a trustworthy military commander for the Union army
-
George McClellan kept missing opportunities to win, which delayed the Union victory
-
Lincoln recalled him
-
-
Lincoln kept firing & replacing his northern military commanders
-
Finally, he found Gen. Ulysses S Grant to be trustworthy & smart enough
-
The smart commanders knew that you need to capture enemy resources to win, not just enemy people
-
-
Confederate army was also disorganized, but its commanders were much smarter
-
Pres. Davis named Robert E Lee as his principal military advisor
-
However, Lee left the job to command forces on his own
-
-
In 1864, Davis named Braxton Bragg as military advisor, but he didn't do much
-
In 1865, Davis created formal position of General in chief & made Robert E Lee that role
-
Most Confederate commanders were graduates from West Point or US Naval Academy
-
Still they weren't as smart or capable
-
-

Advantage of Sea Power
-
North had a very powerful navy
-
North imposed a naval blockade of the South
-
Very few Confederate ships were able to slip through
-
Prevented food from getting to Confederacy
-
-
Confederacy used ironclad warships to try to breach the naval blockade
-
Used US ship Merrimac and retrofitted it with iron
-
Renamed it to Virginia
-
-
In March 1862, Virginia set sail to attack Union's naval blockade
-
However, Union created its own ironclad ship called Monitor, which attacked Virginia
-
-
-
Union's navy took control of Mississippi River in 1863
-
With this, it could easily transport supplies throughout the Union
-
-
South didn't have a good navy, so it could only defend from its fortifications on land

Attempts to Forge European Alliances
-
Union & Confederacy sought to gain the support of Britain & France
-
Both European nations were somewhat neutral but kind of supported the South more
-
Needed southern cotton for its textile mills
-
Sought to weaken industrial centers of northeast US
-
-
Popular opinion in Britain supported the North
-
Believed in antislavery
-
Believed Britain has other cotton markets like Egypt & India
-
-
South sought to use "King Cotton Diplomacy" to gain support of Britain (but it failed)
-
Tried to convince Britain that the South had access to cotton which Britain would need
-
-
-
Trent Affair (1861) hurt diplomatic relations between Union & Britain
-
US warship, San Jacinto, stopped an English ship, Trent, in Havana, Cuba, and arrested 2 Confederate diplomats on board
-
British gov demanded release of the prisoners, so Lincoln agreed as he wanted to avoid conflict
-
This affair hurt relations between Union & Britain
-

Wartime Violence in the West
-
There was a lot of fighting between Unions & Confederates in the West
-
All western states (except Texas) were in Union
-
-
William C Quantrill was captain of Confederacy & organized guerillas to attack Missouri-Kansas border
-
Sacked Lawrence, KS, in Aug 1863, killing 150 people (Lawrence Massacre)
-
Union troops killed Quantrill afterward
-
-
Union guerillas called Jayhawkers attacked Confederates throughout Missouri to get revenge
-
Battle of Wilson's Creek (Aug 1861) was another major battle in Missouri
-
Missouri governor Claiborne Jackson sought to secede & conspired w/ pro-slavery forces
-
Governor Jackson organized an army under Confederate Gen. Ben McCulloch
-
Union Gen. Nathaniel Lyon attacked Confederate forces led by Gen. Ben McCulloch
-
Unions were defeated but Confederates were weakened
-
-
-
Some sought to gain support of the 5 Indian tribes in the Indian Territory
-
Indians were divided among themselves
-
Some hated slavery & supported north
-
Others hated the way US treated them & even owned slaves themselves → Supported South
-
-
Indians didn't formally ally w/ either side
-
Here is a map depicting the Battles in Kansas & Missouri:

Wartime Technology
-
Some new technologies were invented
-
Samuel Colt invented revolver (repeating pistol) in 1835
-
Oliver Winchester invented repeating rifle in 1866
-
These repeating weapons caused so many deaths
-
People created trenches & fortifications
-
-
Used hot air balloons to see enemy fortifications
-
Submarines, torpedoes, ironclad warships
-
-
Railroad & telegraph were super important
-
Railroads would transport soldiers
-
Telegraphs would be used to communicate soldier movements
-
Often unreliable due to lack of infrastructure & trusted operators
-
-
%20(1).jpg)
Reconstruction:
Post-Civil War Situation
Emancipation Proclamation (Jan 1863)
Aug 1861:
1st Confiscation Act
All slaves used in Confederate military are freed
Jul 1862:
2nd Confiscation Act
All slaves whose masters are in Confederate military are freed
Jan 1863:
Emancipation Proclamation
All slaves in Confederacy are freed
Abraham Lincoln's 10% Plan (Dec 1863)
10% of white voters in Confederate states must take oath of loyalty to the Union & US Constitution
After that, constitutional convention would make a constitution w/o slavery & with Black voting rights.
Attempted to reconcile the South during the Civil War to avoid more violence. Never really succeeded
Wade-Davis Bill (Jul 1864)
Also attempted to reconcile the South during Civil War. Vetoed by Lincoln as it was too radical
Instead of Lincoln's proposed 10%, it wanted >50% of white voters in the South to take an oath of loyalty to US & give black voting rights
Proposed by Radical Republicans in Congress. Vetoed by Lincoln as it was too radical. Didn't pass
13th Amendment (Jan 1865, ratified Dec 1865)
Abolished slavery throughout the US
Passed in Congress in Jan 1865
Ratified by all states in Dec 1865
Freedmen's Bureau (est. Mar 1865)
-
Congress was dominated by Republicans as the Democrats of the South seceded & lost their seats
-
These Republicans (most were Radical) enacted many laws to promote black rights
-
-
Congress created Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands
-
Known as "Freedmen's Bureau"
-
Sought to ease transition of blacks into society
-
Established schools for blacks
-
Acted as courts to settle disputes between blacks & whites
-
Assisted the poor
-
US Army accompanied them
-
End of Civil War (Apr 1865)
In Apr 1865, Confederacy surrendered to the Union, ending the Civil War
Congress needed to figure out how to readmit former Confederate states to Union & help newly-freed Blacks adapt to society
The Reconstruction is a series of acts enacted by Congress from 1863-1877 to readmit Confederate states to the Union & help former slaves adapt to society
Lincoln's Assassination & Johnson's Ascendance (Apr 1865)
-
In Apr 1865, Pres. Lincoln was assassinated
-
VP Andrew Johnson (D) became president
-
-
Johnson was a Democrat & didn't fully support Black rights
-
He was Lincoln's running mate in 1864 election to gain support of Peace Democrats
-
Opposed the policies of Lincoln (R) and Radical Republicans in Congress
-
Sought to prevent Radical Republicans in Congress from enacting the Reconstruction
-
Kept vetoing Congressional bills
-
-
-
Johnson's policies were more moderate
-
Gave many pardons to former Confederates & allowed them to serve in Union gov again
-
Sought that former Confederate states only reject secession & don't fully give Blacks civilian rights
-
Only wanted abolition of slavery
-
-
His policies were bad as Southern states only repealed their secession & didn't do much else
-
Black Codes (1865-1866)
-
Governments in the South enacted "Black Codes"
-
Sought to limit the power of Blacks in society after their emancipation as slaves
-
-
Mississippi was first state to enact "Black Codes"
-
Blacks can only rent land within the cities
-
Blacks can't do independent farming
-
Can only work as sharecroppers on White farmers' land
-
-
Blacks must be able to show proof of employment or will be arrested
-
-
South Carolina was 2nd state to enact "Black Codes"
-
Had stricter guidelines
-
Also made sure blacks sign yearly labor contracts as proof of employment
-
Most blacks were servants or sharecroppers
-
-
Reconstruction
Ku Klux Klan (KKK) (Est. Dec 1865)
-
A group of white supremacists that sought to attack blacks
-
Founded by 6 ex-officers of Confederate army
-
Founded in Tennessee
-
-
Attacked, lynched, and assassinated Blacks
-
-
State militias were generally unreliable in suppressing the KKK's actions
-
Many KKK members didn't receive punishment
-
Freedmen's Bureau Act of 1866 (Feb 1866)
Gave more funds to Freedmen's Bureau
Gave it military authority to persecute civil rights violations
Vetoed by President Johnson as it gave national gov too much power. Senate failed to override the veto
Civil Rights Act of 1866 (Apr 1866)
Protects Black citizenship rights
Gives Blacks all civil liberties of whites. Gives Blacks right to sue in court
Vetoed by Pres. Johnson as it favors blacks over whites. Senate overrode it
14th Amendment (Jun 1866)
Officially gives citizenship to Blacks born in the US
Gives equal protection under law to Blacks & Whites
Johnson hated this. He can't veto an amendment, so he instead encouraged states not to ratify it. Finally ratified in Jul 1868
Tennessee Readmitted to Union (Jul 1866)
Tennessee was the only ex-Confederate state to ratify 14th amendment
Congress rewarded Tennessee by readmitted it to the Union
Memphis Race Riot (May 1866) & New Orleans Massacre (Jul 1866)
-
Memphis Riots were when mobs of white people started attacking black neighborhoods
-
Black Union soldiers were partying in the streets & police were called to disperse them
-
Black soldiers refused to leave, so police called reinforcements & opened gunfire
-
One officer accidentally shot himself
-
One Black soldier shot & killed another officer
-
-
All the Whites in Memphis blamed those shootings on the Blacks
-
Mobs of Whites started attacking & looting Black homes, attacked the Black soldiers, etc.
-
-
Federal troops came later to end the violence
-
-
New Orleans Massacre was when armed whites started attacking anti-"Black Code" blacks
-
Many Blacks were part of the convention to create the reconstructed Louisiana constitution
-
Sought to give blacks equality & abolish the "Black Codes"
-
-
As those Blacks were leaving their convention's building, white armed men came & fired at them
-
Federal troops came to end the violence
-
-
These 2 events showed Congress that the South needs to be in stricter control to protect the Blacks
Republican Win in Congressional Election of 1866 (Nov 1866)
Northerners hated growing violence against Blacks in the South. They hated Johnson for vetoing the civil rights acts
Republicans easily won 2/3 majorities in both houses of Congress
This ensured that the Republicans can override any presidential veto & enact their Reconstruction plans
Reconstruction Act of 1867 (Mar 1867)
10 ex-Confederate states in the South (all but Tennessee) would be divided into 5 districts, each ruled by a US army general
Each state would create a voter registration board & allow black men to vote. Ex-Confederate officials can't hold office
The voters would create a constitutional convention that would create a constitution & ratify 14th amendment
Once enough states have ratified 14th amendment, the state can elect people to Congress. Then, the state is fully Reconstructed
Tenure of Office Act (Mar 1867) & Johnson's Impeachment (Feb 1868)
Republicans relied on Edwin Stanton (Secretary of War) to support US Army's involvement in the South
Congress passed Tenure of Office Act (1867), preventing the president from firing federal officials w/o Senate's approval
Johnson defiantly fired Stanton, so Congress impeached him. Senate narrowly acquitted him.
More States Readmitted to Union (Jun-Jul 1868)
Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, North Carolina, South Carolina were readmitted to the Union (Jun-Jul 1868)
In Georgia, Democrats removed 28 black congressmen from state legislature. Thus, Georgia was put again under military rule until Jul 1870
Presidential Election of 1868 (Nov 1868)
Republican Congressmen hoped they could have a president that doesn't veto all their plans
Former Union Gen. Ulysses S Grant (R) beat Horatio Seymour (D)
The margin was only 300,000 votes, so Congress wanted to give universal voting rights to Black men to boost their support
15th Amendment (Feb 1869)
Prohibits depriving citizens the right to vote based on color or race
Proposed by Republicans in Congress to boost Republican support in future elections
Forced the 4 unreconstructed states (GA, MS, TX, VA) to ratify it before readmission to Union. Ratified in Feb 1860
Republican Governments in the South
-
Many Blacks participated in Southern republican governments
-
Many were elected to local & state offices
-
Some were even elected to national office
-
Black voters were a majority of the electorate in AL, FL, LA, MS, and SC
-
-
Some whites were also Republican
-
"Carpetbeggars" were Whites who migrated from North to the South to find work
-
"Scalawags" were native Southern Whites who were Republican
-
Most were poor & supported centralized Yankee vision of life
-
-
-
Black Republicans in the South passed laws to end discrimination
-
Created public schools, railroads, etc.
-
Had few factions among them (compared to other political parties)
-
-
There was lots of violence toward Republicans
-
People would refuse to go to their businesses, they'd be attacked, etc.
-
-
Most Whites were Democrats & opposed Black equality
First Redeemer Governments (late 1869 - early 1870)
Tennessee becomes the first state to replace its Republican-dominated government with an all-white Democratic one (late 1869).
Georgia and North Carolina soon create all-white Democratic governments (early 1870).
US military returns to Georgia
Final Batch of States Readmitted to Union (Jan - Jul 1870)
Virginia, Mississippi, Texas, and Georgia were readmitted to the Union in 1870
This was the 2nd time Georgia was readmitted because US army had to go back there after White Democrats unseated the Black Republicans from state congress.
The Enforcements Acts / KKK Acts (1870 - 1871)
Summary:
Meant to preserve Black voting rights & prevent voter intimidation (especially by KKK). Known as Enforcement Acts, Force Acts, or Ku Klux Klan Acts
Enforcement Act of 1870:
Banned discrimination of voter registration based on race or color. Allowed federal marshals to enforce the act
Enforcement Act of 1871:
Allowed federal government to supervise state & local elections in a town of >20k residents
Ku Klux Klan Act (1871):
Allowed president to use militias to suppress any anti-Black activity. Gave federal courts the right to incriminate anti-Black discrimination
End of Reconstruction
End of Freedmen's Bureau (Jul 1872)
-
Freedmen's Bureau had many successes but was unsuccessful in the long term
-
White southerners still believed Blacks to be inferior & wouldn't respect Black equality
-
You cannot change the opinion of millions of White southerners in a few years (obviously)
-
-
Many of the achievements made toward Black integration were undone
-
Some Whites reacquired the land given the Blacks
-
Many White Democrats retook Southern governments
-
Whites still had lots of violence toward Blacks
-
-
-
In Jul 1872, White Southerners pressured Congress to abolish the Freedmen's Bureau
-
It was also too expensive to maintain & had little reward, so Congress sought to abolish it
-
Election of 1872 (Nov 1872)
Liberal Republicans hated economic effects of Radical Reconstruction. They supported Democrats
Incumbent Ulysses S Grant (R) beat Horace Greeley (D)
After this, Democrats & Liberal Republicans gained support from those who opposed Radical Reconstruction
"Redemption" of Southern Governments by White Democrats (1872 - 1877)
-
White Southerners (Democrats) started to take over ("redeem") their state governments
-
Wanted to return to "home rule" of whites
-
Believed Radical Republicans to be corrupt
-
Believed Radical Reconstruction was hurting the economy
-
-
Started in 1869 with Tennessee, but redemption gained momentum in 1872
-
-
Bands of white people (notably White Leagues and Red Shirts) invaded Republican capitol buildings
-
Louisiana witnessed lots of violence between Democrats & Republicans since 1872
-
In Governor election of 1872, both sides (Dems & Republicans) claimed victory
-
Democratic Whites then killed hundreds of Blacks in the Colfax Massacre (1873)
-
In 1874, "White Leagues" (bands of White Democrats) invaded the capitol building
-
Pres. Grant used Federal troops to restore Republican government there
-
-
-
Most other states started "redeeming" their governments & returning White Democrat rule
-
All states had been "redeemed" by 1877
-
Slaughterhouse Cases (Apr 1873)
Louisiana gave a monopoly to a slaughterhouse. Other slaughterhouses filed a lawsuit against the monopoly, claiming the 14th amendment allows them to freely conduct their labor
Court ruled in favor of the monopoly. Said that 14th amendment is limited to what's written in Constitution & doesn't include states' privileges to certain individuals
Summary:
Thus, states can do things that favor certain people over another, and this wouldn't violate 14th amendment
Panic of 1873 (Sep 1873) & Congressional Election of 1874 (Nov 1874)
Panic of 1873:
Collapse in US railroad industry triggered huge financial panic that caused the stocks to fall. People blamed this on the Radical Reconstruction & the Republicans
Congressional Election of 1874:
Democrats took a majority in House of Representatives for the 1st time since Civil War
Significance:
This was a significant event in decline of Reconstruction. Panic of 1873 made many people support Democrats over Republicans in favor of the economy
Civil Rights Act of 1875 (Mar 1875)
Equality of men before the law. Prohibited racial discrimination in public facilities, public transportation, & jury selection
Last federal civil rights law until Civil Rights Act of 1957
Declared unconstitutional by Supreme Court in 1883
Situation in Louisiana & Mississippi (1875)
After the situation in Louisiana with the "White Leagues" in 1874 (described above), Democrats tried to take control of the state gov by putting 5 assembly members in legislature
Louisiana's Republican governor ordered the US army to remove those unelected Democratic assembly members from their seats
This incident provoked backlash in the North as Northern Democrats (and even Republicans) were horrified by the idea of having troops forcibly ejecting legislators
In late 1875, "White Leagues" of Mississippi terrorized the Republican party there & sought to take control of the Republican state government
President Grant refused to send an army there to avoid the political backlash that happened when an army was sent to Louisiana earlier that year (described above)
Thus, Democrats took control of the Mississippi government. Just like this, Democrats took control of many Southern governments
Election of 1876 (Nov 1876) & Compromise of 1877 (Mar 1877)
-
Rutherford B Hayes (R) vs Samuel J Tilden (D)
-
Hayes was a Liberal Republican, believed in reforming Republican corruption & enacting laws that favor both Blacks & Whites
-
Tilden was similar to Hayes
-
-
Election result was disputed in 3 Southern states
-
South Carolina, Florida, Louisiana were the 3 only states where US army still remained
-
In these 3 states, the election result was disputed
-
-
If all 3 states voted for Hayes, he'd win by one electoral vote
-
"Red Shirts" sought to intimidate Blacks & prevent them from voting
-
However, enough Black voters turned out to give Hayes the victory in all 3 states
-
-
In the end, all 3 states gave electoral votes to Hayes, so he won by 1 point
-
-
Democrats dominated Congress & tried to slow down the inauguration & transition process
-
Sought to slow down electoral vote counting
-
-
Democrats & Republicans created a political compromise at Wormley's Hotel in DC
-
Democrats would allow Hayes (Republican) to win the election
-
However, federal troops must be removed from the 3 remaining Southern states (SC, FL, LA)
-
This is known as the Compromise of 1877
-
-
This Compromise ended Reconstruction as the last federal troops were removed from the South
Important Terms & People
Link to flashcards: https://quizlet.com/557729773/apush-unit-5-flash-cards/
Summary
Manifest Destiny:
The Manifest Destiny was a period in the 1840s when the US acquired lots of land in the West. Mexico called for Americans to settle in Texas to boost the Texan economy, but Texans wanted independence, so after a few battles, Sam Houston won independence for Texas in 1836. Texas was annexed by the US in 1845. Also, the US got half of the Oregon territory in 1846 after a compromise with Britain. The bigger problem was the land in the West: Many Americans settled in the West, and the US sought to annex it as well. A dispute over the boundary of Texas caused the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), and in the end, the US gained so much more territory in the West. The problem was whether these new lands should be free of slavery or not, and this led to the Compromise of 1850.
Post-1850 Sectional Conflicts:
The Compromise of 1850 didn't fully resolve the sectional conflict. The Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854) caused more sectional conflict over the issue of slavery in the unorganized territory east of Missouri & Iowa. Anti-slavery activists caused a lot of turmoil in Kansas as they hated that Kansas as a slave state would repeal the Missouri Compromise. Thus, after a lot of violence (known as "Bleeding Kansas"), Kansas became a free state in 1861. Furthermore, there was more sectional conflict, especially caused by the Dred Scott Supreme Court Case (1857), which provoked lots of controversy about the status of Blacks. Finally, these issues led to political realignment, which ended the Whig party and created the Republican party, a sectional party that advocated for free-soil (no expansion of slavery in the West). The election of Lincoln in 1860 angered the south, which sought to secede from the Union.
Civil War:
After the election of Lincoln in 1860, the South hated that he only served the interests of the North, so the Southern states seceded from the Union & formed the Confederacy. Lincoln was angered and sought to preserve the Union, but after failing to protect Fort Sumter, the Civil War began. Both the Union & Confederacy mobilized their economies and armies and passed laws to promote the war. The Battle of Antietam (1863) was the deadliest battle, and soon after, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing all slaves in the Confederacy. This added a moral cause to the war: The War wasn't just to preserve the Union; it was also to abolish slavery. Lincoln made many pro-war speeches, most notably the Gettysburg Address, which all sought to promote the war effort & restate the causes to preserve the Union. The Emancipation Proclamation also allowed Blacks to flee from the South & join the Union armies, which helped the Union forces win in the end. The Union victory led to many questions about how to assimilate the freedmen (former slaves) into society.
Reconstruction:
The Union victory in the Civil War led to the question of how to assimilate the former slaves (freedmen) into society. The Reconstruction was a series of events led by Radical Republicans in Congress that helped assimilate the Blacks into society. After Lincoln's assassination in April 1865, his VP, Andrew Johnson, took over, and he was a white supremacist who tried to sabotage the reconstruction efforts of Congress, but Congress kept overriding his vetos. Congress drafted the 14th amendment, which gave citizenship to all Blacks born in the US. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 put the South under US military control and established a framework for states to be readmitted to the Union, which included giving voting rights to Blacks. Congress passed many more acts, such as the 15th amendment, preventing discrimination of voting rights based on race or color. However, Democrats & Liberal Republicans believed the reconstruction agenda to be too radical as it focused too much on Blacks' rights and not on the economy, and especially after the Panic of 1873, support for the Republicans declined. In 1874, Democrats took majority control of the House of Representatives, and a political bargain in 1877 removed the military from the South, ending the Reconstruction. Throughout the early 1870s, White Southern Democrats had been taking over the Southern Republican governments, reestablishing White rule in the South. Overall, the Reconstruction was unsuccessful in the long term.
